Anmol Walia
Retrieval Augmented Correction of Named Entity Speech Recognition Errors
Sep 09, 2024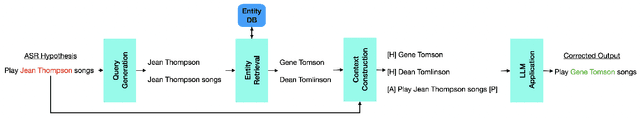
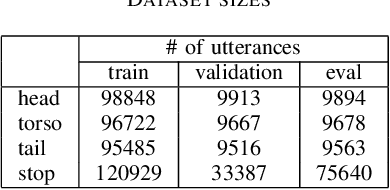
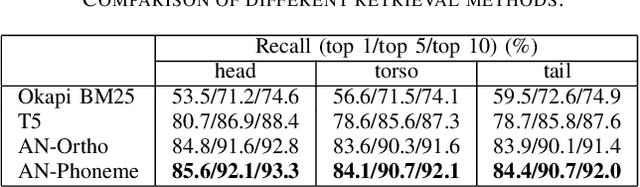
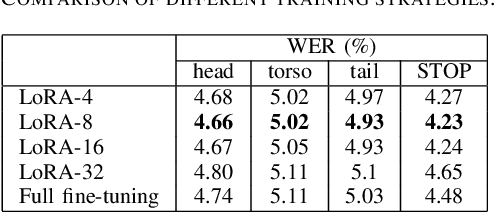
Abstract:In recent years, end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have proven themselves remarkably accurate and performant, but these systems still have a significant error rate for entity names which appear infrequently in their training data. In parallel to the rise of end-to-end ASR systems, large language models (LLMs) have proven to be a versatile tool for various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. In NLP tasks where a database of relevant knowledge is available, retrieval augmented generation (RAG) has achieved impressive results when used with LLMs. In this work, we propose a RAG-like technique for correcting speech recognition entity name errors. Our approach uses a vector database to index a set of relevant entities. At runtime, database queries are generated from possibly errorful textual ASR hypotheses, and the entities retrieved using these queries are fed, along with the ASR hypotheses, to an LLM which has been adapted to correct ASR errors. Overall, our best system achieves 33%-39% relative word error rate reductions on synthetic test sets focused on voice assistant queries of rare music entities without regressing on the STOP test set, a publicly available voice assistant test set covering many domains.
Training Large-Vocabulary Neural Language Models by Private Federated Learning for Resource-Constrained Devices
Jul 18, 2022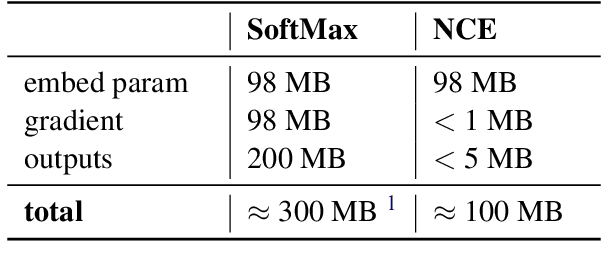
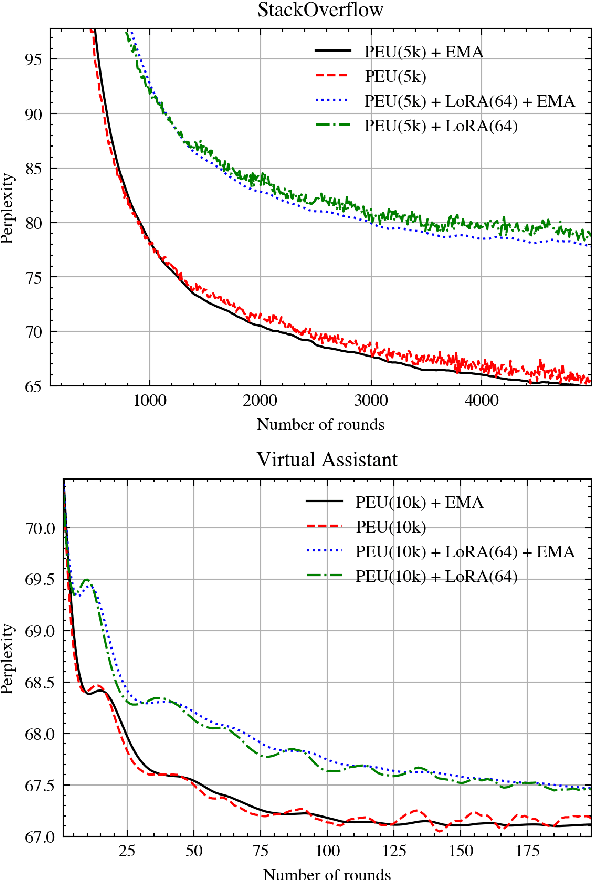

Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a technique to train models using data distributed across devices. Differential Privacy (DP) provides a formal privacy guarantee for sensitive data. Our goal is to train a large neural network language model (NNLM) on compute-constrained devices while preserving privacy using FL and DP. However, the DP-noise introduced to the model increases as the model size grows, which often prevents convergence. We propose Partial Embedding Updates (PEU), a novel technique to decrease noise by decreasing payload size. Furthermore, we adopt Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and Noise Contrastive Estimation (NCE) to reduce the memory demands of large models on compute-constrained devices. This combination of techniques makes it possible to train large-vocabulary language models while preserving accuracy and privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge