Vladimir Vlasov
Reducing Popularity Influence by Addressing Position Bias
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Position bias poses a persistent challenge in recommender systems, with much of the existing research focusing on refining ranking relevance and driving user engagement. However, in practical applications, the mitigation of position bias does not always result in detectable short-term improvements in ranking relevance. This paper provides an alternative, practically useful view of what position bias reduction methods can achieve. It demonstrates that position debiasing can spread visibility and interactions more evenly across the assortment, effectively reducing a skew in the popularity of items induced by the position bias through a feedback loop. We offer an explanation of how position bias affects item popularity. This includes an illustrative model of the item popularity histogram and the effect of the position bias on its skewness. Through offline and online experiments on our large-scale e-commerce platform, we show that position debiasing can significantly improve assortment utilization, without any degradation in user engagement or financial metrics. This makes the ranking fairer and helps attract more partners or content providers, benefiting the customers and the business in the long term.
Efficient slot labelling
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:Slot labelling is an essential component of any dialogue system, aiming to find important arguments in every user turn. Common approaches involve large pre-trained language models (PLMs) like BERT or RoBERTa, but they face challenges such as high computational requirements and dependence on pre-training data. In this work, we propose a lightweight method which performs on par or better than the state-of-the-art PLM-based methods, while having almost 10x less trainable parameters. This makes it especially applicable for real-life industry scenarios.
UNICON: A unified framework for behavior-based consumer segmentation in e-commerce
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:Data-driven personalization is a key practice in fashion e-commerce, improving the way businesses serve their consumers needs with more relevant content. While hyper-personalization offers highly targeted experiences to each consumer, it requires a significant amount of private data to create an individualized journey. To alleviate this, group-based personalization provides a moderate level of personalization built on broader common preferences of a consumer segment, while still being able to personalize the results. We introduce UNICON, a unified deep learning consumer segmentation framework that leverages rich consumer behavior data to learn long-term latent representations and utilizes them to extract two pivotal types of segmentation catering various personalization use-cases: lookalike, expanding a predefined target seed segment with consumers of similar behavior, and data-driven, revealing non-obvious consumer segments with similar affinities. We demonstrate through extensive experimentation our framework effectiveness in fashion to identify lookalike Designer audience and data-driven style segments. Furthermore, we present experiments that showcase how segment information can be incorporated in a hybrid recommender system combining hyper and group-based personalization to exploit the advantages of both alternatives and provide improvements on consumer experience.
DIET: Lightweight Language Understanding for Dialogue Systems
May 11, 2020
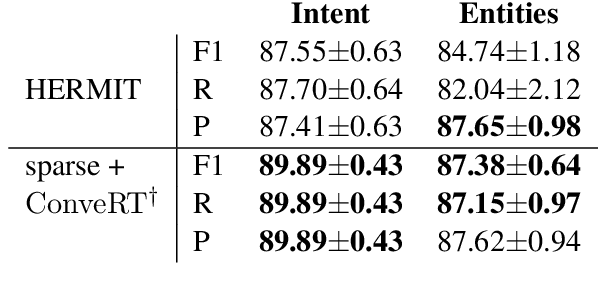
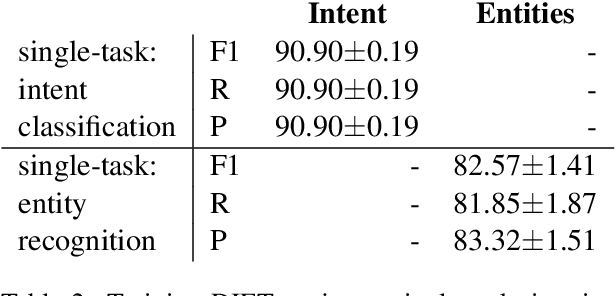
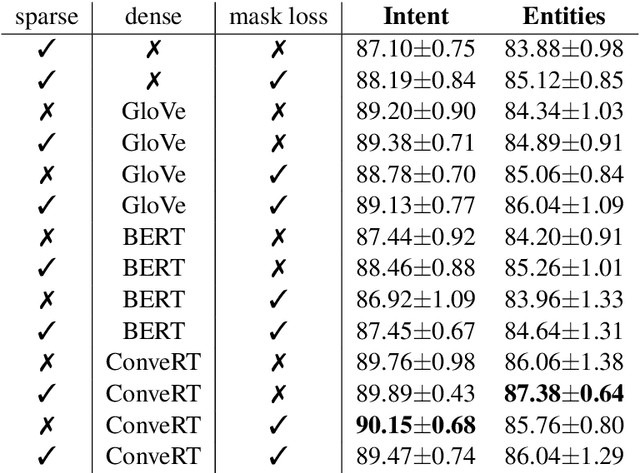
Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained language models have shown impressive results on language understanding benchmarks like GLUE and SuperGLUE, improving considerably over other pre-training methods like distributed representations (GloVe) and purely supervised approaches. We introduce the Dual Intent and Entity Transformer (DIET) architecture, and study the effectiveness of different pre-trained representations on intent and entity prediction, two common dialogue language understanding tasks. DIET advances the state of the art on a complex multi-domain NLU dataset and achieves similarly high performance on other simpler datasets. Surprisingly, we show that there is no clear benefit to using large pre-trained models for this task, and in fact DIET improves upon the current state of the art even in a purely supervised setup without any pre-trained embeddings. Our best performing model outperforms fine-tuning BERT and is about six times faster to train.
Where is the context? -- A critique of recent dialogue datasets
Apr 22, 2020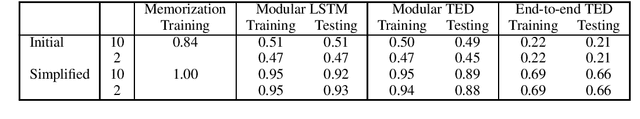

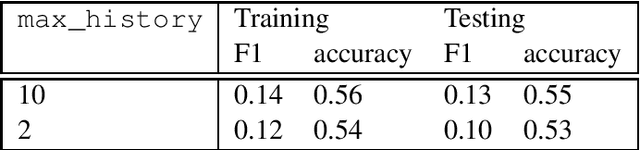
Abstract:Recent dialogue datasets like MultiWOZ 2.1 and Taskmaster-1 constitute some of the most challenging tasks for present-day dialogue models and, therefore, are widely used for system evaluation. We identify several issues with the above-mentioned datasets, such as history independence, strong knowledge base dependence, and ambiguous system responses. Finally, we outline key desiderata for future datasets that we believe would be more suitable for the construction of conversational artificial intelligence.
Dialogue Transformers
Oct 01, 2019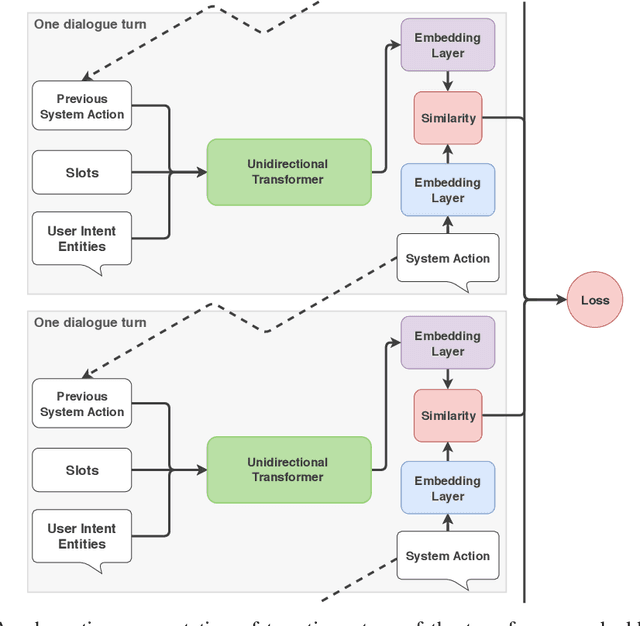


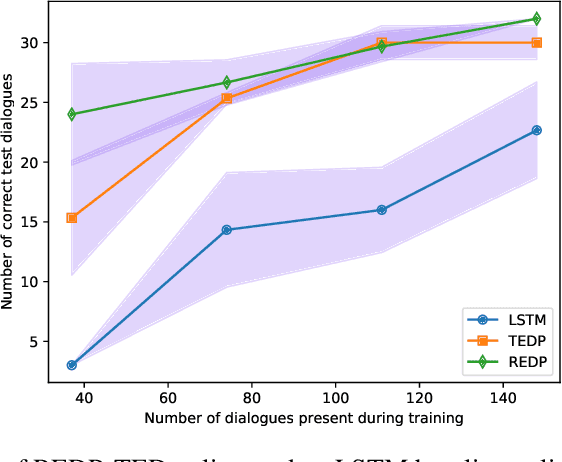
Abstract:We introduce a dialogue policy based on a transformer architecture, where the self-attention mechanism operates over the sequence of dialogue turns. Recent work has used hierarchical recurrent neural networks to encode multiple utterances in a dialogue context, but we argue that a pure self-attention mechanism is more suitable. By default, an RNN assumes that every item in a sequence is relevant for producing an encoding of the full sequence, but a single conversation can consist of multiple overlapping discourse segments as speakers interleave multiple topics. A transformer picks which turns to include in its encoding of the current dialogue state, and is naturally suited to selectively ignoring or attending to dialogue history. We compare the performance of the Transformer Embedding Dialogue (TED) policy to an LSTM and to the REDP, which was specifically designed to overcome this limitation of RNNs. We show that the TED policy's behaviour compares favourably, both in terms of accuracy and speed.
Few-Shot Generalization Across Dialogue Tasks
Nov 28, 2018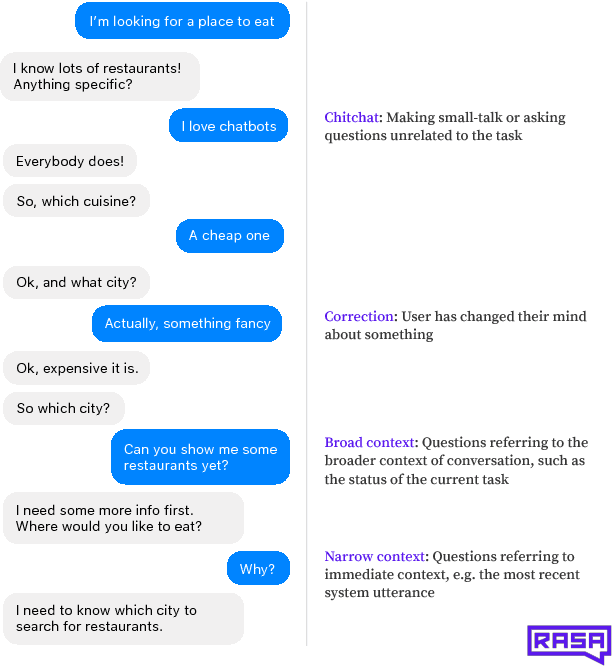
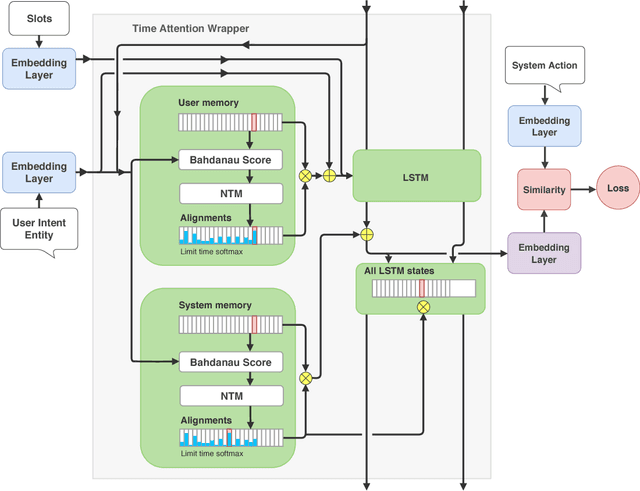
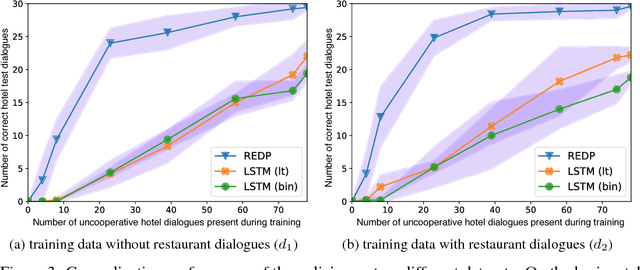
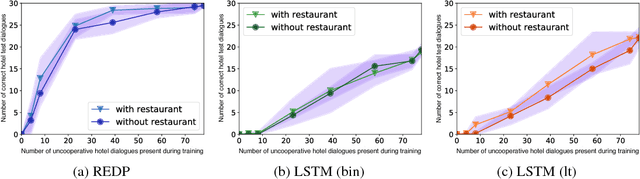
Abstract:Machine-learning based dialogue managers are able to learn complex behaviors in order to complete a task, but it is not straightforward to extend their capabilities to new domains. We investigate different policies' ability to handle uncooperative user behavior, and how well expertise in completing one task (such as restaurant reservations) can be reapplied when learning a new one (e.g. booking a hotel). We introduce the Recurrent Embedding Dialogue Policy (REDP), which embeds system actions and dialogue states in the same vector space. REDP contains a memory component and attention mechanism based on a modified Neural Turing Machine, and significantly outperforms a baseline LSTM classifier on this task. We also show that both our architecture and baseline solve the bAbI dialogue task, achieving 100% test accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge