Andrew Tang
ClusterSC: Advancing Synthetic Control with Donor Selection
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:In causal inference with observational studies, synthetic control (SC) has emerged as a prominent tool. SC has traditionally been applied to aggregate-level datasets, but more recent work has extended its use to individual-level data. As they contain a greater number of observed units, this shift introduces the curse of dimensionality to SC. To address this, we propose Cluster Synthetic Control (ClusterSC), based on the idea that groups of individuals may exist where behavior aligns internally but diverges between groups. ClusterSC incorporates a clustering step to select only the relevant donors for the target. We provide theoretical guarantees on the improvements induced by ClusterSC, supported by empirical demonstrations on synthetic and real-world datasets. The results indicate that ClusterSC consistently outperforms classical SC approaches.
MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge
Jun 17, 2022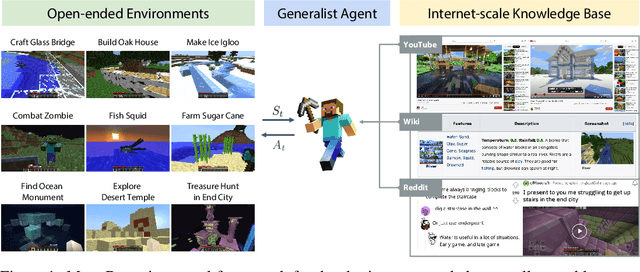
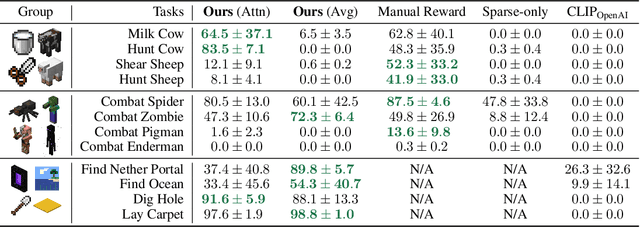
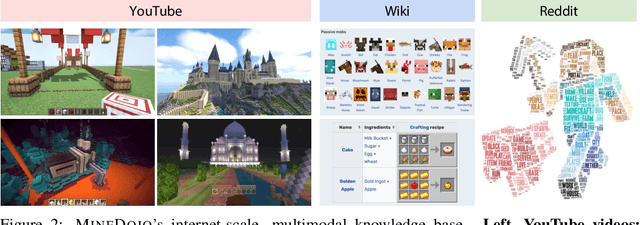
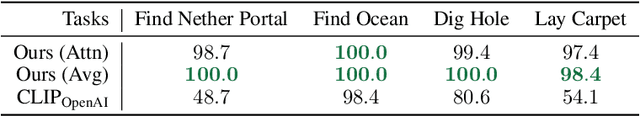
Abstract:Autonomous agents have made great strides in specialist domains like Atari games and Go. However, they typically learn tabula rasa in isolated environments with limited and manually conceived objectives, thus failing to generalize across a wide spectrum of tasks and capabilities. Inspired by how humans continually learn and adapt in the open world, we advocate a trinity of ingredients for building generalist agents: 1) an environment that supports a multitude of tasks and goals, 2) a large-scale database of multimodal knowledge, and 3) a flexible and scalable agent architecture. We introduce MineDojo, a new framework built on the popular Minecraft game that features a simulation suite with thousands of diverse open-ended tasks and an internet-scale knowledge base with Minecraft videos, tutorials, wiki pages, and forum discussions. Using MineDojo's data, we propose a novel agent learning algorithm that leverages large pre-trained video-language models as a learned reward function. Our agent is able to solve a variety of open-ended tasks specified in free-form language without any manually designed dense shaping reward. We open-source the simulation suite and knowledge bases (https://minedojo.org) to promote research towards the goal of generally capable embodied agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge