An Mo
Upside down: affordable high-performance motion platform
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:Parallel robots are capable of high-speed manipulation and have become essential tools in the industry. The proximal placement of their motors and the low weight of their end effectors make them ideal for generating highly dynamic motion. Therefore, parallel robots can be adopted for motion platform designs, as long as end effector loads are low. Traditional motion platforms can be large and powerful to generate multiple g acceleration. However, these designs tend to be expensive and large. Similar but smaller motion platforms feature a small work range with reduced degrees of freedom (DoFs) and a limited payload. Here we seek a medium-sized affordable parallel robot capable of powerful and high-speed 6-DoF motion in a comparably large workspace. This work explores the concept of a quadruped robot flipped upside-down, with the motion platform fixed between its feet. In particular, we exploit the high-power dynamic brushless actuation and the four-leg redundancy when moving the motion platform. We characterize the resulting motion platform by tracking sinusoidal and circular trajectories with varying loads. Dynamic motions in 6 DoFs up to 10 Hz and ~10 mm amplitude are possible when moving a mass of 300 grams. We demonstrate single-axis end-effector translations up to ~20 mm at 10 Hz for higher loads of 1.2 kg. The motion platform can be replicated easily by 3D printing and off-the-shelf components. All motion platform-related hardware and the custom-written software required to replicate are open-source.
Slack-based tunable damping leads to a trade-off between robustness and efficiency in legged locomotion
Dec 01, 2022Abstract:Animals run robustly in diverse terrain. This locomotion robustness is puzzling because axon conduction velocity is limited to a few ten meters per second. If reflex loops deliver sensory information with significant delays, one would expect a destabilizing effect on sensorimotor control. Hence, an alternative explanation describes a hierarchical structure of low-level adaptive mechanics and high-level sensorimotor control to help mitigate the effects of transmission delays. Motivated by the concept of an adaptive mechanism triggering an immediate response, we developed a tunable physical damper system. Our mechanism combines a tendon with adjustable slackness connected to a physical damper. The slack damper allows adjustment of damping force, onset timing, effective stroke, and energy dissipation. We characterize the slack damper mechanism mounted to a legged robot controlled in open-loop mode. The robot hops vertically and planar over varying terrains and perturbations. During forward hopping, slack-based damping improves faster perturbation recovery (up to 170%) at higher energetic cost (27%). The tunable slack mechanism auto-engages the damper during perturbations, leading to a perturbation-trigger damping, improving robustness at minimum energetic cost. With the results from the slack damper mechanism, we propose a new functional interpretation of animals' redundant muscle tendons as tunable dampers.
Multi-segmented Adaptive Feet for Versatile Legged Locomotion in Natural Terrain
Sep 18, 2022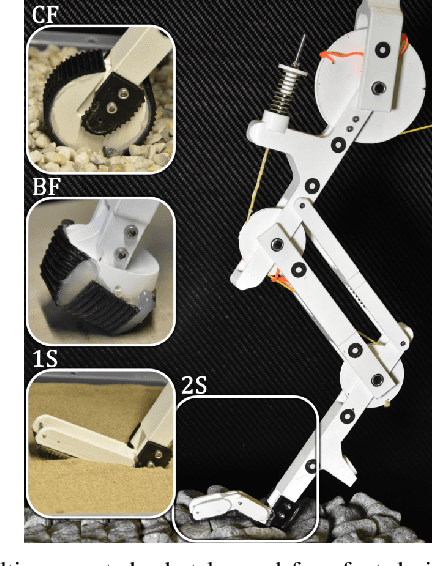
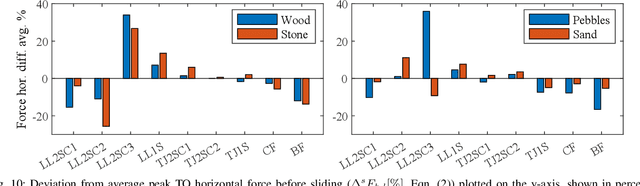
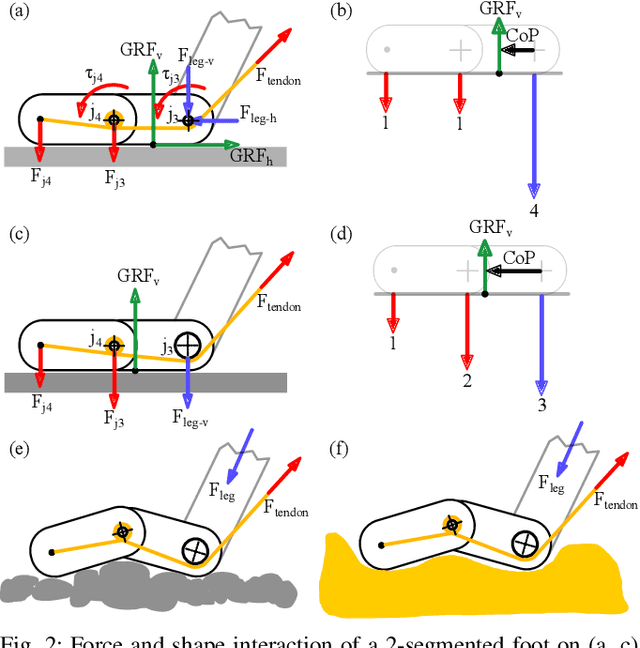
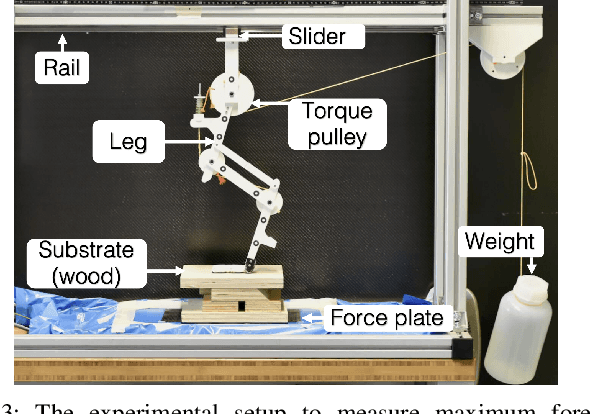
Abstract:Most legged robots are built with leg structures from serially mounted links and actuators and are controlled through complex controllers and sensor feedback. In comparison, animals developed multi-segment legs, mechanical coupling between joints, and multi-segmented feet. They run agile over all terrains, arguably with simpler locomotion control. Here we focus on developing foot mechanisms that resist slipping and sinking also in natural terrain. We present first results of multi-segment feet mounted to a bird-inspired robot leg with multi-joint mechanical tendon coupling. Our one- and two-segment, mechanically adaptive feet show increased viable horizontal forces on multiple soft and hard substrates before starting to slip. We also observe that segmented feet reduce sinking on soft substrates compared to ball-feet and cylinder-feet. We report how multi-segmented feet provide a large range of viable centre of pressure points well suited for bipedal robots, but also for quadruped robots on slopes and natural terrain. Our results also offer a functional understanding of segmented feet in animals like ratite birds.
Diaphragm Ankle Actuation for Efficient Series Elastic Legged Robot Hopping
Mar 04, 2022



Abstract:Robots need lightweight legs for agile locomotion, and intrinsic series elastic compliance has proven to be a major ingredient for energy-efficient locomotion and robust locomotion control. Animals' anatomy and locomotion capabilities emphasize the importance of that lightweight legs and integrated, compact, series elastically actuated for distal leg joints. But unlike robots, animals achieve series elastic actuation by their muscle-tendon units. So far no designs are available that feature all characteristics of a perfect distal legged locomotion actuator; a low-weight and low-inertia design, with high mechanical efficiency, no stick and sliding friction, low mechanical complexity, high-power output while being easy to mount. Ideally, such an actuator can be controlled directly and without mechanical cross-coupling, for example remotely. With this goal in mind, we propose a low-friction, lightweight Series ELastic Diaphragm distal Actuator (SELDA) which meets many, although not all, of the above requirements. We develop, implement, and characterize a bioinspired robot leg that features a SELDA-actuated foot segment. We compare two leg configurations controlled by a central pattern generator that both feature agile forward hopping. By tuning SELDA's activation timing, we effectively adjust the robot's hopping height by 11% and its forward velocity by 14%, even with comparatively low power injection to the distal joint.
Investigation on a bipedal robot: Why do humans need both Soleus andGastrocnemius muscles for ankle push-off during walking?
Mar 03, 2022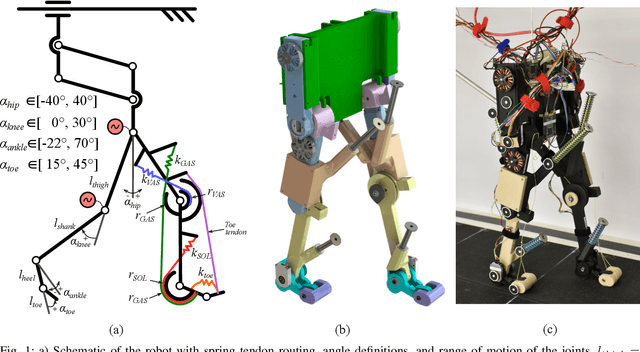
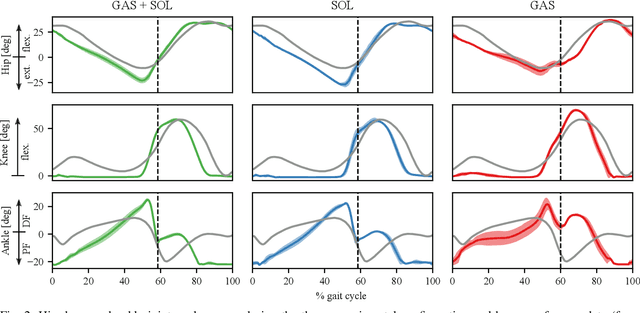
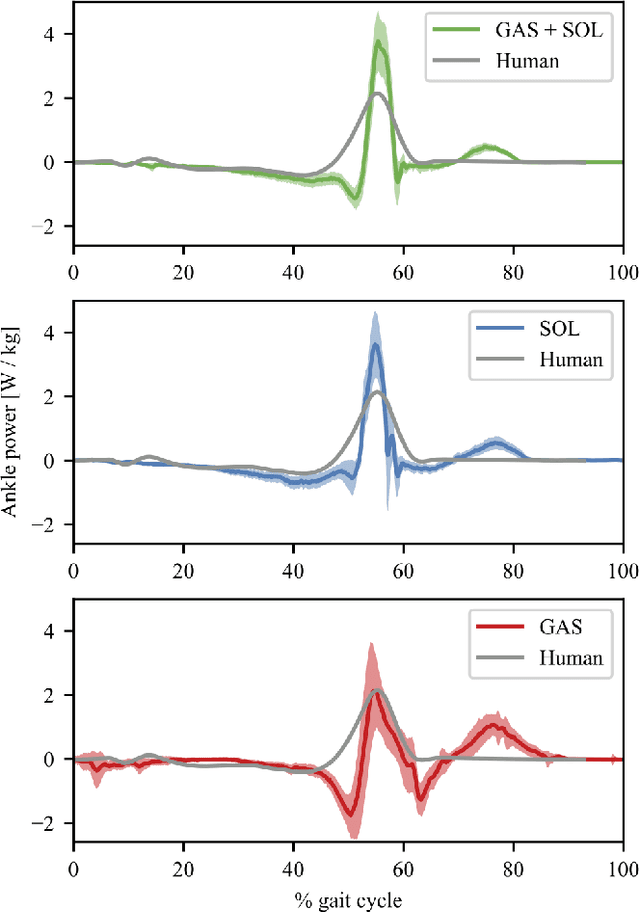
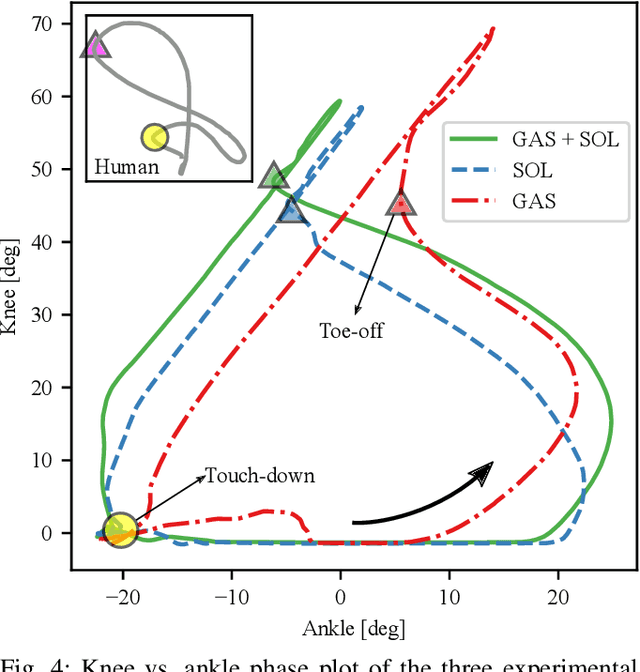
Abstract:Legged locomotion in humans is influenced by mechanics and neural control. One mechanism assumed to contribute to the high efficiency of human walking is the impulsive ankle push-off, which potentially powers the human swing leg catapult. However, the mechanics of the human's lower leg with its complex muscle-tendon units spanning over single and multiple joints is not yet understood. Legged robots allow testing the interaction between complex leg mechanics, control, and environment in real-world walking gait. We custom developed a small, 2.2 kg human-like bipedal robot with soleus and gastrocnemius muscles represented by linear springs, acting as mono- and biarticular elasticities around the robot's ankle and knee joints. We tested the influence of three soleus and gastrocnemius spring configurations on the ankle power curves, on the synchronization of the ankle and knee joint movements, on the total cost of transport, and on walking speed. We controlled the robot with a feed-forward central pattern generator, leading to walking speeds between 0.35 m/s and 0.57 m/s at 1.0 Hz locomotion frequency, at 0.35 m leg length. We found differences between all three configurations; the soleus spring supports the robot's speed and energy efficiency by ankle power amplification, while the GAS spring facilitates the synchronization between knee and ankle joints during push-off.
Effective Viscous Damping Enables Morphological Computation in Legged Locomotion
Jun 06, 2020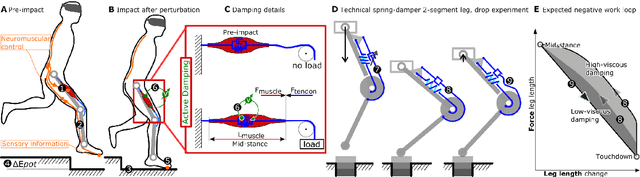
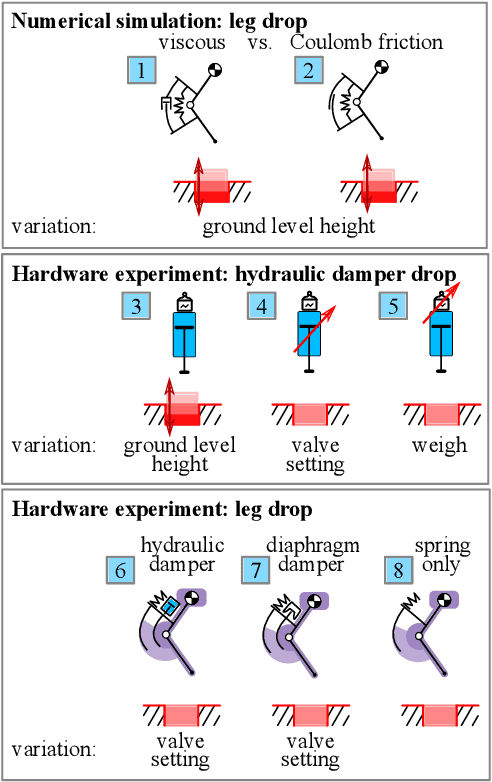

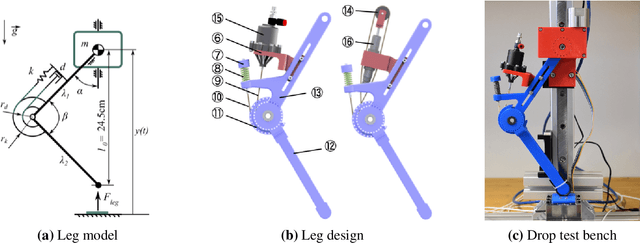
Abstract:Muscle models and animal observations suggest that physical damping is beneficial for stabilization. Still, only a few implementations of mechanical damping exist in compliant robotic legged locomotion. It remains unclear how physical damping can be exploited for locomotion tasks, while its advantages as sensor-free, adaptive force- and negative work-producing actuators are promising. In a simplified numerical leg model, we studied the energy dissipation from viscous and Coulomb damping during vertical drops with ground-level perturbations. A parallel spring-damper is engaged between touch-down and mid-stance, and its damper auto-disengages during mid-stance and takeoff. Our simulations indicate that an adjustable and viscous damper is desired. In hardware we explored effective viscous damping and adjustability and quantified the dissipated energy. We tested two mechanical, leg-mounted damping mechanisms; a commercial hydraulic damper, and a custom-made pneumatic damper. The pneumatic damper exploits a rolling diaphragm with an adjustable orifice, minimizing Coulomb damping effects while permitting adjustable resistance. Experimental results show that the leg-mounted, hydraulic damper exhibits the most effective viscous damping. Adjusting the orifice setting did not result in substantial changes of dissipated energy per drop, unlike adjusting damping parameters in the numerical model. Consequently, we also emphasize the importance of characterizing physical dampers during real legged impacts to evaluate their effectiveness for compliant legged locomotion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge