Alexander Raistrick
Evaluating Robustness of Monocular Depth Estimation with Procedural Scene Perturbations
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Recent years have witnessed substantial progress on monocular depth estimation, particularly as measured by the success of large models on standard benchmarks. However, performance on standard benchmarks does not offer a complete assessment, because most evaluate accuracy but not robustness. In this work, we introduce PDE (Procedural Depth Evaluation), a new benchmark which enables systematic robustness evaluation. PDE uses procedural generation to create 3D scenes that test robustness to various controlled perturbations, including object, camera, material and lighting changes. Our analysis yields interesting findings on what perturbations are challenging for state-of-the-art depth models, which we hope will inform further research. Code and data are available at https://github.com/princeton-vl/proc-depth-eval.
Infinigen-Sim: Procedural Generation of Articulated Simulation Assets
May 19, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Infinigen-Sim, a toolkit which enables users to create diverse and realistic articulated object procedural generators. These tools are composed of high-level utilities for use creating articulated assets in Blender, as well as an export pipeline to integrate the resulting assets into common robotics simulators. We demonstrate our system by creating procedural generators for 5 common articulated object categories. Experiments show that assets sampled from these generators are useful for movable object segmentation, training generalizable reinforcement learning policies, and sim-to-real transfer of imitation learning policies.
Procedural Dataset Generation for Zero-Shot Stereo Matching
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Synthetic datasets are a crucial ingredient for training stereo matching networks, but the question of what makes a stereo dataset effective remains largely unexplored. We investigate the design space of synthetic datasets by varying the parameters of a procedural dataset generator, and report the effects on zero-shot stereo matching performance using standard benchmarks. We collect the best settings to produce Infinigen-Stereo, a procedural generator specifically optimized for zero-shot stereo datasets. Models trained only on data from our system outperform robust baselines trained on a combination of existing synthetic datasets and have stronger zero-shot stereo matching performance than public checkpoints from prior works. We open source our system at https://github.com/princeton-vl/InfinigenStereo to enable further research on procedural stereo datasets.
Infinigen Indoors: Photorealistic Indoor Scenes using Procedural Generation
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Infinigen Indoors, a Blender-based procedural generator of photorealistic indoor scenes. It builds upon the existing Infinigen system, which focuses on natural scenes, but expands its coverage to indoor scenes by introducing a diverse library of procedural indoor assets, including furniture, architecture elements, appliances, and other day-to-day objects. It also introduces a constraint-based arrangement system, which consists of a domain-specific language for expressing diverse constraints on scene composition, and a solver that generates scene compositions that maximally satisfy the constraints. We provide an export tool that allows the generated 3D objects and scenes to be directly used for training embodied agents in real-time simulators such as Omniverse and Unreal. Infinigen Indoors is open-sourced under the BSD license. Please visit https://infinigen.org for code and videos.
View-Dependent Octree-based Mesh Extraction in Unbounded Scenes for Procedural Synthetic Data
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Procedural synthetic data generation has received increasing attention in computer vision. Procedural signed distance functions (SDFs) are a powerful tool for modeling large-scale detailed scenes, but existing mesh extraction methods have artifacts or performance profiles that limit their use for synthetic data. We propose OcMesher, a mesh extraction algorithm that efficiently handles high-detail unbounded scenes with perfect view-consistency, with easy export to downstream real-time engines. The main novelty of our solution is an algorithm to construct an octree based on a given SDF and multiple camera views. We performed extensive experiments, and show our solution produces better synthetic data for training and evaluation of computer vision models.
Infinite Photorealistic Worlds using Procedural Generation
Jun 26, 2023
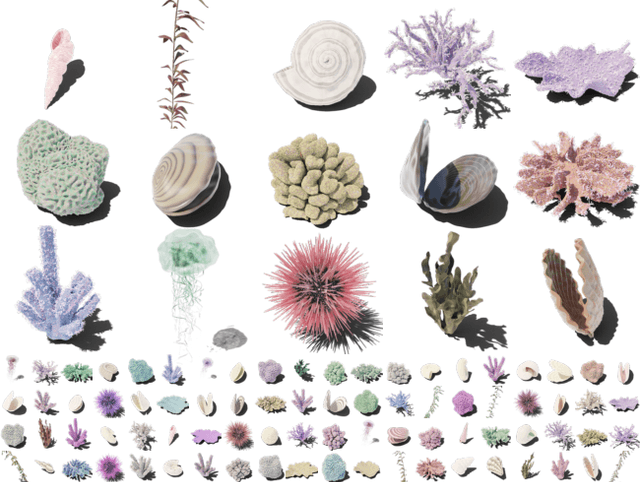
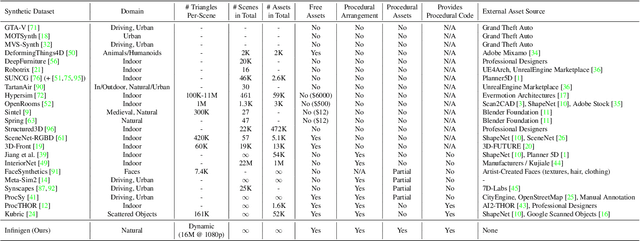


Abstract:We introduce Infinigen, a procedural generator of photorealistic 3D scenes of the natural world. Infinigen is entirely procedural: every asset, from shape to texture, is generated from scratch via randomized mathematical rules, using no external source and allowing infinite variation and composition. Infinigen offers broad coverage of objects and scenes in the natural world including plants, animals, terrains, and natural phenomena such as fire, cloud, rain, and snow. Infinigen can be used to generate unlimited, diverse training data for a wide range of computer vision tasks including object detection, semantic segmentation, optical flow, and 3D reconstruction. We expect Infinigen to be a useful resource for computer vision research and beyond. Please visit https://infinigen.org for videos, code and pre-generated data.
Collision Replay: What Does Bumping Into Things Tell You About Scene Geometry?
May 03, 2021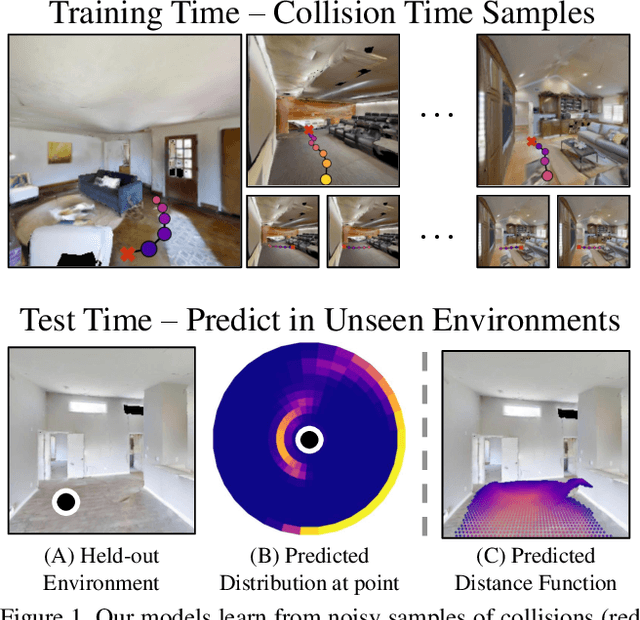
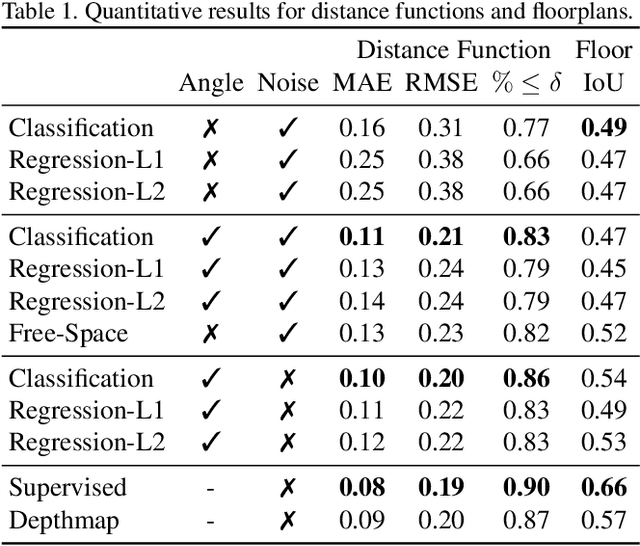
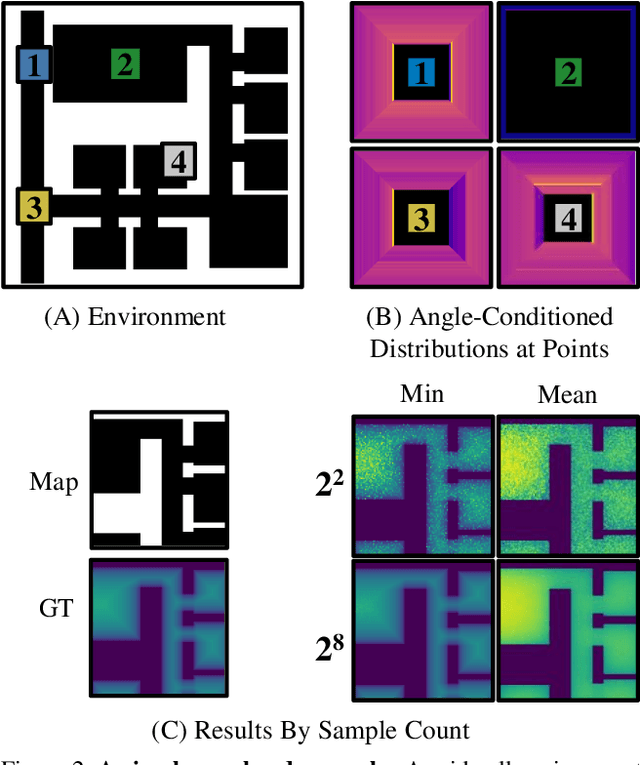
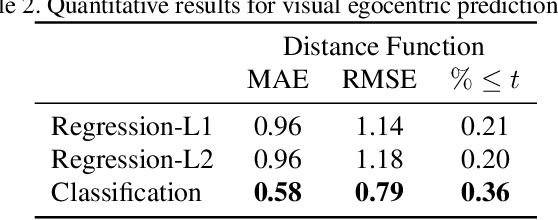
Abstract:What does bumping into things in a scene tell you about scene geometry? In this paper, we investigate the idea of learning from collisions. At the heart of our approach is the idea of collision replay, where we use examples of a collision to provide supervision for observations at a past frame. We use collision replay to train convolutional neural networks to predict a distribution over collision time from new images. This distribution conveys information about the navigational affordances (e.g., corridors vs open spaces) and, as we show, can be converted into the distance function for the scene geometry. We analyze this approach with an agent that has noisy actuation in a photorealistic simulator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge