B-TMS: Bayesian Traversable Terrain Modeling and Segmentation Across 3D LiDAR Scans and Maps for Enhanced Off-Road Navigation
Paper and Code
Jun 26, 2024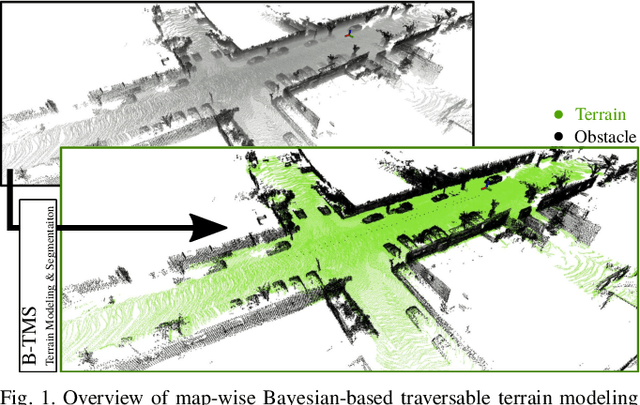
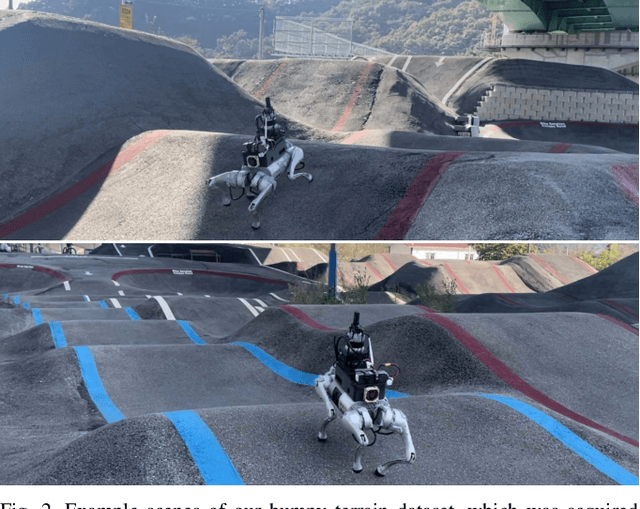

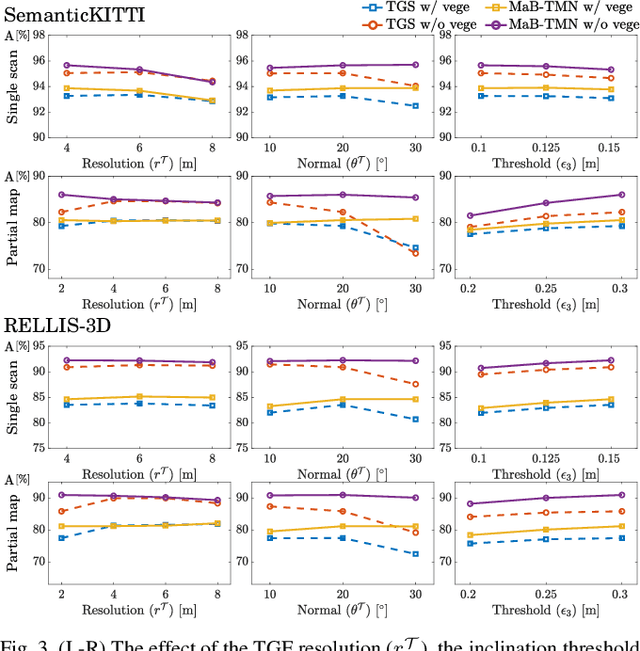
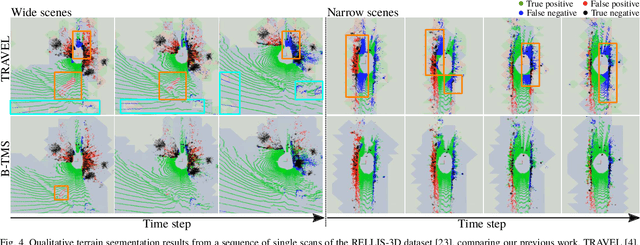
Recognizing traversable terrain from 3D point cloud data is critical, as it directly impacts the performance of autonomous navigation in off-road environments. However, existing segmentation algorithms often struggle with challenges related to changes in data distribution, environmental specificity, and sensor variations. Moreover, when encountering sunken areas, their performance is frequently compromised, and they may even fail to recognize them. To address these challenges, we introduce B-TMS, a novel approach that performs map-wise terrain modeling and segmentation by utilizing Bayesian generalized kernel (BGK) within the graph structure known as the tri-grid field (TGF). Our experiments encompass various data distributions, ranging from single scans to partial maps, utilizing both public datasets representing urban scenes and off-road environments, and our own dataset acquired from extremely bumpy terrains. Our results demonstrate notable contributions, particularly in terms of robustness to data distribution variations, adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, and resilience against the challenges associated with parameter changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge