Zohaib Iqbal
Accurate Real Time Localization Tracking in A Clinical Environment using Bluetooth Low Energy and Deep Learning
Oct 15, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning has started to revolutionize several different industries, and the applications of these methods in medicine are now becoming more commonplace. This study focuses on investigating the feasibility of tracking patients and clinical staff wearing Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) tags in a radiation oncology clinic using artificial neural networks (ANNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The performance of these networks was compared to relative received signal strength indicator (RSSI) thresholding and triangulation. By utilizing temporal information, a combined CNN+ANN network was capable of correctly identifying the location of the BLE tag with an accuracy of 99.9%. It outperformed a CNN model (accuracy = 94%), a thresholding model employing majority voting (accuracy = 95%), and a triangulation classifier utilizing majority voting (accuracy = 95%). Future studies will seek to deploy this affordable real time location system in hospitals to improve clinical workflow, efficiency, and patient safety.
Three-Dimensional Radiotherapy Dose Prediction on Head and Neck Cancer Patients with a Hierarchically Densely Connected U-net Deep Learning Architecture
May 25, 2018


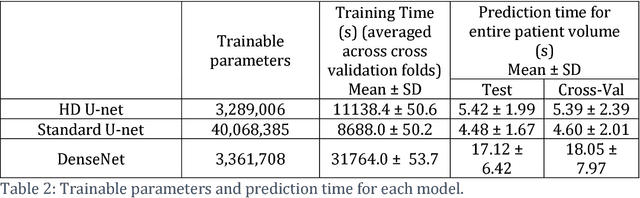
Abstract:The treatment planning process for patients with head and neck (H&N) cancer is regarded as one of the most complicated due large target volume, multiple prescription dose levels, and many radiation-sensitive critical structures near the target. Treatment planning for this site requires a high level of human expertise and a tremendous amount of effort to produce personalized high quality plans, taking as long as a week, which deteriorates the chances of tumor control and patient survival. To solve this problem, we propose to investigate a deep learning-based dose prediction model, Hierarchically Densely Connected U-net, based on two highly popular network architectures: U-net and DenseNet. We find that this new architecture is able to accurately and efficiently predict the dose distribution, outperforming the other two models, the Standard U-net and DenseNet, in homogeneity, dose conformity, and dose coverage on the test data. On average, our proposed model is capable of predicting the OAR max dose within 6.3% and mean dose within 5.1% of the prescription dose on the test data. The other models, the Standard U-net and DenseNet, performed worse, having an OAR max dose prediction error of 8.2% and 9.3%, respectively, and mean dose prediction error of 6.4% and 6.8%, respectively. In addition, our proposed model used 12 times less trainable parameters than the Standard U-net, and predicted the patient dose 4 times faster than DenseNet.
Dose Prediction with U-net: A Feasibility Study for Predicting Dose Distributions from Contours using Deep Learning on Prostate IMRT Patients
May 23, 2018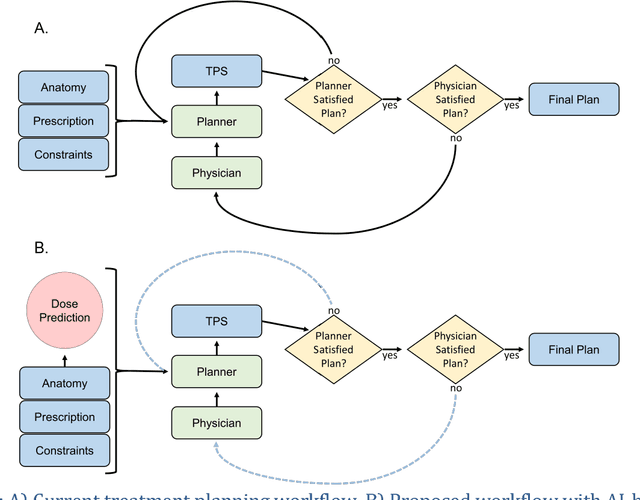
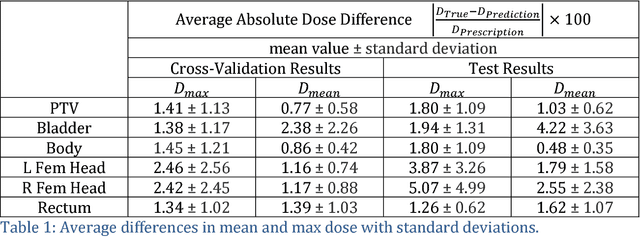
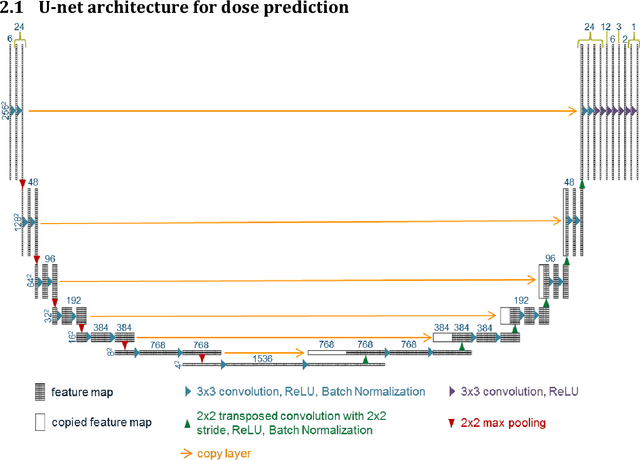
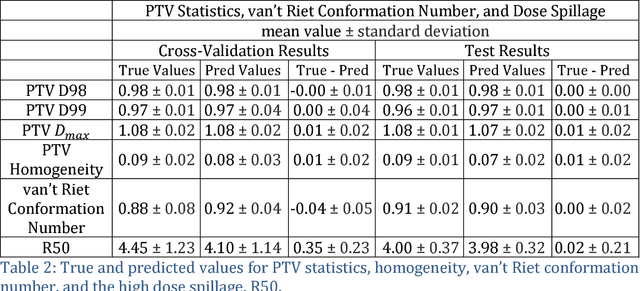
Abstract:With the advancement of treatment modalities in radiation therapy for cancer patients, outcomes have improved, but at the cost of increased treatment plan complexity and planning time. The accurate prediction of dose distributions would alleviate this issue by guiding clinical plan optimization to save time and maintain high quality plans. We have modified a convolutional deep network model, U-net (originally designed for segmentation purposes), for predicting dose from patient image contours. We show that, as an example, we are able to accurately predict the dose of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for prostate cancer patients, where the average dice similarity coefficient is 0.91 when comparing the predicted vs. true isodose volumes between 0% and 100% of the prescription dose. The average value of the absolute differences in [max, mean] dose is found to be under 5% of the prescription dose, specifically for each structure is [1.80%, 1.03%](PTV), [1.94%, 4.22%](Bladder), [1.80%, 0.48%](Body), [3.87%, 1.79%](L Femoral Head), [5.07%, 2.55%](R Femoral Head), and [1.26%, 1.62%](Rectum) of the prescription dose. We thus managed to map a desired radiation dose distribution from a patient's PTV and OAR contours. As an additional advantage, relatively little data was used in the techniques and models described in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge