SkyNet: a Hardware-Efficient Method for Object Detection and Tracking on Embedded Systems
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2019
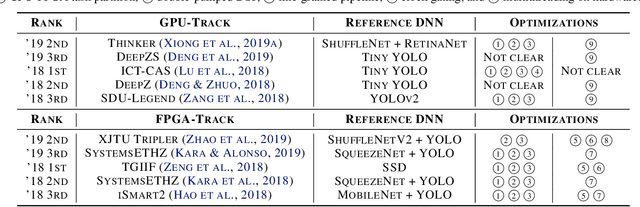


Developing object detection and tracking on resource-constrained embedded systems is challenging. While object detection is one of the most compute-intensive tasks from the artificial intelligence domain, it is only allowed to use limited computation and memory resources on embedded devices. In the meanwhile, such resource-constrained implementations are often required to satisfy additional demanding requirements such as real-time response, high-throughput performance, and reliable inference accuracy. To overcome these challenges, we propose SkyNet, a hardware-efficient method to deliver the state-of-the-art detection accuracy and speed for embedded systems. Instead of following the common top-down flow for compact DNN design, SkyNet provides a bottom-up DNN design approach with comprehensive understanding of the hardware constraints at the very beginning to deliver hardware-efficient DNNs. The effectiveness of SkyNet is demonstrated by winning the extremely competitive System Design Contest for low power object detection in the 56th IEEE/ACM Design Automation Conference (DAC-SDC), where our SkyNet significantly outperforms all other 100+ competitors: it delivers 0.731 Intersection over Union (IoU) and 67.33 frames per second (FPS) on a TX2 embedded GPU; and 0.716 IoU and 25.05 FPS on an Ultra96 embedded FPGA. The evaluation of SkyNet is also extended to GOT-10K, a recent large-scale high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. For state-of-the-art object trackers SiamRPN++ and SiamMask, where ResNet-50 is employed as the backbone, implementations using our SkyNet as the backbone DNN are 1.60X and 1.73X faster with better or similar accuracy when running on a 1080Ti GPU, and 37.20X smaller in terms of parameter size for significantly better memory and storage footprint.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge