Protein-Ligand Docking Surrogate Models: A SARS-CoV-2 Benchmark for Deep Learning Accelerated Virtual Screening
Paper and Code
Jun 30, 2021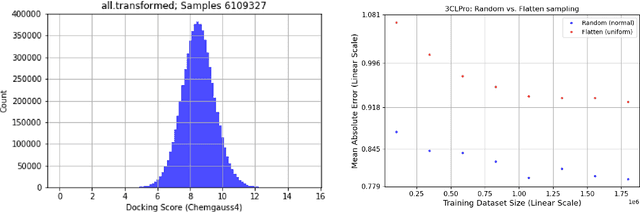

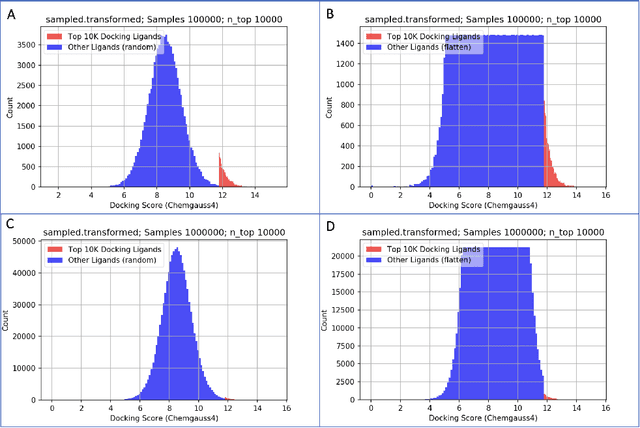
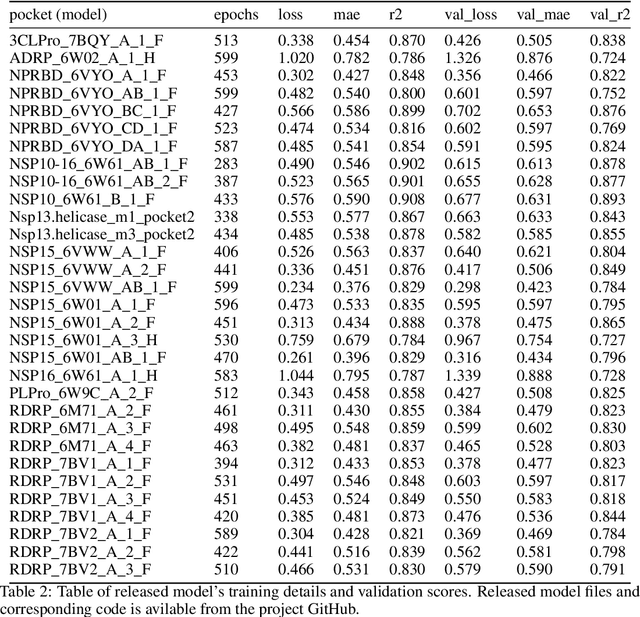
We propose a benchmark to study surrogate model accuracy for protein-ligand docking. We share a dataset consisting of 200 million 3D complex structures and 2D structure scores across a consistent set of 13 million "in-stock" molecules over 15 receptors, or binding sites, across the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. Our work shows surrogate docking models have six orders of magnitude more throughput than standard docking protocols on the same supercomputer node types. We demonstrate the power of high-speed surrogate models by running each target against 1 billion molecules in under a day (50k predictions per GPU seconds). We showcase a workflow for docking utilizing surrogate ML models as a pre-filter. Our workflow is ten times faster at screening a library of compounds than the standard technique, with an error rate less than 0.01\% of detecting the underlying best scoring 0.1\% of compounds. Our analysis of the speedup explains that to screen more molecules under a docking paradigm, another order of magnitude speedup must come from model accuracy rather than computing speed (which, if increased, will not anymore alter our throughput to screen molecules). We believe this is strong evidence for the community to begin focusing on improving the accuracy of surrogate models to improve the ability to screen massive compound libraries 100x or even 1000x faster than current techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge