Large Language Model Inference Acceleration: A Comprehensive Hardware Perspective
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2024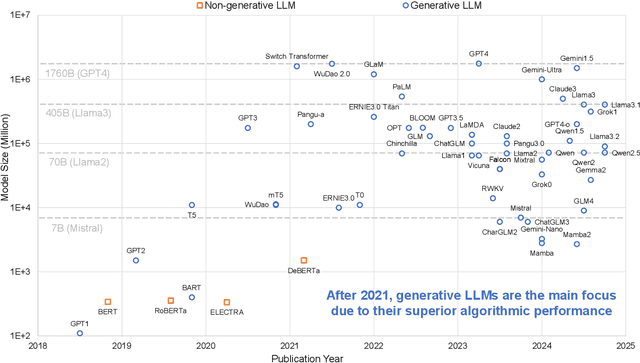
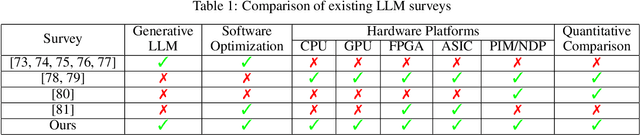
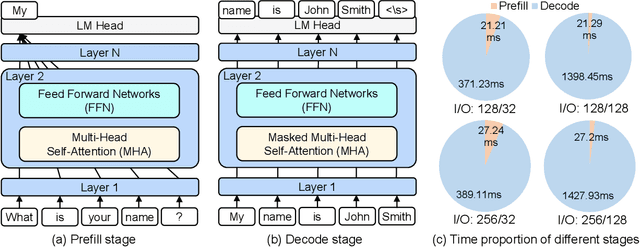
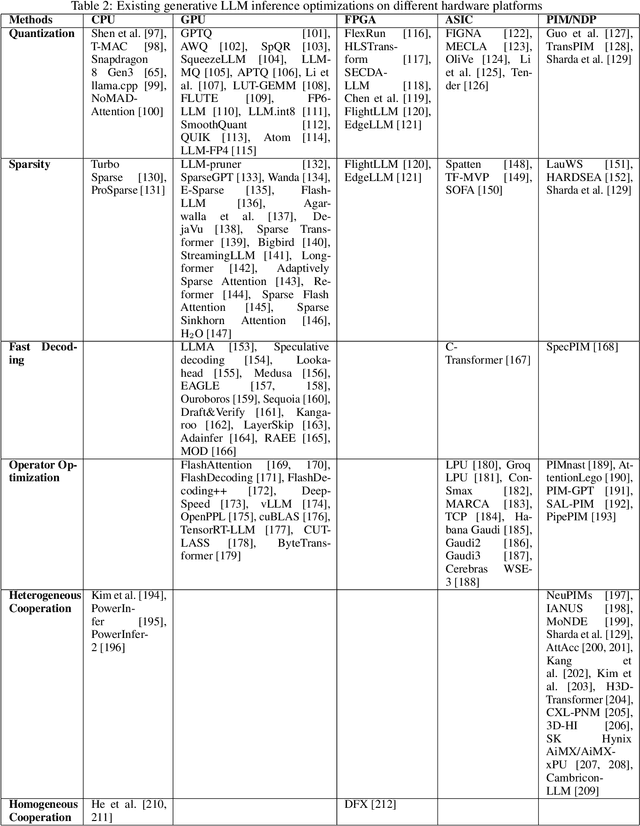
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various fields, from natural language understanding to text generation. Compared to non-generative LLMs like BERT and DeBERTa, generative LLMs like GPT series and Llama series are currently the main focus due to their superior algorithmic performance. The advancements in generative LLMs are closely intertwined with the development of hardware capabilities. Various hardware platforms exhibit distinct hardware characteristics, which can help improve LLM inference performance. Therefore, this paper comprehensively surveys efficient generative LLM inference on different hardware platforms. First, we provide an overview of the algorithm architecture of mainstream generative LLMs and delve into the inference process. Then, we summarize different optimization methods for different platforms such as CPU, GPU, FPGA, ASIC, and PIM/NDP, and provide inference results for generative LLMs. Furthermore, we perform a qualitative and quantitative comparison of inference performance with batch sizes 1 and 8 on different hardware platforms by considering hardware power consumption, absolute inference speed (tokens/s), and energy efficiency (tokens/J). We compare the performance of the same optimization methods across different hardware platforms, the performance across different hardware platforms, and the performance of different methods on the same hardware platform. This provides a systematic and comprehensive summary of existing inference acceleration work by integrating software optimization methods and hardware platforms, which can point to the future trends and potential developments of generative LLMs and hardware technology for edge-side scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge