Diffusion Models as Constrained Samplers for Optimization with Unknown Constraints
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2024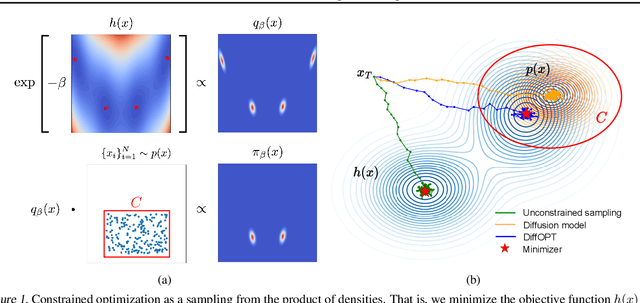
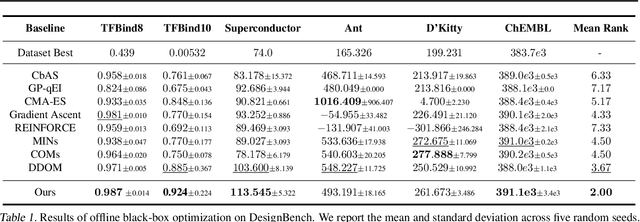
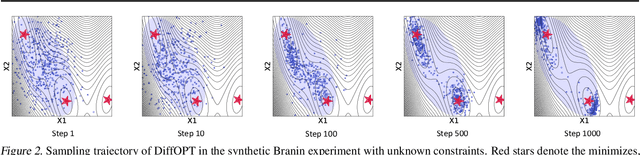
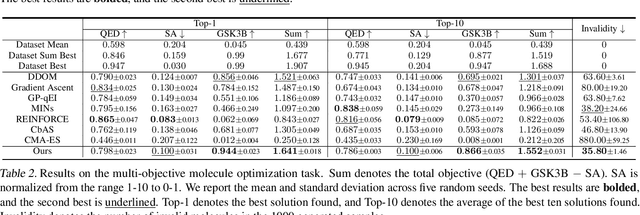
Addressing real-world optimization problems becomes particularly challenging when analytic objective functions or constraints are unavailable. While numerous studies have addressed the issue of unknown objectives, limited research has focused on scenarios where feasibility constraints are not given explicitly. Overlooking these constraints can lead to spurious solutions that are unrealistic in practice. To deal with such unknown constraints, we propose to perform optimization within the data manifold using diffusion models. To constrain the optimization process to the data manifold, we reformulate the original optimization problem as a sampling problem from the product of the Boltzmann distribution defined by the objective function and the data distribution learned by the diffusion model. To enhance sampling efficiency, we propose a two-stage framework that begins with a guided diffusion process for warm-up, followed by a Langevin dynamics stage for further correction. Theoretical analysis shows that the initial stage results in a distribution focused on feasible solutions, thereby providing a better initialization for the later stage. Comprehensive experiments on a synthetic dataset, six real-world black-box optimization datasets, and a multi-objective optimization dataset show that our method achieves better or comparable performance with previous state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge