Ana Peleteiro Ramallo
Retrieve, Annotate, Evaluate, Repeat: Leveraging Multimodal LLMs for Large-Scale Product Retrieval Evaluation
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating production-level retrieval systems at scale is a crucial yet challenging task due to the limited availability of a large pool of well-trained human annotators. Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to address this scaling issue and offer a viable alternative to humans for the bulk of annotation tasks. In this paper, we propose a framework for assessing the product search engines in a large-scale e-commerce setting, leveraging Multimodal LLMs for (i) generating tailored annotation guidelines for individual queries, and (ii) conducting the subsequent annotation task. Our method, validated through deployment on a large e-commerce platform, demonstrates comparable quality to human annotations, significantly reduces time and cost, facilitates rapid problem discovery, and provides an effective solution for production-level quality control at scale.
Building a Scalable, Effective, and Steerable Search and Ranking Platform
Sep 04, 2024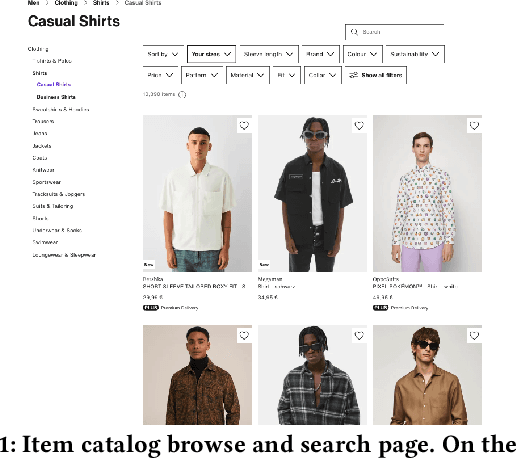
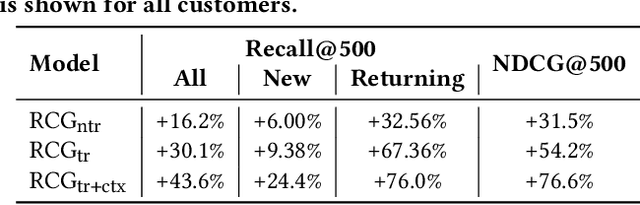
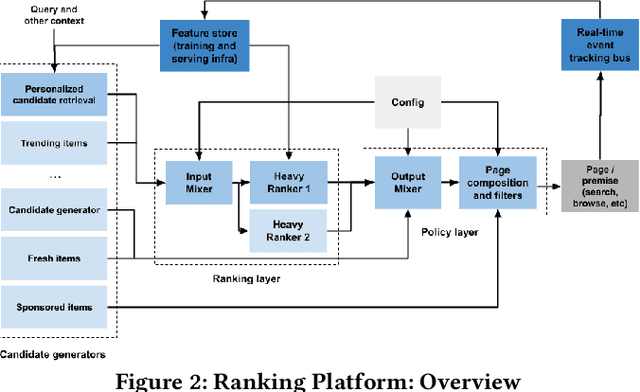
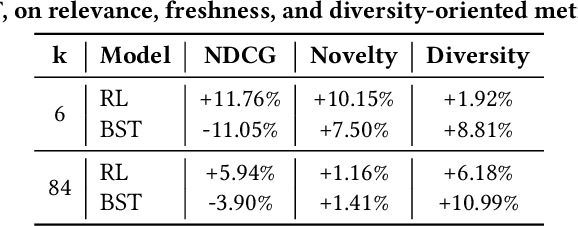
Abstract:Modern e-commerce platforms offer vast product selections, making it difficult for customers to find items that they like and that are relevant to their current session intent. This is why it is key for e-commerce platforms to have near real-time scalable and adaptable personalized ranking and search systems. While numerous methods exist in the scientific literature for building such systems, many are unsuitable for large-scale industrial use due to complexity and performance limitations. Consequently, industrial ranking systems often resort to computationally efficient yet simplistic retrieval or candidate generation approaches, which overlook near real-time and heterogeneous customer signals, which results in a less personalized and relevant experience. Moreover, related customer experiences are served by completely different systems, which increases complexity, maintenance, and inconsistent experiences. In this paper, we present a personalized, adaptable near real-time ranking platform that is reusable across various use cases, such as browsing and search, and that is able to cater to millions of items and customers under heavy load (thousands of requests per second). We employ transformer-based models through different ranking layers which can learn complex behavior patterns directly from customer action sequences while being able to incorporate temporal (e.g. in-session) and contextual information. We validate our system through a series of comprehensive offline and online real-world experiments at a large online e-commerce platform, and we demonstrate its superiority when compared to existing systems, both in terms of customer experience as well as in net revenue. Finally, we share the lessons learned from building a comprehensive, modern ranking platform for use in a large-scale e-commerce environment.
What should I wear to a party in a Greek taverna? Evaluation for Conversational Agents in the Fashion Domain
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are poised to revolutionize the domain of online fashion retail, enhancing customer experience and discovery of fashion online. LLM-powered conversational agents introduce a new way of discovery by directly interacting with customers, enabling them to express in their own ways, refine their needs, obtain fashion and shopping advice that is relevant to their taste and intent. For many tasks in e-commerce, such as finding a specific product, conversational agents need to convert their interactions with a customer to a specific call to different backend systems, e.g., a search system to showcase a relevant set of products. Therefore, evaluating the capabilities of LLMs to perform those tasks related to calling other services is vital. However, those evaluations are generally complex, due to the lack of relevant and high quality datasets, and do not align seamlessly with business needs, amongst others. To this end, we created a multilingual evaluation dataset of 4k conversations between customers and a fashion assistant in a large e-commerce fashion platform to measure the capabilities of LLMs to serve as an assistant between customers and a backend engine. We evaluate a range of models, showcasing how our dataset scales to business needs and facilitates iterative development of tools.
UNICON: A unified framework for behavior-based consumer segmentation in e-commerce
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:Data-driven personalization is a key practice in fashion e-commerce, improving the way businesses serve their consumers needs with more relevant content. While hyper-personalization offers highly targeted experiences to each consumer, it requires a significant amount of private data to create an individualized journey. To alleviate this, group-based personalization provides a moderate level of personalization built on broader common preferences of a consumer segment, while still being able to personalize the results. We introduce UNICON, a unified deep learning consumer segmentation framework that leverages rich consumer behavior data to learn long-term latent representations and utilizes them to extract two pivotal types of segmentation catering various personalization use-cases: lookalike, expanding a predefined target seed segment with consumers of similar behavior, and data-driven, revealing non-obvious consumer segments with similar affinities. We demonstrate through extensive experimentation our framework effectiveness in fashion to identify lookalike Designer audience and data-driven style segments. Furthermore, we present experiments that showcase how segment information can be incorporated in a hybrid recommender system combining hyper and group-based personalization to exploit the advantages of both alternatives and provide improvements on consumer experience.
Reusable Self-Attention Recommender Systems in Fashion Industry Applications
Jan 17, 2023Abstract:A large number of empirical studies on applying self-attention models in the domain of recommender systems are based on offline evaluation and metrics computed on standardized datasets. Moreover, many of them do not consider side information such as item and customer metadata although deep-learning recommenders live up to their full potential only when numerous features of heterogeneous type are included. Also, normally the model is used only for a single use case. Due to these shortcomings, even if relevant, previous works are not always representative of their actual effectiveness in real-world industry applications. In this talk, we contribute to bridging this gap by presenting live experimental results demonstrating improvements in user retention of up to 30\%. Moreover, we share our learnings and challenges from building a re-usable and configurable recommender system for various applications from the fashion industry. In particular, we focus on fashion inspiration use-cases, such as outfit ranking, outfit recommendation and real-time personalized outfit generation.
Reusable Self-Attention-based Recommender System for Fashion
Nov 29, 2022
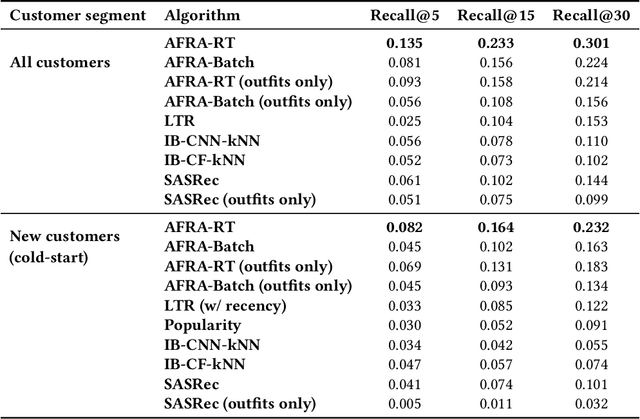
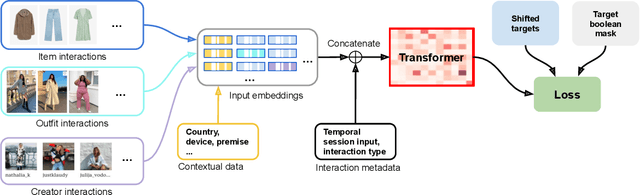

Abstract:A large number of empirical studies on applying self-attention models in the domain of recommender systems are based on offline evaluation and metrics computed on standardized datasets, without insights on how these models perform in real life scenarios. Moreover, many of them do not consider information such as item and customer metadata, although deep-learning recommenders live up to their full potential only when numerous features of heterogeneous types are included. Also, typically recommendation models are designed to serve well only a single use case, which increases modeling complexity and maintenance costs, and may lead to inconsistent customer experience. In this work, we present a reusable Attention-based Fashion Recommendation Algorithm (AFRA), that utilizes various interaction types with different fashion entities such as items (e.g., shirt), outfits and influencers, and their heterogeneous features. Moreover, we leverage temporal and contextual information to address both short and long-term customer preferences. We show its effectiveness on outfit recommendation use cases, in particular: 1) personalized ranked feed; 2) outfit recommendations by style; 3) similar item recommendation and 4) in-session recommendations inspired by most recent customer actions. We present both offline and online experimental results demonstrating substantial improvements in customer retention and engagement.
* FashionXRecSys'22: Workshop on Recommender Systems in Fashion, September 23, 2022, Seattle, WA. Parts published in RecSys 2022 (industry track)
Outfit Generation and Recommendation -- An Experimental Study
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:Over the past years, fashion-related challenges have gained a lot of attention in the research community. Outfit generation and recommendation, i.e., the composition of a set of items of different types (e.g., tops, bottom, shoes, accessories) that go well together, are among the most challenging ones. That is because items have to be both compatible amongst each other and also personalized to match the taste of the customer. Recently there has been a plethora of work targeted at tackling these problems by adopting various techniques and algorithms from the machine learning literature. However, to date, there is no extensive comparison of the performance of the different algorithms for outfit generation and recommendation. In this paper, we close this gap by providing a broad evaluation and comparison of various algorithms, including both personalized and non-personalized approaches, using online, real-world user data from one of Europe's largest fashion stores. We present the adaptations we made to some of those models to make them suitable for personalized outfit generation. Moreover, we provide insights for models that have not yet been evaluated on this task, specifically, GPT, BERT and Seq-to-Seq LSTM.
* fashionXrecsys '20: Workshop on Recommender Systems in Fashion, 14th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, September 22--26, 2020, Virtual Event, Brazil
Contextual BERT: Conditioning the Language Model Using a Global State
Oct 29, 2020
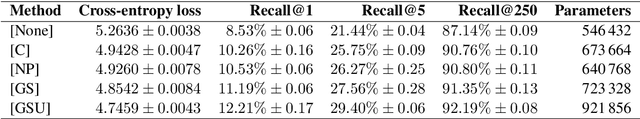
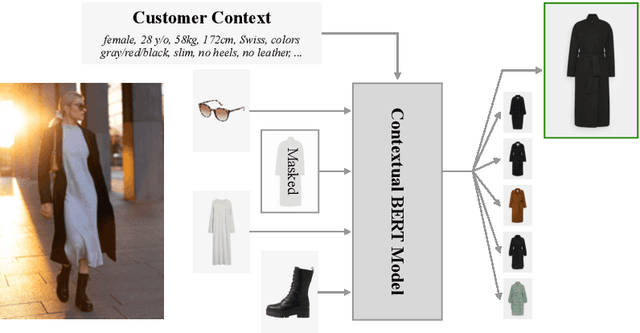
Abstract:BERT is a popular language model whose main pre-training task is to fill in the blank, i.e., predicting a word that was masked out of a sentence, based on the remaining words. In some applications, however, having an additional context can help the model make the right prediction, e.g., by taking the domain or the time of writing into account. This motivates us to advance the BERT architecture by adding a global state for conditioning on a fixed-sized context. We present our two novel approaches and apply them to an industry use-case, where we complete fashion outfits with missing articles, conditioned on a specific customer. An experimental comparison to other methods from the literature shows that our methods improve personalization significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge