Avishai Sintov
IMU-based Real-Time Crutch Gait Phase and Step Detections in Lower-Limb Exoskeletons
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Lower limb exoskeletons and prostheses require precise, real time gait phase and step detections to ensure synchronized motion and user safety. Conventional methods often rely on complex force sensing hardware that introduces control latency. This paper presents a minimalist framework utilizing a single, low cost Inertial-Measurement Unit (IMU) integrated into the crutch hand grip, eliminating the need for mechanical modifications. We propose a five phase classification system, including standard gait phases and a non locomotor auxiliary state, to prevent undesired motion. Three deep learning architectures were benchmarked on both a PC and an embedded system. To improve performance under data constrained conditions, models were augmented with a Finite State Machine (FSM) to enforce biomechanical consistency. The Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) emerged as the superior architecture, yielding the highest success rates and lowest latency. Notably, the model generalized to a paralyzed user despite being trained exclusively on healthy participants. Achieving a 94% success rate in detecting crutch steps, this system provides a high performance, cost effective solution for real time exoskeleton control.
DiG-Net: Enhancing Quality of Life through Hyper-Range Dynamic Gesture Recognition in Assistive Robotics
May 30, 2025Abstract:Dynamic hand gestures play a pivotal role in assistive human-robot interaction (HRI), facilitating intuitive, non-verbal communication, particularly for individuals with mobility constraints or those operating robots remotely. Current gesture recognition methods are mostly limited to short-range interactions, reducing their utility in scenarios demanding robust assistive communication from afar. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach designed specifically for assistive robotics, enabling dynamic gesture recognition at extended distances of up to 30 meters, thereby significantly improving accessibility and quality of life. Our proposed Distance-aware Gesture Network (DiG-Net) effectively combines Depth-Conditioned Deformable Alignment (DADA) blocks with Spatio-Temporal Graph modules, enabling robust processing and classification of gesture sequences captured under challenging conditions, including significant physical attenuation, reduced resolution, and dynamic gesture variations commonly experienced in real-world assistive environments. We further introduce the Radiometric Spatio-Temporal Depth Attenuation Loss (RSTDAL), shown to enhance learning and strengthen model robustness across varying distances. Our model demonstrates significant performance improvement over state-of-the-art gesture recognition frameworks, achieving a recognition accuracy of 97.3% on a diverse dataset with challenging hyper-range gestures. By effectively interpreting gestures from considerable distances, DiG-Net significantly enhances the usability of assistive robots in home healthcare, industrial safety, and remote assistance scenarios, enabling seamless and intuitive interactions for users regardless of physical limitations
ORACLE-Grasp: Zero-Shot Task-Oriented Robotic Grasping using Large Multimodal Models
May 13, 2025Abstract:Grasping unknown objects in unstructured environments remains a fundamental challenge in robotics, requiring both semantic understanding and spatial reasoning. Existing methods often rely on dense training datasets or explicit geometric modeling, limiting their scalability to real-world tasks. Recent advances in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) offer new possibilities for integrating vision and language understanding, but their application to autonomous robotic grasping remains largely unexplored. We present ORACLE-Grasp, a zero-shot framework that leverages LMMs as semantic oracles to guide grasp selection without requiring additional training or human input. The system formulates grasp prediction as a structured, iterative decision process, using dual-prompt tool calling to first extract high-level object context and then select task-relevant grasp regions. By discretizing the image space and reasoning over candidate areas, ORACLE-Grasp mitigates the spatial imprecision common in LMMs and produces human-like, task-driven grasp suggestions. Early stopping and depth-based refinement steps further enhance efficiency and physical grasp reliability. Experiments demonstrate that the predicted grasps achieve low positional and orientation errors relative to human-annotated ground truth and lead to high success rates in real-world pick up tasks. These results highlight the potential of combining language-driven reasoning with lightweight vision techniques to enable robust, autonomous grasping without task-specific datasets or retraining.
Speech-to-Trajectory: Learning Human-Like Verbal Guidance for Robot Motion
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Full integration of robots into real-life applications necessitates their ability to interpret and execute natural language directives from untrained users. Given the inherent variability in human language, equivalent directives may be phrased differently, yet require consistent robot behavior. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced language understanding, they often falter in handling user phrasing variability, rely on predefined commands, and exhibit unpredictable outputs. This letter introduces the Directive Language Model (DLM), a novel speech-to-trajectory framework that directly maps verbal commands to executable motion trajectories, bypassing predefined phrases. DLM utilizes Behavior Cloning (BC) on simulated demonstrations of human-guided robot motion. To enhance generalization, GPT-based semantic augmentation generates diverse paraphrases of training commands, labeled with the same motion trajectory. DLM further incorporates a diffusion policy-based trajectory generation for adaptive motion refinement and stochastic sampling. In contrast to LLM-based methods, DLM ensures consistent, predictable motion without extensive prompt engineering, facilitating real-time robotic guidance. As DLM learns from trajectory data, it is embodiment-agnostic, enabling deployment across diverse robotic platforms. Experimental results demonstrate DLM's improved command generalization, reduced dependence on structured phrasing, and achievement of human-like motion.
Embodiment-Agnostic Navigation Policy Trained with Visual Demonstrations
Dec 28, 2024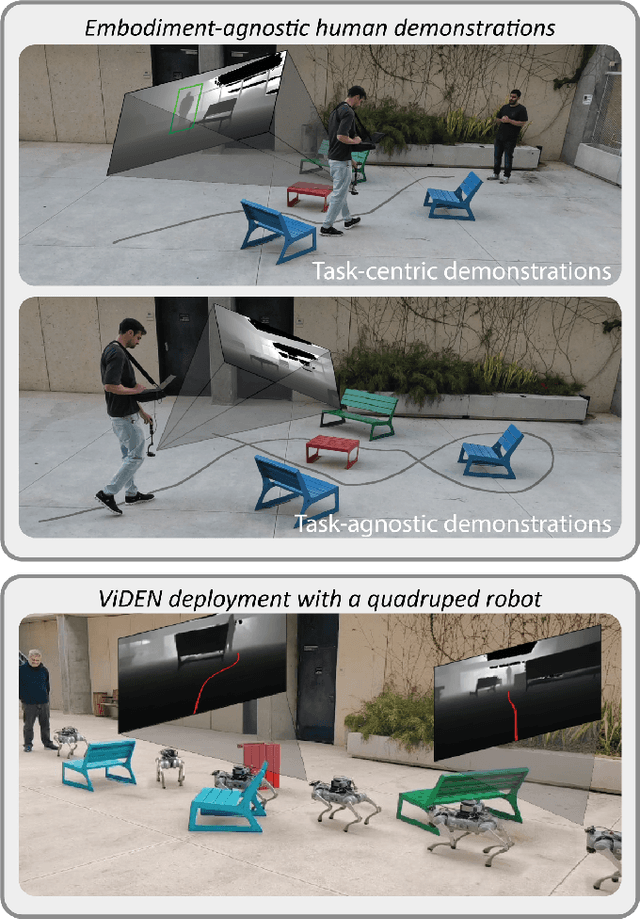
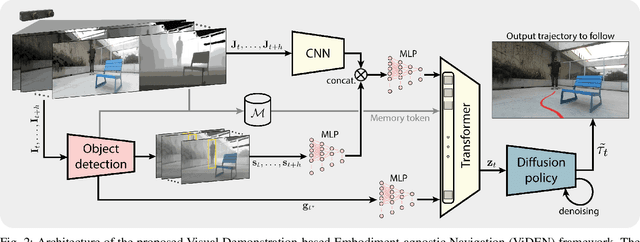

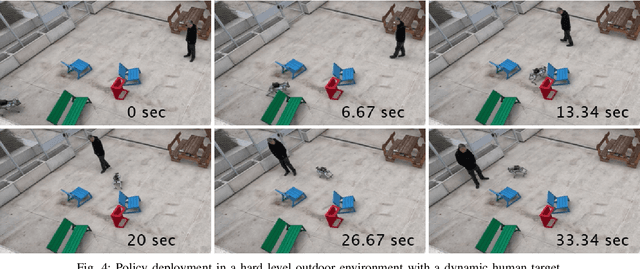
Abstract:Learning to navigate in unstructured environments is a challenging task for robots. While reinforcement learning can be effective, it often requires extensive data collection and can pose risk. Learning from expert demonstrations, on the other hand, offers a more efficient approach. However, many existing methods rely on specific robot embodiments, pre-specified target images and require large datasets. We propose the Visual Demonstration-based Embodiment-agnostic Navigation (ViDEN) framework, a novel framework that leverages visual demonstrations to train embodiment-agnostic navigation policies. ViDEN utilizes depth images to reduce input dimensionality and relies on relative target positions, making it more adaptable to diverse environments. By training a diffusion-based policy on task-centric and embodiment-agnostic demonstrations, ViDEN can generate collision-free and adaptive trajectories in real-time. Our experiments on human reaching and tracking demonstrate that ViDEN outperforms existing methods, requiring a small amount of data and achieving superior performance in various indoor and outdoor navigation scenarios. Project website: https://nimicurtis.github.io/ViDEN/.
Vibration-based Full State In-Hand Manipulation of Thin Objects
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Robotic hands offer advanced manipulation capabilities, while their complexity and cost often limit their real-world applications. In contrast, simple parallel grippers, though affordable, are restricted to basic tasks like pick-and-place. Recently, a vibration-based mechanism was proposed to augment parallel grippers and enable in-hand manipulation capabilities for thin objects. By utilizing the stick-slip phenomenon, a simple controller was able to drive a grasped object to a desired position. However, due to the underactuated nature of the mechanism, direct control of the object's orientation was not possible. In this letter, we address the challenge of manipulating the entire state of the object. Hence, we present the excitation of a cyclic phenomenon where the object's center-of-mass rotates in a constant radius about the grasping point. With this cyclic motion, we propose an algorithm for manipulating the object to desired states. In addition to a full analytical analysis of the cyclic phenomenon, we propose the use of duty cycle modulation in operating the vibration actuator to provide more accurate manipulation. Finite element analysis, experiments and task demonstrations validate the proposed algorithm.
Robust Dynamic Gesture Recognition at Ultra-Long Distances
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Dynamic hand gestures play a crucial role in conveying nonverbal information for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), eliminating the need for complex interfaces. Current models for dynamic gesture recognition suffer from limitations in effective recognition range, restricting their application to close proximity scenarios. In this letter, we present a novel approach to recognizing dynamic gestures in an ultra-range distance of up to 28 meters, enabling natural, directive communication for guiding robots in both indoor and outdoor environments. Our proposed SlowFast-Transformer (SFT) model effectively integrates the SlowFast architecture with Transformer layers to efficiently process and classify gesture sequences captured at ultra-range distances, overcoming challenges of low resolution and environmental noise. We further introduce a distance-weighted loss function shown to enhance learning and improve model robustness at varying distances. Our model demonstrates significant performance improvement over state-of-the-art gesture recognition frameworks, achieving a recognition accuracy of 95.1% on a diverse dataset with challenging ultra-range gestures. This enables robots to react appropriately to human commands from a far distance, providing an essential enhancement in HRI, especially in scenarios requiring seamless and natural interaction.
Human Arm Pose Estimation with a Shoulder-worn Force-Myography Device for Human-Robot Interaction
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Accurate human pose estimation is essential for effective Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). By observing a user's arm movements, robots can respond appropriately, whether it's providing assistance or avoiding collisions. While visual perception offers potential for human pose estimation, it can be hindered by factors like poor lighting or occlusions. Additionally, wearable inertial sensors, though useful, require frequent calibration as they do not provide absolute position information. Force-myography (FMG) is an alternative approach where muscle perturbations are externally measured. It has been used to observe finger movements, but its application to full arm state estimation is unexplored. In this letter, we investigate the use of a wearable FMG device that can observe the state of the human arm for real-time applications of HRI. We propose a Transformer-based model to map FMG measurements from the shoulder of the user to the physical pose of the arm. The model is also shown to be transferable to other users with limited decline in accuracy. Through real-world experiments with a robotic arm, we demonstrate collision avoidance without relying on visual perception.
Visuotactile-Based Learning for Insertion with Compliant Hands
Nov 10, 2024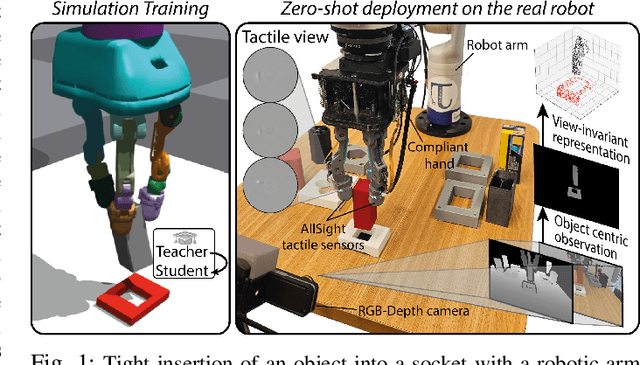
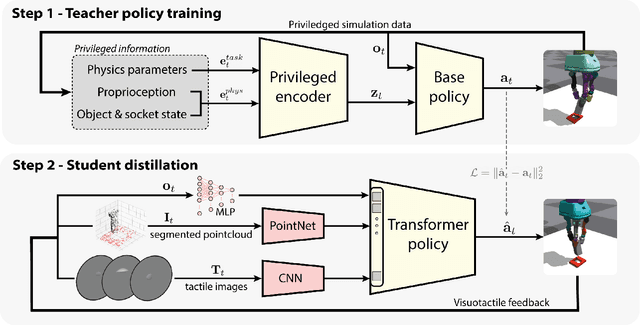

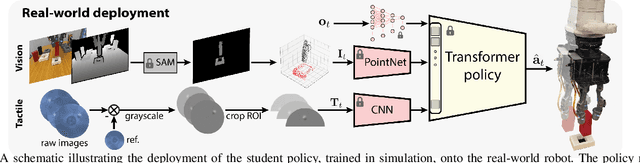
Abstract:Compared to rigid hands, underactuated compliant hands offer greater adaptability to object shapes, provide stable grasps, and are often more cost-effective. However, they introduce uncertainties in hand-object interactions due to their inherent compliance and lack of precise finger proprioception as in rigid hands. These limitations become particularly significant when performing contact-rich tasks like insertion. To address these challenges, additional sensing modalities are required to enable robust insertion capabilities. This letter explores the essential sensing requirements for successful insertion tasks with compliant hands, focusing on the role of visuotactile perception. We propose a simulation-based multimodal policy learning framework that leverages all-around tactile sensing and an extrinsic depth camera. A transformer-based policy, trained through a teacher-student distillation process, is successfully transferred to a real-world robotic system without further training. Our results emphasize the crucial role of tactile sensing in conjunction with visual perception for accurate object-socket pose estimation, successful sim-to-real transfer and robust task execution.
Motion Planning for Minimally Actuated Serial Robots
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:Modern manipulators are acclaimed for their precision but often struggle to operate in confined spaces. This limitation has driven the development of hyper-redundant and continuum robots. While these present unique advantages, they face challenges in, for instance, weight, mechanical complexity, modeling and costs. The Minimally Actuated Serial Robot (MASR) has been proposed as a light-weight, low-cost and simpler alternative where passive joints are actuated with a Mobile Actuator (MA) moving along the arm. Yet, Inverse Kinematics (IK) and a general motion planning algorithm for the MASR have not be addressed. In this letter, we propose the MASR-RRT* motion planning algorithm specifically developed for the unique kinematics of MASR. The main component of the algorithm is a data-based model for solving the IK problem while considering minimal traverse of the MA. The model is trained solely using the forward kinematics of the MASR and does not require real data. With the model as a local-connection mechanism, MASR-RRT* minimizes a cost function expressing the action time. In a comprehensive analysis, we show that MASR-RRT* is superior in performance to the straight-forward implementation of the standard RRT*. Experiments on a real robot in different environments with obstacles validate the proposed algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge