Andrey Boytsov
CallNavi: A Study and Challenge on Function Calling Routing and Invocation in Large Language Models
Jan 09, 2025
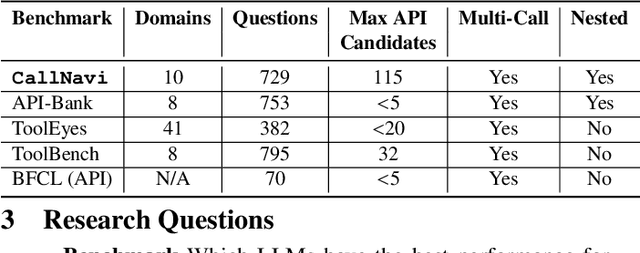


Abstract:Interacting with a software system via a chatbot can be challenging, especially when the chatbot needs to generate API calls, in the right order and with the right parameters, to communicate with the system. API calling in chatbot systems poses significant challenges, particularly in complex, multi-step tasks requiring accurate API selection and execution. We contribute to this domain in three ways: first, by introducing a novel dataset designed to assess models on API function selection, parameter generation, and nested API calls; second, by benchmarking state-of-the-art language models across varying levels of complexity to evaluate their performance in API function generation and parameter accuracy; and third, by proposing an enhanced API routing method that combines general-purpose large language models for API selection with fine-tuned models for parameter generation and some prompt engineering approach. These approaches lead to substantial improvements in handling complex API tasks, offering practical advancements for real-world API-driven chatbot systems.
Visualizing and Exploring Dynamic High-Dimensional Datasets with LION-tSNE
Aug 16, 2017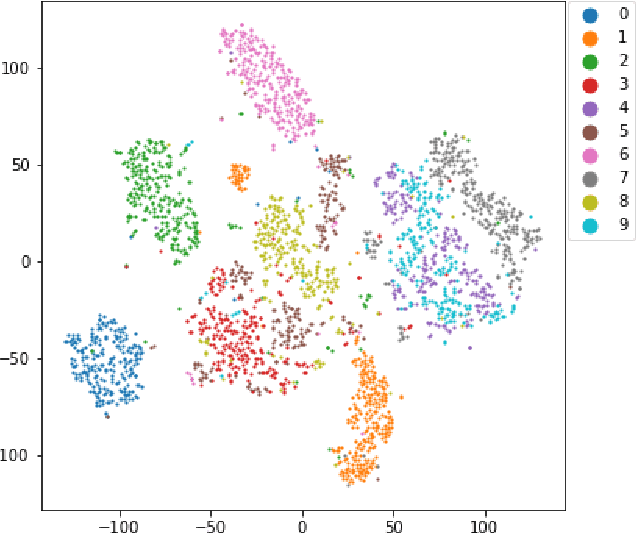
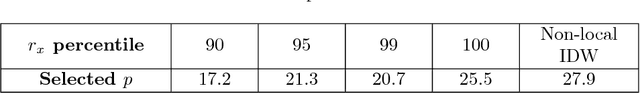
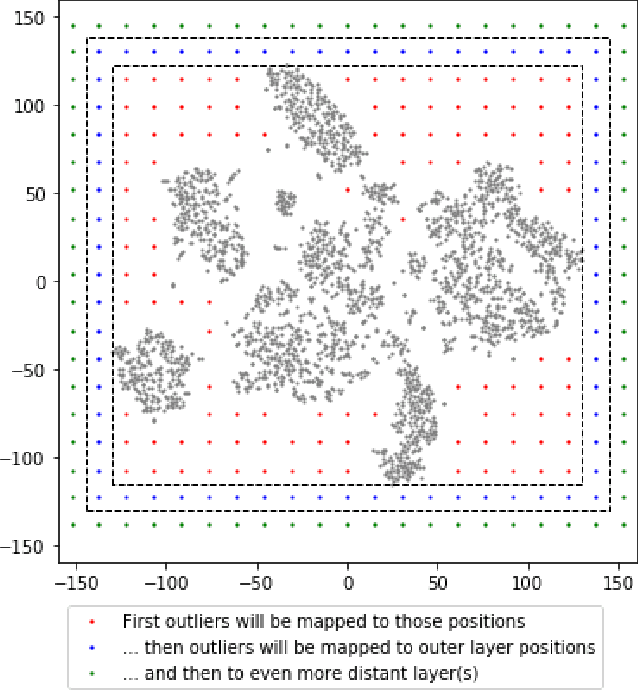
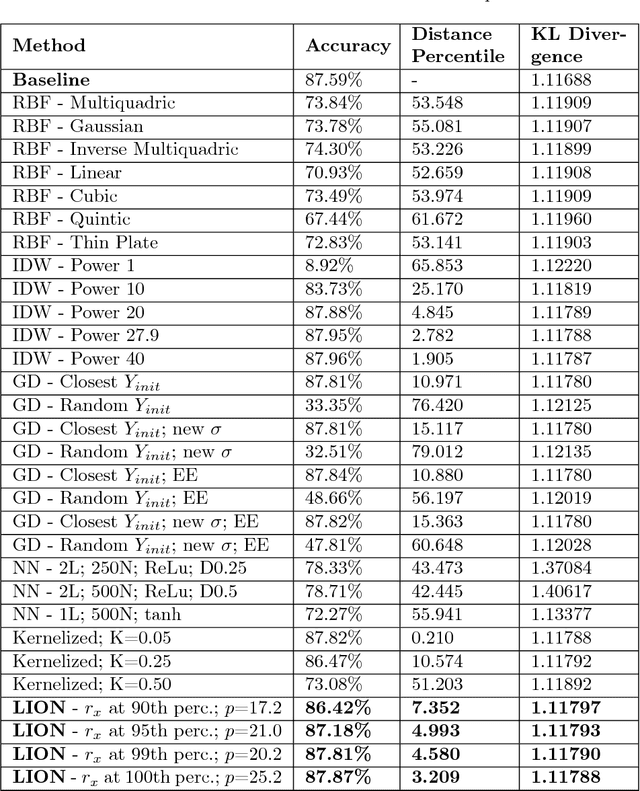
Abstract:T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) is a popular and prize-winning approach for dimensionality reduction and visualizing high-dimensional data. However, tSNE is non-parametric: once visualization is built, tSNE is not designed to incorporate additional data into existing representation. It highly limits the applicability of tSNE to the scenarios where data are added or updated over time (like dashboards or series of data snapshots). In this paper we propose, analyze and evaluate LION-tSNE (Local Interpolation with Outlier coNtrol) - a novel approach for incorporating new data into tSNE representation. LION-tSNE is based on local interpolation in the vicinity of training data, outlier detection and a special outlier mapping algorithm. We show that LION-tSNE method is robust both to outliers and to new samples from existing clusters. We also discuss multiple possible improvements for special cases. We compare LION-tSNE to a comprehensive list of possible benchmark approaches that include multiple interpolation techniques, gradient descent for new data, and neural network approximation.
The Top 10 Topics in Machine Learning Revisited: A Quantitative Meta-Study
Mar 29, 2017
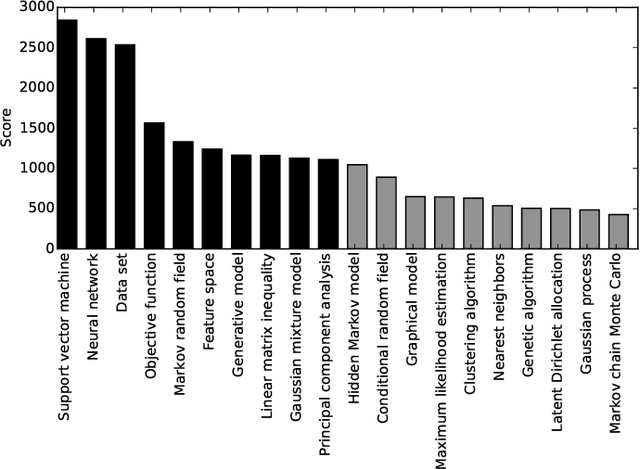
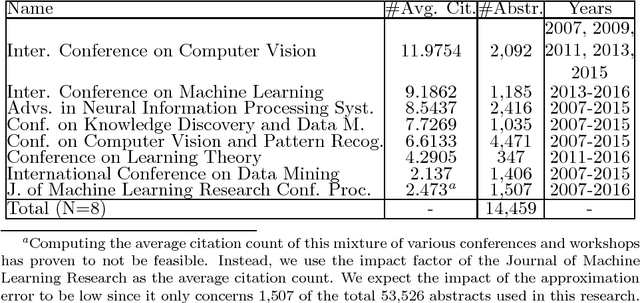
Abstract:Which topics of machine learning are most commonly addressed in research? This question was initially answered in 2007 by doing a qualitative survey among distinguished researchers. In our study, we revisit this question from a quantitative perspective. Concretely, we collect 54K abstracts of papers published between 2007 and 2016 in leading machine learning journals and conferences. We then use machine learning in order to determine the top 10 topics in machine learning. We not only include models, but provide a holistic view across optimization, data, features, etc. This quantitative approach allows reducing the bias of surveys. It reveals new and up-to-date insights into what the 10 most prolific topics in machine learning research are. This allows researchers to identify popular topics as well as new and rising topics for their research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge