Agustin Marinovic
Fast Detection of Maximum Common Subgraph via Deep Q-Learning
Feb 20, 2020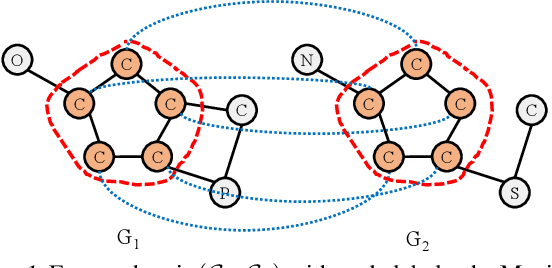

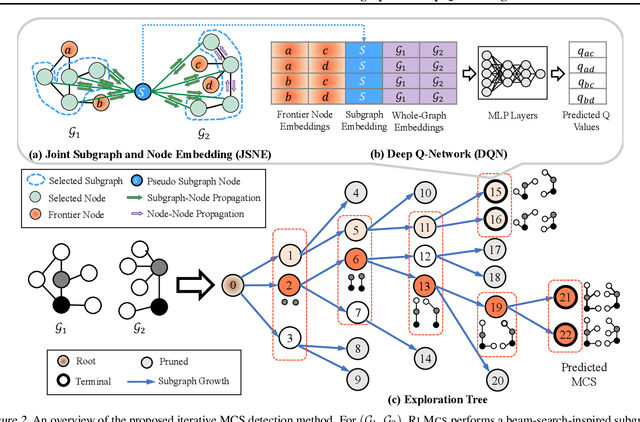
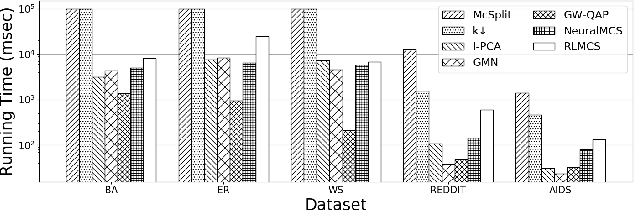
Abstract:Detecting the Maximum Common Subgraph (MCS) between two input graphs is fundamental for applications in biomedical analysis, malware detection, cloud computing, etc. This is especially important in the task of drug design, where the successful extraction of common substructures in compounds can reduce the number of experiments needed to be conducted by humans. However, MCS computation is NP-hard, and state-of-the-art exact MCS solvers do not have worst-case time complexity guarantee and cannot handle large graphs in practice. Designing learning based models to find the MCS between two graphs in an approximate yet accurate way while utilizing as few labeled MCS instances as possible remains to be a challenging task. Here we propose RLMCS, a Graph Neural Network based model for MCS detection through reinforcement learning. Our model uses an exploration tree to extract subgraphs in two graphs one node pair at a time, and is trained to optimize subgraph extraction rewards via Deep Q-Networks. A novel graph embedding method is proposed to generate state representations for nodes and extracted subgraphs jointly at each step. Experiments on real graph datasets demonstrate that our model performs favorably to exact MCS solvers and supervised neural graph matching network models in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
Unsupervised Inductive Whole-Graph Embedding by Preserving Graph Proximity
Apr 01, 2019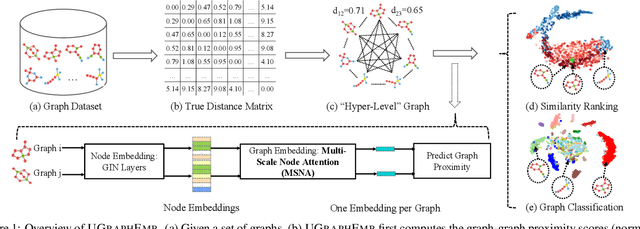


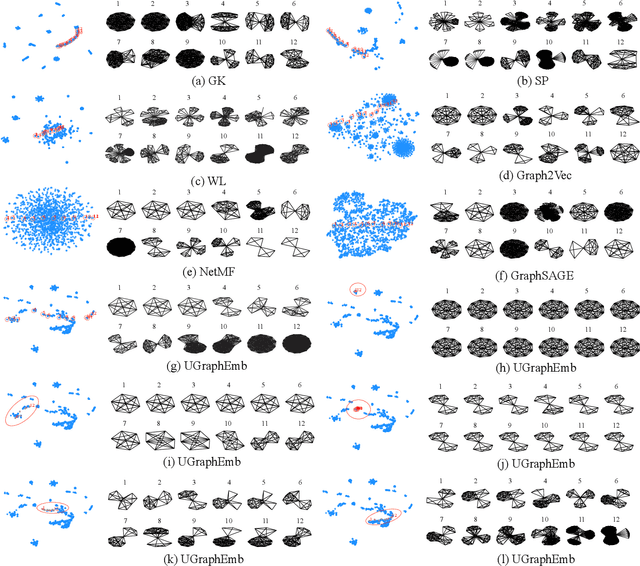
Abstract:We introduce a novel approach to graph-level representation learning, which is to embed an entire graph into a vector space where the embeddings of two graphs preserve their graph-graph proximity. Our approach, UGRAPHEMB, is a general framework that provides a novel means to performing graph-level embedding in a completely unsupervised and inductive manner. The learned neural network can be considered as a function that receives any graph as input, either seen or unseen in the training set, and transforms it into an embedding. A novel graph-level embedding generation mechanism called Multi-Scale Node Attention (MSNA), is proposed. Experiments on five real graph datasets show that UGRAPHEMB achieves competitive accuracy in the tasks of graph classification, similarity ranking, and graph visualization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge