TripletUNet: Multi-Task U-Net with Online Voxel-Wise Learning for Precise CT Prostate Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 21, 2020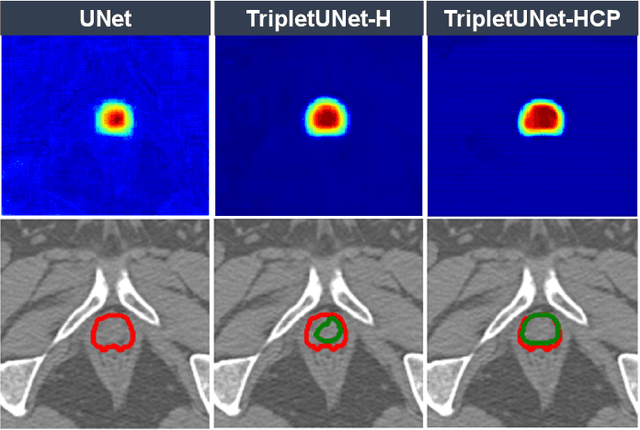
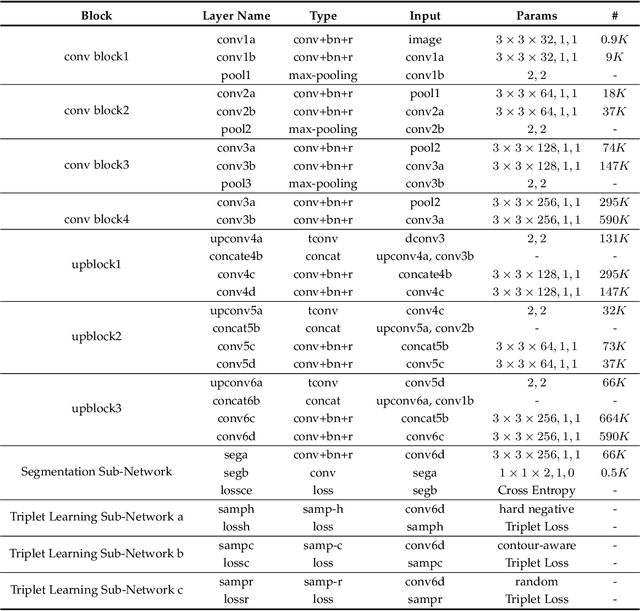
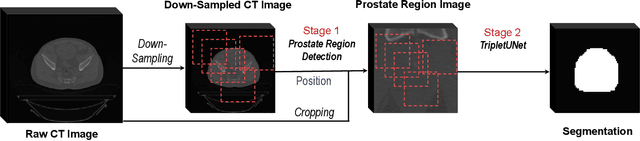
Fully convolutional networks (FCNs), including U-Net and V-Net, are widely-used network architecture for semantic segmentation in recent studies. However, conventional FCNs are typically trained by the cross-entropy loss or dice loss, in which the relationships among voxels are neglected. This often results in non-smooth neighborhoods in the output segmentation map. This problem becomes more serious in CT prostate segmentation as CT images are usually of low tissue contrast. To address this problem, we propose a two-stage framework. The first stage quickly localizes the prostate region. Then, the second stage precisely segments the prostate by a multi-task FCN-based on the U-Net architecture. We introduce a novel online voxel-triplet learning module through metric learning and voxel feature embeddings in the multi-task network. The proposed network has two branches guided by two tasks: 1) a segmentation sub-network aiming to generate prostate segmentation, and 2) a triplet learning sub-network aiming to improve the quality of the learned feature space supervised by a mixed of triplet and pair-wise loss function. The triplet learning sub-network samples triplets from the inter-mediate heatmap. Unlike conventional deep triplet learning methods that generate triplets before the training phase, our proposed voxel-triplets are sampled in an online manner and operates in an end-to-end fashion via multi-task learning. To evaluate the proposed method, we implement comprehensive experiments on a CT image dataset consisting of 339 patients. The ablation studies show that our method can effectively learn more representative voxel-level features compared with the conventional FCN network. And the comparisons show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge