Alexis Lechervy
Facilitating Cognitive Accessibility with LLMs: A Multi-Task Approach to Easy-to-Read Text Generation
Oct 01, 2025
Abstract:Simplifying complex texts is essential for ensuring equitable access to information, especially for individuals with cognitive impairments. The Easy-to-Read (ETR) initiative offers a framework for making content accessible to the neurodivergent population, but the manual creation of such texts remains time-consuming and resource-intensive. In this work, we investigate the potential of large language models (LLMs) to automate the generation of ETR content. To address the scarcity of aligned corpora and the specificity of ETR constraints, we propose a multi-task learning (MTL) approach that trains models jointly on text summarization, text simplification, and ETR generation. We explore two different strategies: multi-task retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for in-context learning, and MTL-LoRA for parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Our experiments with Mistral-7B and LLaMA-3-8B, based on ETR-fr, a new high-quality dataset, demonstrate the benefits of multi-task setups over single-task baselines across all configurations. Moreover, results show that the RAG-based strategy enables generalization in out-of-domain settings, while MTL-LoRA outperforms all learning strategies within in-domain configurations.
Inclusive Easy-to-Read Generation for Individuals with Cognitive Impairments
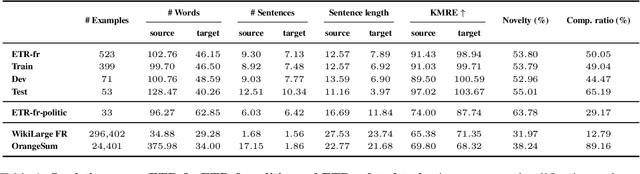
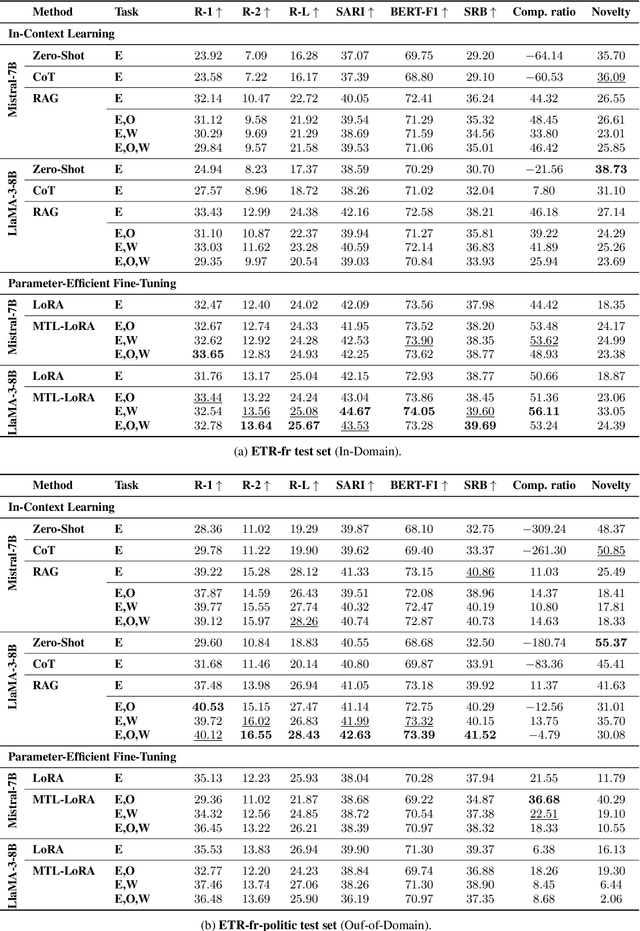
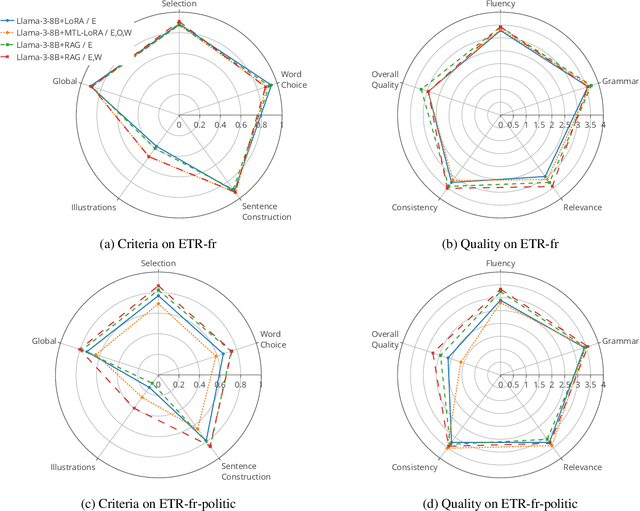
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Ensuring accessibility for individuals with cognitive impairments is essential for autonomy, self-determination, and full citizenship. However, manual Easy-to-Read (ETR) text adaptations are slow, costly, and difficult to scale, limiting access to crucial information in healthcare, education, and civic life. AI-driven ETR generation offers a scalable solution but faces key challenges, including dataset scarcity, domain adaptation, and balancing lightweight learning of Large Language Models (LLMs). In this paper, we introduce ETR-fr, the first dataset for ETR text generation fully compliant with European ETR guidelines. We implement parameter-efficient fine-tuning on PLMs and LLMs to establish generative baselines. To ensure high-quality and accessible outputs, we introduce an evaluation framework based on automatic metrics supplemented by human assessments. The latter is conducted using a 36-question evaluation form that is aligned with the guidelines. Overall results show that PLMs perform comparably to LLMs and adapt effectively to out-of-domain texts.
Structure-Preserving Transformers for Sequences of SPD Matrices
Sep 25, 2023


Abstract:In recent years, Transformer-based auto-attention mechanisms have been successfully applied to the analysis of a variety of context-reliant data types, from texts to images and beyond, including data from non-Euclidean geometries. In this paper, we present such a mechanism, designed to classify sequences of Symmetric Positive Definite matrices while preserving their Riemannian geometry throughout the analysis. We apply our method to automatic sleep staging on timeseries of EEG-derived covariance matrices from a standard dataset, obtaining high levels of stage-wise performance.
Training face verification models from generated face identity data
Aug 02, 2021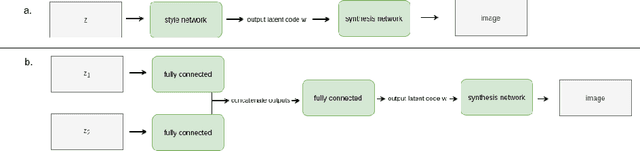
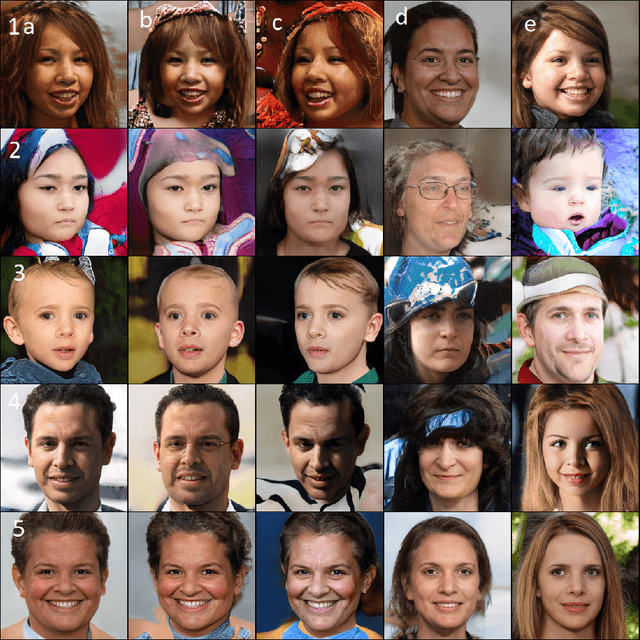
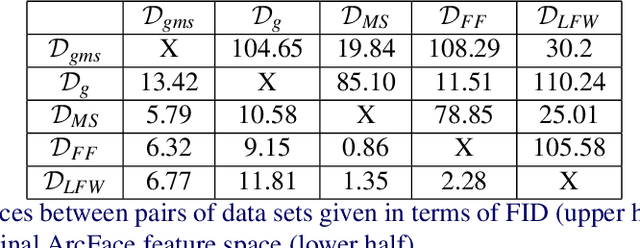

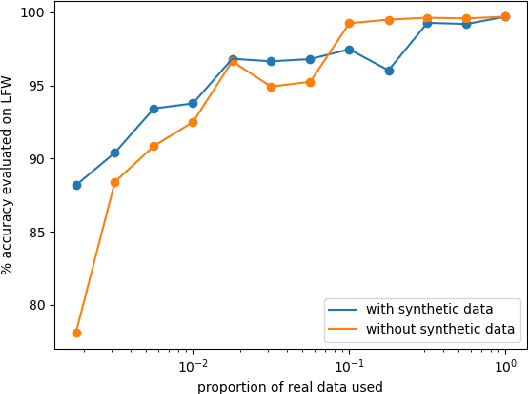
Abstract:Machine learning tools are becoming increasingly powerful and widely used. Unfortunately membership attacks, which seek to uncover information from data sets used in machine learning, have the potential to limit data sharing. In this paper we consider an approach to increase the privacy protection of data sets, as applied to face recognition. Using an auxiliary face recognition model, we build on the StyleGAN generative adversarial network and feed it with latent codes combining two distinct sub-codes, one encoding visual identity factors, and, the other, non-identity factors. By independently varying these vectors during image generation, we create a synthetic data set of fictitious face identities. We use this data set to train a face recognition model. The model performance degrades in comparison to the state-of-the-art of face verification. When tested with a simple membership attack our model provides good privacy protection, however the model performance degrades in comparison to the state-of-the-art of face verification. We find that the addition of a small amount of private data greatly improves the performance of our model, which highlights the limitations of using synthetic data to train machine learning models.
Towards a General Model of Knowledge for Facial Analysis by Multi-Source Transfer Learning
Nov 08, 2019

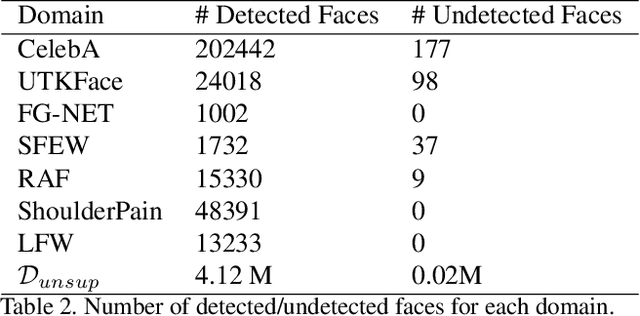

Abstract:This paper proposes a step toward obtaining general models of knowledge for facial analysis, by addressing the question of multi-source transfer learning. More precisely, the proposed approach consists in two successive training steps: the first one consists in applying a combination operator to define a common embedding for the multiple sources materialized by different existing trained models. The proposed operator relies on an auto-encoder, trained on a large dataset, efficient both in terms of compression ratio and transfer learning performance. In a second step we exploit a distillation approach to obtain a lightweight student model mimicking the collection of the fused existing models. This model outperforms its teacher on novel tasks, achieving results on par with state-of-the-art methods on 15 facial analysis tasks (and domains), at an affordable training cost. Moreover, this student has 75 times less parameters than the original teacher and can be applied to a variety of novel face-related tasks.
Multi-Level Sensor Fusion with Deep Learning
Nov 05, 2018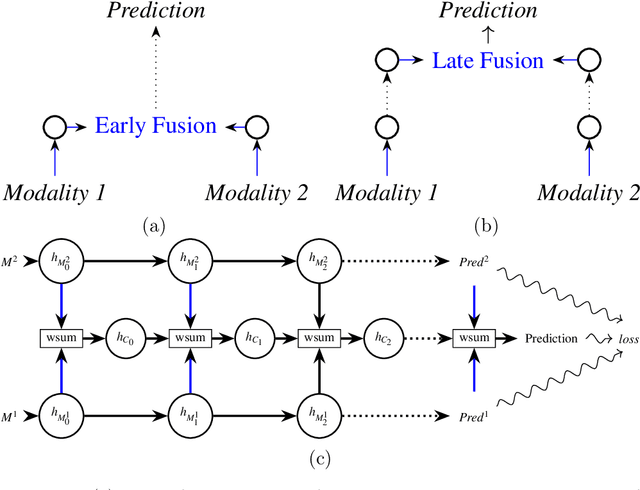


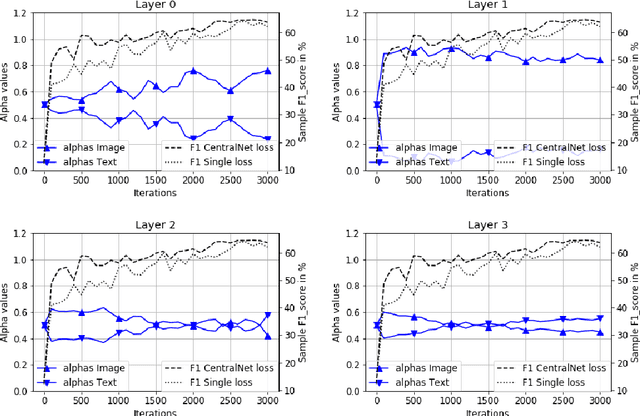
Abstract:In the context of deep learning, this article presents an original deep network, namely CentralNet, for the fusion of information coming from different sensors. This approach is designed to efficiently and automatically balance the trade-off between early and late fusion (i.e. between the fusion of low-level vs high-level information). More specifically, at each level of abstraction-the different levels of deep networks-uni-modal representations of the data are fed to a central neural network which combines them into a common embedding. In addition, a multi-objective regularization is also introduced, helping to both optimize the central network and the unimodal networks. Experiments on four multimodal datasets not only show state-of-the-art performance, but also demonstrate that CentralNet can actually choose the best possible fusion strategy for a given problem.
RPNet: an End-to-End Network for Relative Camera Pose Estimation
Sep 22, 2018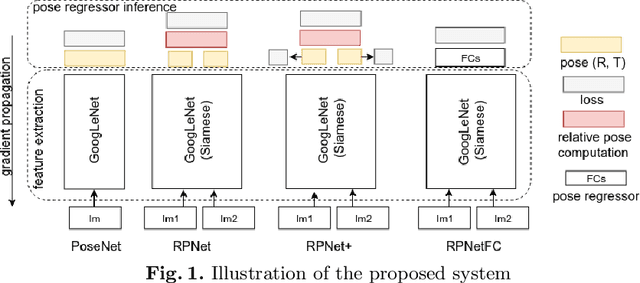
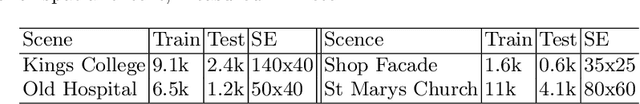

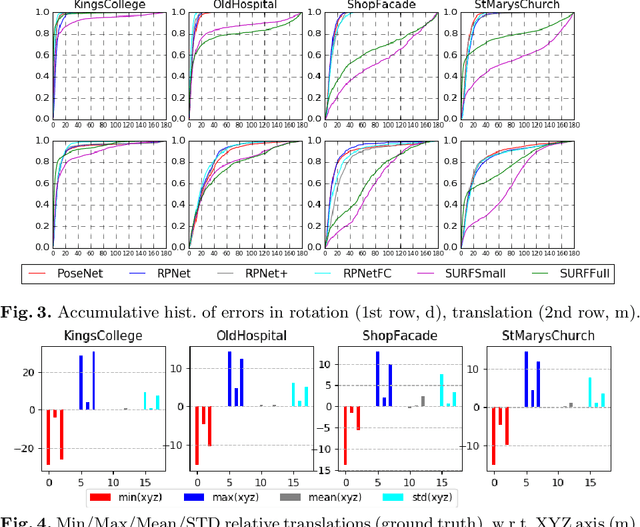
Abstract:This paper addresses the task of relative camera pose estimation from raw image pixels, by means of deep neural networks. The proposed RPNet network takes pairs of images as input and directly infers the relative poses, without the need of camera intrinsic/extrinsic. While state-of-the-art systems based on SIFT + RANSAC, are able to recover the translation vector only up to scale, RPNet is trained to produce the full translation vector, in an end-to-end way. Experimental results on the Cambridge Landmark dataset show very promising results regarding the recovery of the full translation vector. They also show that RPNet produces more accurate and more stable results than traditional approaches, especially for hard images (repetitive textures, textureless images, etc). To the best of our knowledge, RPNet is the first attempt to recover full translation vectors in relative pose estimation.
CentralNet: a Multilayer Approach for Multimodal Fusion
Aug 22, 2018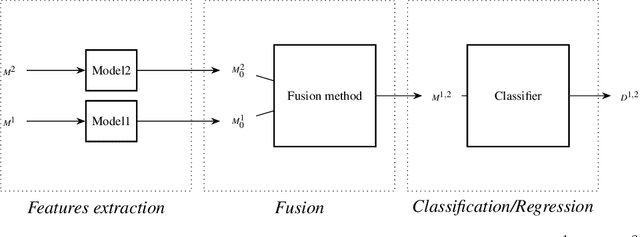
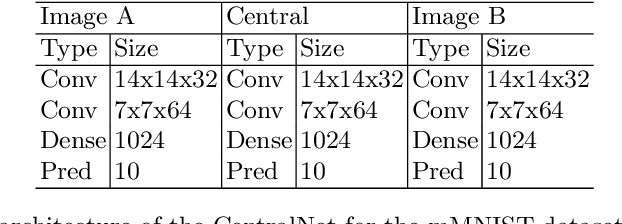
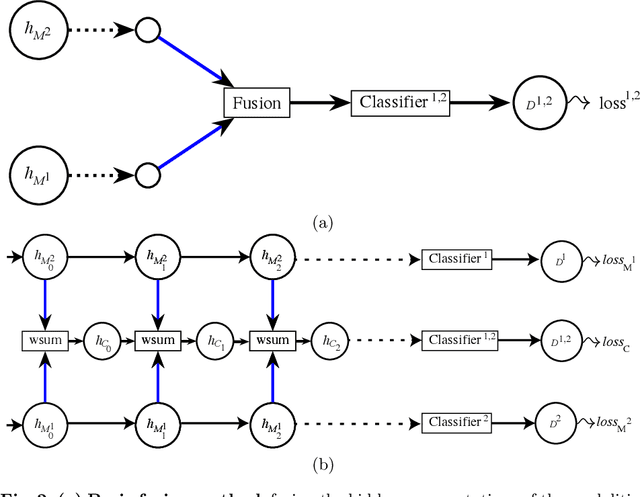
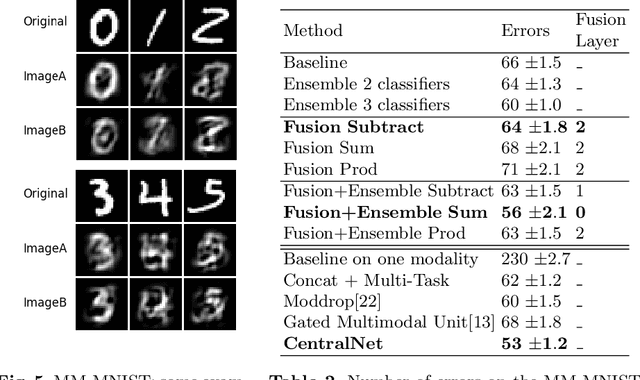
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel multimodal fusion approach, aiming to produce best possible decisions by integrating information coming from multiple media. While most of the past multimodal approaches either work by projecting the features of different modalities into the same space, or by coordinating the representations of each modality through the use of constraints, our approach borrows from both visions. More specifically, assuming each modality can be processed by a separated deep convolutional network, allowing to take decisions independently from each modality, we introduce a central network linking the modality specific networks. This central network not only provides a common feature embedding but also regularizes the modality specific networks through the use of multi-task learning. The proposed approach is validated on 4 different computer vision tasks on which it consistently improves the accuracy of existing multimodal fusion approaches.
An Occam's Razor View on Learning Audiovisual Emotion Recognition with Small Training Sets
Aug 08, 2018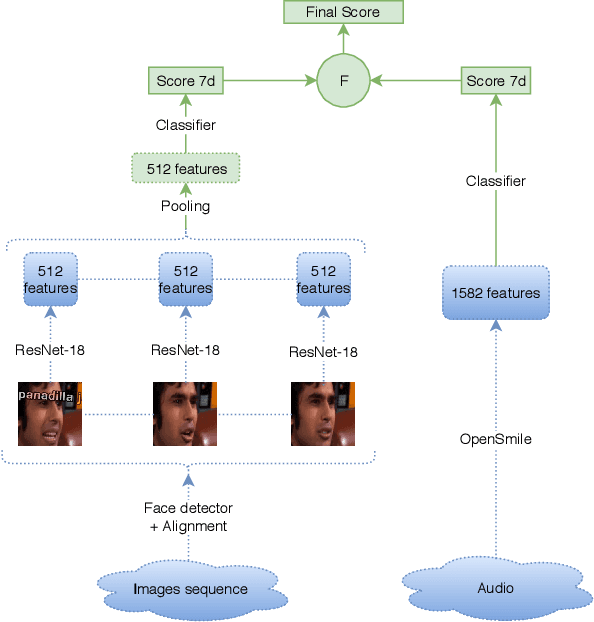

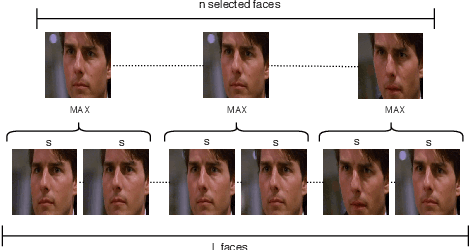
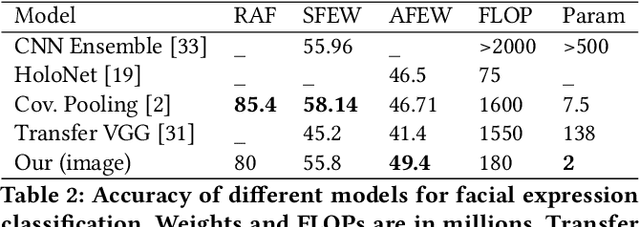
Abstract:This paper presents a light-weight and accurate deep neural model for audiovisual emotion recognition. To design this model, the authors followed a philosophy of simplicity, drastically limiting the number of parameters to learn from the target datasets, always choosing the simplest earning methods: i) transfer learning and low-dimensional space embedding allows to reduce the dimensionality of the representations. ii) The isual temporal information is handled by a simple score-per-frame selection process, averaged across time. iii) A simple frame selection echanism is also proposed to weight the images of a sequence. iv) The fusion of the different modalities is performed at prediction level (late usion). We also highlight the inherent challenges of the AFEW dataset and the difficulty of model selection with as few as 383 validation equences. The proposed real-time emotion classifier achieved a state-of-the-art accuracy of 60.64 % on the test set of AFEW, and ranked 4th at he Emotion in the Wild 2018 challenge.
CAKE: Compact and Accurate K-dimensional representation of Emotion
Aug 03, 2018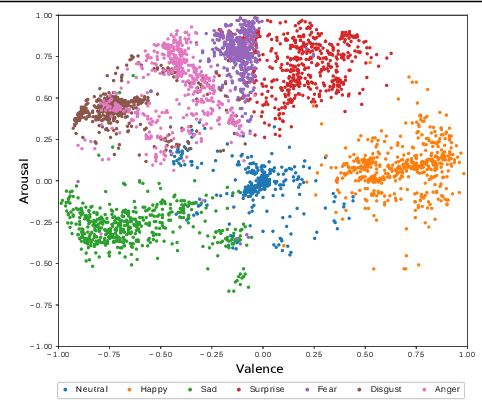

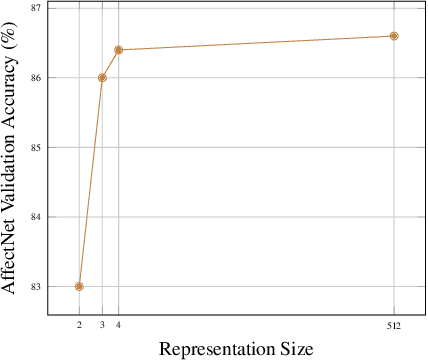

Abstract:Numerous models describing the human emotional states have been built by the psychology community. Alongside, Deep Neural Networks (DNN) are reaching excellent performances and are becoming interesting features extraction tools in many computer vision tasks.Inspired by works from the psychology community, we first study the link between the compact two-dimensional representation of the emotion known as arousal-valence, and discrete emotion classes (e.g. anger, happiness, sadness, etc.) used in the computer vision community. It enables to assess the benefits -- in terms of discrete emotion inference -- of adding an extra dimension to arousal-valence (usually named dominance). Building on these observations, we propose CAKE, a 3-dimensional representation of emotion learned in a multi-domain fashion, achieving accurate emotion recognition on several public datasets. Moreover, we visualize how emotions boundaries are organized inside DNN representations and show that DNNs are implicitly learning arousal-valence-like descriptions of emotions. Finally, we use the CAKE representation to compare the quality of the annotations of different public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge