Arnd Kleyer
ShaRPy: Shape Reconstruction and Hand Pose Estimation from RGB-D with Uncertainty
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Despite their potential, markerless hand tracking technologies are not yet applied in practice to the diagnosis or monitoring of the activity in inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases. One reason is that the focus of most methods lies in the reconstruction of coarse, plausible poses for gesture recognition or AR/VR applications, whereas in the clinical context, accurate, interpretable, and reliable results are required. Therefore, we propose ShaRPy, the first RGB-D Shape Reconstruction and hand Pose tracking system, which provides uncertainty estimates of the computed pose to guide clinical decision-making. Our method requires only a light-weight setup with a single consumer-level RGB-D camera yet it is able to distinguish similar poses with only small joint angle deviations. This is achieved by combining a data-driven dense correspondence predictor with traditional energy minimization, optimizing for both, pose and hand shape parameters. We evaluate ShaRPy on a keypoint detection benchmark and show qualitative results on recordings of a patient.
Towards Super-Resolution CEST MRI for Visualization of Small Structures
Dec 03, 2021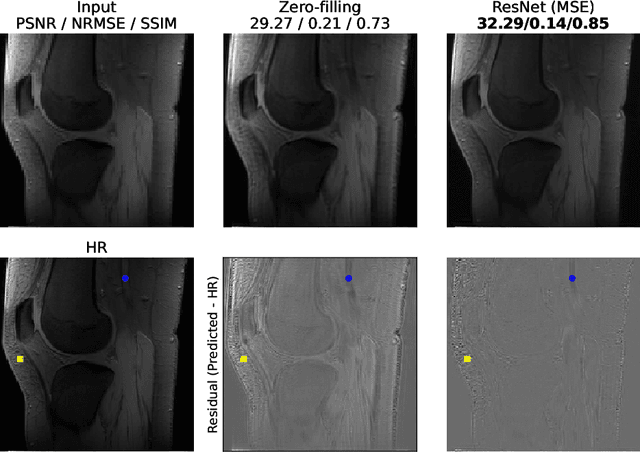
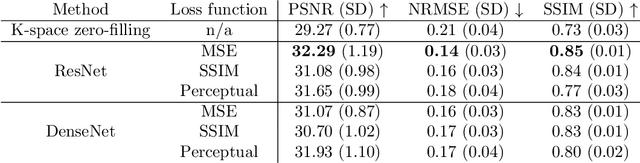
Abstract:The onset of rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis is typically subclinical, which results in challenging early detection of the disease. However, characteristic changes in the anatomy can be detected using imaging techniques such as MRI or CT. Modern imaging techniques such as chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI drive the hope to improve early detection even further through the imaging of metabolites in the body. To image small structures in the joints of patients, typically one of the first regions where changes due to the disease occur, a high resolution for the CEST MR imaging is necessary. Currently, however, CEST MR suffers from an inherently low resolution due to the underlying physical constraints of the acquisition. In this work we compared established up-sampling techniques to neural network-based super-resolution approaches. We could show, that neural networks are able to learn the mapping from low-resolution to high-resolution unsaturated CEST images considerably better than present methods. On the test set a PSNR of 32.29dB (+10%), a NRMSE of 0.14 (+28%), and a SSIM of 0.85 (+15%) could be achieved using a ResNet neural network, improving the baseline considerably. This work paves the way for the prospective investigation of neural networks for super-resolution CEST MRI and, followingly, might lead to a earlier detection of the onset of rheumatic diseases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge