Alexander Rutherford
Multi-Agent Craftax: Benchmarking Open-Ended Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning at the Hyperscale
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Progress in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) requires challenging benchmarks that assess the limits of current methods. However, existing benchmarks often target narrow short-horizon challenges that do not adequately stress the long-term dependencies and generalization capabilities inherent in many multi-agent systems. To address this, we first present \textit{Craftax-MA}: an extension of the popular open-ended RL environment, Craftax, that supports multiple agents and evaluates a wide range of general abilities within a single environment. Written in JAX, \textit{Craftax-MA} is exceptionally fast with a training run using 250 million environment interactions completing in under an hour. To provide a more compelling challenge for MARL, we also present \textit{Craftax-Coop}, an extension introducing heterogeneous agents, trading and more mechanics that require complex cooperation among agents for success. We provide analysis demonstrating that existing algorithms struggle with key challenges in this benchmark, including long-horizon credit assignment, exploration and cooperation, and argue for its potential to drive long-term research in MARL.
An Optimisation Framework for Unsupervised Environment Design
May 27, 2025Abstract:For reinforcement learning agents to be deployed in high-risk settings, they must achieve a high level of robustness to unfamiliar scenarios. One method for improving robustness is unsupervised environment design (UED), a suite of methods aiming to maximise an agent's generalisability across configurations of an environment. In this work, we study UED from an optimisation perspective, providing stronger theoretical guarantees for practical settings than prior work. Whereas previous methods relied on guarantees if they reach convergence, our framework employs a nonconvex-strongly-concave objective for which we provide a provably convergent algorithm in the zero-sum setting. We empirically verify the efficacy of our method, outperforming prior methods in a number of environments with varying difficulties.
No Regrets: Investigating and Improving Regret Approximations for Curriculum Discovery
Aug 27, 2024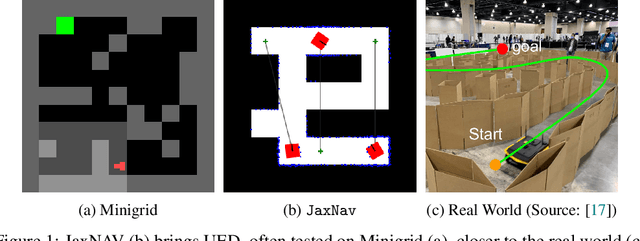
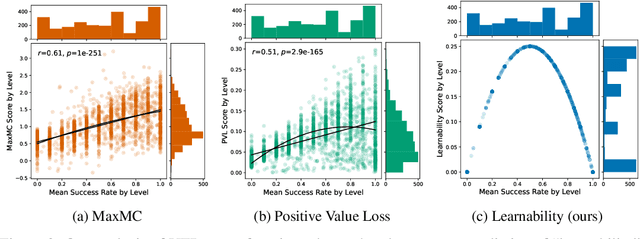
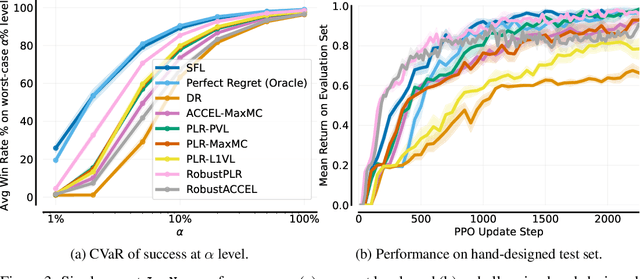
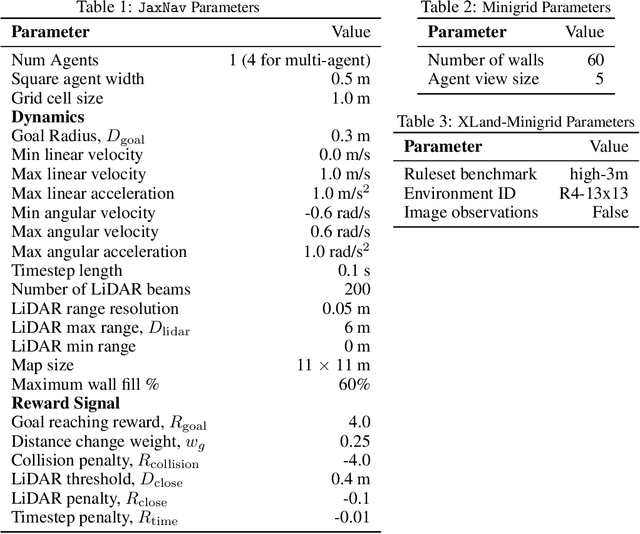
Abstract:What data or environments to use for training to improve downstream performance is a longstanding and very topical question in reinforcement learning. In particular, Unsupervised Environment Design (UED) methods have gained recent attention as their adaptive curricula enable agents to be robust to in- and out-of-distribution tasks. We ask to what extent these methods are themselves robust when applied to a novel setting, closely inspired by a real-world robotics problem. Surprisingly, we find that the state-of-the-art UED methods either do not improve upon the na\"{i}ve baseline of Domain Randomisation (DR), or require substantial hyperparameter tuning to do so. Our analysis shows that this is due to their underlying scoring functions failing to predict intuitive measures of ``learnability'', i.e., in finding the settings that the agent sometimes solves, but not always. Based on this, we instead directly train on levels with high learnability and find that this simple and intuitive approach outperforms UED methods and DR in several binary-outcome environments, including on our domain and the standard UED domain of Minigrid. We further introduce a new adversarial evaluation procedure for directly measuring robustness, closely mirroring the conditional value at risk (CVaR). We open-source all our code and present visualisations of final policies here: https://github.com/amacrutherford/sampling-for-learnability.
JaxMARL: Multi-Agent RL Environments in JAX
Nov 20, 2023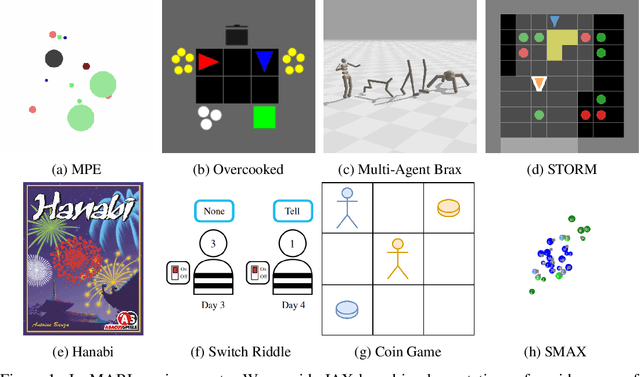

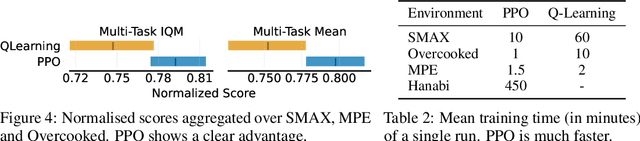
Abstract:Benchmarks play an important role in the development of machine learning algorithms. For example, research in reinforcement learning (RL) has been heavily influenced by available environments and benchmarks. However, RL environments are traditionally run on the CPU, limiting their scalability with typical academic compute. Recent advancements in JAX have enabled the wider use of hardware acceleration to overcome these computational hurdles, enabling massively parallel RL training pipelines and environments. This is particularly useful for multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) research. First of all, multiple agents must be considered at each environment step, adding computational burden, and secondly, the sample complexity is increased due to non-stationarity, decentralised partial observability, or other MARL challenges. In this paper, we present JaxMARL, the first open-source code base that combines ease-of-use with GPU enabled efficiency, and supports a large number of commonly used MARL environments as well as popular baseline algorithms. When considering wall clock time, our experiments show that per-run our JAX-based training pipeline is up to 12500x faster than existing approaches. This enables efficient and thorough evaluations, with the potential to alleviate the evaluation crisis of the field. We also introduce and benchmark SMAX, a vectorised, simplified version of the popular StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge, which removes the need to run the StarCraft II game engine. This not only enables GPU acceleration, but also provides a more flexible MARL environment, unlocking the potential for self-play, meta-learning, and other future applications in MARL. We provide code at https://github.com/flairox/jaxmarl.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge