RIS-assisted Coverage Enhancement in mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communication Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 07, 2024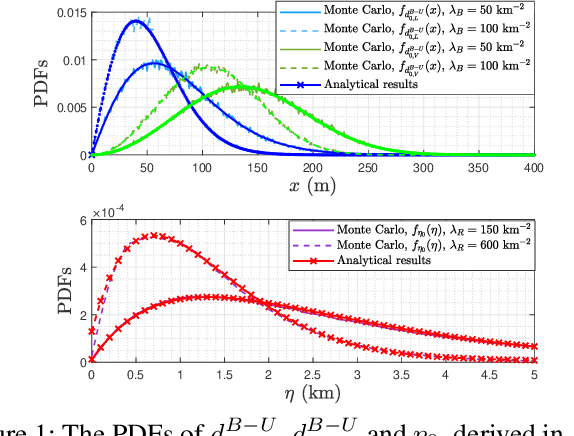


Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a promising technology to facilitate high-rate communications and super-resolution sensing, particularly operating in the millimeter wave (mmWave) band. However, the vulnerability of mmWave signals to blockages severely impairs ISAC capabilities and coverage. To tackle this, an efficient and low-cost solution is to deploy distributed reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) to construct virtual links between the base stations (BSs) and users in a controllable fashion. In this paper, we investigate the generalized RIS-assisted mmWave ISAC networks considering the blockage effect, and examine the beneficial impact of RISs on the coverage rate utilizing stochastic geometry. Specifically, taking into account the coupling effect of ISAC dual functions within the same network topology, we derive the conditional coverage probability of ISAC performance for two association cases, based on the proposed beam pattern model and user association policies. Then, the marginal coverage rate is calculated by combining these two cases through the distance-dependent thinning method. Simulation results verify the accuracy of derived theoretical formulations and provide valuable guidelines for the practical network deployment. Specifically, our results indicate the superiority of the RIS deployment with the density of 40 km${}^{-2}$ BSs, and that the joint coverage rate of ISAC performance exhibits potential growth from $67.1\%$ to $92.2\%$ with the deployment of RISs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge