Antonios Liapis
The Procedural Content Generation Benchmark: An Open-source Testbed for Generative Challenges in Games
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces the Procedural Content Generation Benchmark for evaluating generative algorithms on different game content creation tasks. The benchmark comes with 12 game-related problems with multiple variants on each problem. Problems vary from creating levels of different kinds to creating rule sets for simple arcade games. Each problem has its own content representation, control parameters, and evaluation metrics for quality, diversity, and controllability. This benchmark is intended as a first step towards a standardized way of comparing generative algorithms. We use the benchmark to score three baseline algorithms: a random generator, an evolution strategy, and a genetic algorithm. Results show that some problems are easier to solve than others, as well as the impact the chosen objective has on quality, diversity, and controllability of the generated artifacts.
Affectively Framework: Towards Human-like Affect-Based Agents
Jul 25, 2024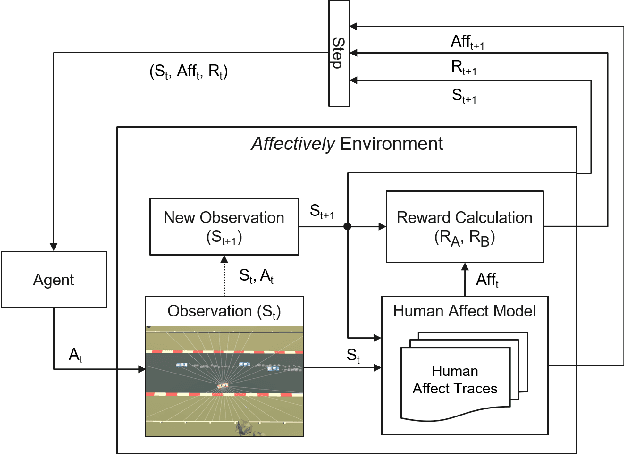
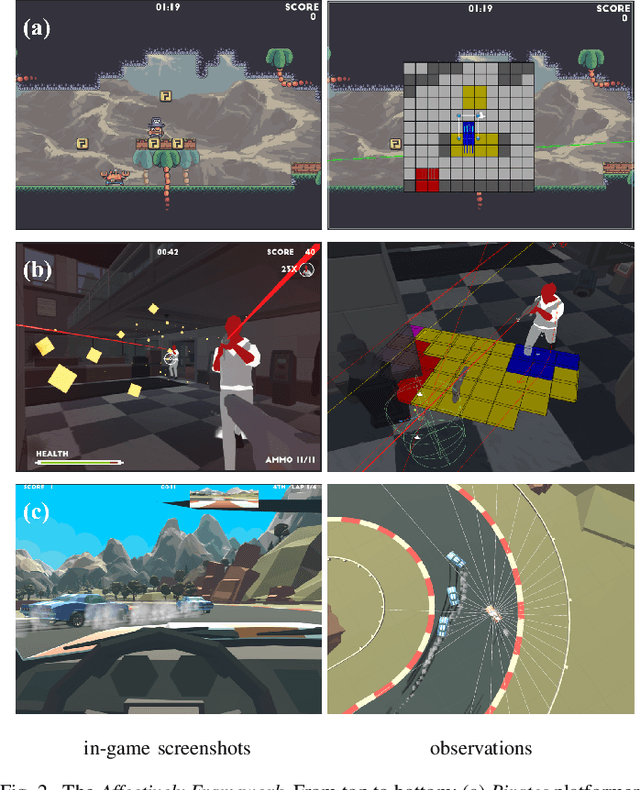
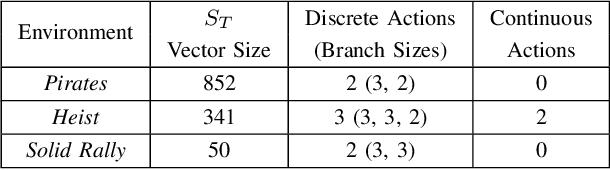
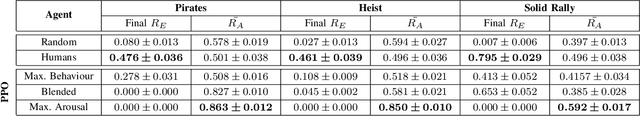
Abstract:Game environments offer a unique opportunity for training virtual agents due to their interactive nature, which provides diverse play traces and affect labels. Despite their potential, no reinforcement learning framework incorporates human affect models as part of their observation space or reward mechanism. To address this, we present the \emph{Affectively Framework}, a set of Open-AI Gym environments that integrate affect as part of the observation space. This paper introduces the framework and its three game environments and provides baseline experiments to validate its effectiveness and potential.
Dynamic Quality-Diversity Search
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Evolutionary search via the quality-diversity (QD) paradigm can discover highly performing solutions in different behavioural niches, showing considerable potential in complex real-world scenarios such as evolutionary robotics. Yet most QD methods only tackle static tasks that are fixed over time, which is rarely the case in the real world. Unlike noisy environments, where the fitness of an individual changes slightly at every evaluation, dynamic environments simulate tasks where external factors at unknown and irregular intervals alter the performance of the individual with a severity that is unknown a priori. Literature on optimisation in dynamic environments is extensive, yet such environments have not been explored in the context of QD search. This paper introduces a novel and generalisable Dynamic QD methodology that aims to keep the archive of past solutions updated in the case of environment changes. Secondly, we present a novel characterisation of dynamic environments that can be easily applied to well-known benchmarks, with minor interventions to move them from a static task to a dynamic one. Our Dynamic QD intervention is applied on MAP-Elites and CMA-ME, two powerful QD algorithms, and we test the dynamic variants on different dynamic tasks.
MAP-Elites with Transverse Assessment for Multimodal Problems in Creative Domains
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:The recent advances in language-based generative models have paved the way for the orchestration of multiple generators of different artefact types (text, image, audio, etc.) into one system. Presently, many open-source pre-trained models combine text with other modalities, thus enabling shared vector embeddings to be compared across different generators. Within this context we propose a novel approach to handle multimodal creative tasks using Quality Diversity evolution. Our contribution is a variation of the MAP-Elites algorithm, MAP-Elites with Transverse Assessment (MEliTA), which is tailored for multimodal creative tasks and leverages deep learned models that assess coherence across modalities. MEliTA decouples the artefacts' modalities and promotes cross-pollination between elites. As a test bed for this algorithm, we generate text descriptions and cover images for a hypothetical video game and assign each artefact a unique modality-specific behavioural characteristic. Results indicate that MEliTA can improve text-to-image mappings within the solution space, compared to a baseline MAP-Elites algorithm that strictly treats each image-text pair as one solution. Our approach represents a significant step forward in multimodal bottom-up orchestration and lays the groundwork for more complex systems coordinating multimodal creative agents in the future.
Large Language Models and Games: A Survey and Roadmap
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Recent years have seen an explosive increase in research on large language models (LLMs), and accompanying public engagement on the topic. While starting as a niche area within natural language processing, LLMs have shown remarkable potential across a broad range of applications and domains, including games. This paper surveys the current state of the art across the various applications of LLMs in and for games, and identifies the different roles LLMs can take within a game. Importantly, we discuss underexplored areas and promising directions for future uses of LLMs in games and we reconcile the potential and limitations of LLMs within the games domain. As the first comprehensive survey and roadmap at the intersection of LLMs and games, we are hopeful that this paper will serve as the basis for groundbreaking research and innovation in this exciting new field.
Simulator-Free Visual Domain Randomization via Video Games
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Domain randomization is an effective computer vision technique for improving transferability of vision models across visually distinct domains exhibiting similar content. Existing approaches, however, rely extensively on tweaking complex and specialized simulation engines that are difficult to construct, subsequently affecting their feasibility and scalability. This paper introduces BehAVE, a video understanding framework that uniquely leverages the plethora of existing commercial video games for domain randomization, without requiring access to their simulation engines. Under BehAVE (1) the inherent rich visual diversity of video games acts as the source of randomization and (2) player behavior -- represented semantically via textual descriptions of actions -- guides the *alignment* of videos with similar content. We test BehAVE on 25 games of the first-person shooter (FPS) genre across various video and text foundation models and we report its robustness for domain randomization. BehAVE successfully aligns player behavioral patterns and is able to zero-shot transfer them to multiple unseen FPS games when trained on just one FPS game. In a more challenging setting, BehAVE manages to improve the zero-shot transferability of foundation models to unseen FPS games (up to 22%) even when trained on a game of a different genre (Minecraft). Code and dataset can be found at https://github.com/nrasajski/BehAVE.
Towards General Game Representations: Decomposing Games Pixels into Content and Style
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:On-screen game footage contains rich contextual information that players process when playing and experiencing a game. Learning pixel representations of games can benefit artificial intelligence across several downstream tasks including game-playing agents, procedural content generation, and player modelling. The generalizability of these methods, however, remains a challenge, as learned representations should ideally be shared across games with similar game mechanics. This could allow, for instance, game-playing agents trained on one game to perform well in similar games with no re-training. This paper explores how generalizable pre-trained computer vision encoders can be for such tasks, by decomposing the latent space into content embeddings and style embeddings. The goal is to minimize the domain gap between games of the same genre when it comes to game content critical for downstream tasks, and ignore differences in graphical style. We employ a pre-trained Vision Transformer encoder and a decomposition technique based on game genres to obtain separate content and style embeddings. Our findings show that the decomposed embeddings achieve style invariance across multiple games while still maintaining strong content extraction capabilities. We argue that the proposed decomposition of content and style offers better generalization capacities across game environments independently of the downstream task.
From the Lab to the Wild: Affect Modeling via Privileged Information
May 18, 2023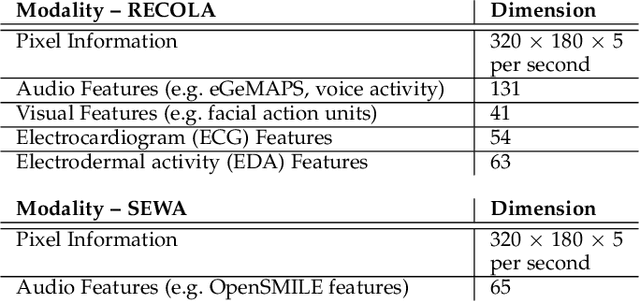
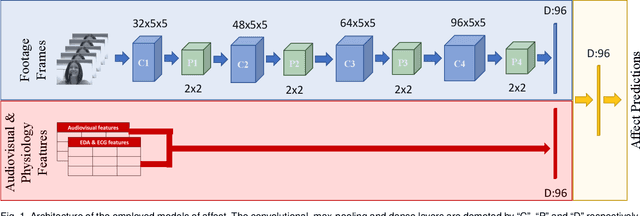
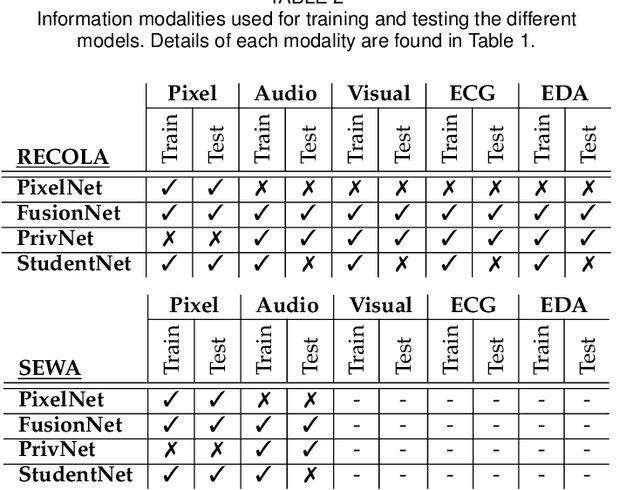
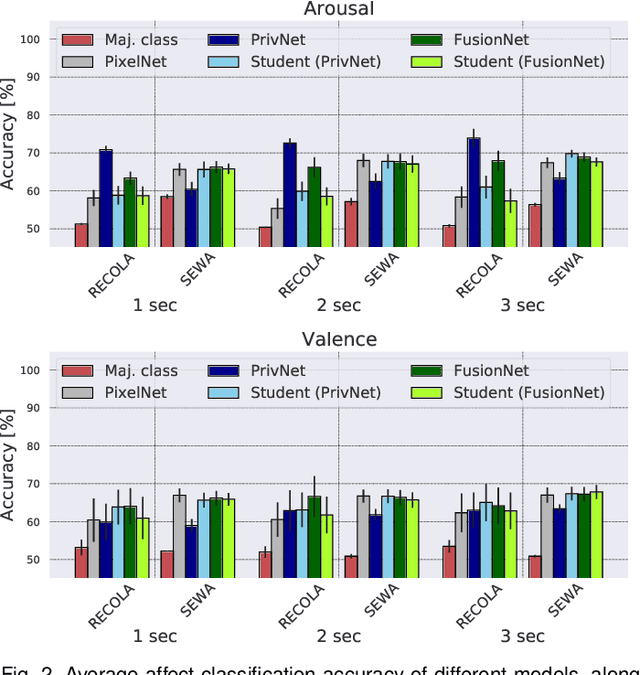
Abstract:How can we reliably transfer affect models trained in controlled laboratory conditions (in-vitro) to uncontrolled real-world settings (in-vivo)? The information gap between in-vitro and in-vivo applications defines a core challenge of affective computing. This gap is caused by limitations related to affect sensing including intrusiveness, hardware malfunctions and availability of sensors. As a response to these limitations, we introduce the concept of privileged information for operating affect models in real-world scenarios (in the wild). Privileged information enables affect models to be trained across multiple modalities available in a lab, and ignore, without significant performance drops, those modalities that are not available when they operate in the wild. Our approach is tested in two multimodal affect databases one of which is designed for testing models of affect in the wild. By training our affect models using all modalities and then using solely raw footage frames for testing the models, we reach the performance of models that fuse all available modalities for both training and testing. The results are robust across both classification and regression affect modeling tasks which are dominant paradigms in affective computing. Our findings make a decisive step towards realizing affect interaction in the wild.
Controllable Exploration of a Design Space via Interactive Quality Diversity
Apr 07, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces a user-driven evolutionary algorithm based on Quality Diversity (QD) search. During a design session, the user iteratively selects among presented alternatives and their selections affect the upcoming results. We aim to address two major concerns of interactive evolution: (a) the user must be presented with few alternatives, to reduce cognitive load; (b) presented alternatives should be diverse but similar to the previous user selection, to reduce user fatigue. To address these concerns, we implement a variation of the MAP-Elites algorithm where the presented alternatives are sampled from a small region (window) of the behavioral space. After a user selection, the window is centered on the selected individual's behavior characterization, evolution selects parents from within this window to produce offspring, and new alternatives are sampled. Essentially we define an adaptive system of local QD, where the user's selections guide the search towards specific regions of the behavioral space. The system is tested on the generation of architectural layouts, a constrained optimization task, leveraging QD through a two-archive approach. Results show that while global exploration is not as pronounced as in MAP-Elites, the system finds more appropriate solutions to the user's taste, based on experiments with controllable artificial users.
Architext: Language-Driven Generative Architecture Design
Mar 15, 2023



Abstract:Architectural design is a highly complex practice that involves a wide diversity of disciplines, technologies, proprietary design software, expertise, and an almost infinite number of constraints, across a vast array of design tasks. Enabling intuitive, accessible, and scalable design processes is an important step towards performance-driven and sustainable design for all. To that end, we introduce Architext, a novel semantic generation assistive tool. Architext enables design generation with only natural language prompts, given to large-scale Language Models, as input. We conduct a thorough quantitative evaluation of Architext's downstream task performance, focusing on semantic accuracy and diversity for a number of pre-trained language models ranging from 120 million to 6 billion parameters. Architext models are able to learn the specific design task, generating valid residential layouts at a near 100% rate. Accuracy shows great improvement when scaling the models, with the largest model (GPT-J) yielding impressive accuracy ranging between 25% to over 80% for different prompt categories. We open source the finetuned Architext models and our synthetic dataset, hoping to inspire experimentation in this exciting area of design research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge