Zihe Zheng
Trend and Thoughts: Understanding Climate Change Concern using Machine Learning and Social Media Data
Nov 06, 2021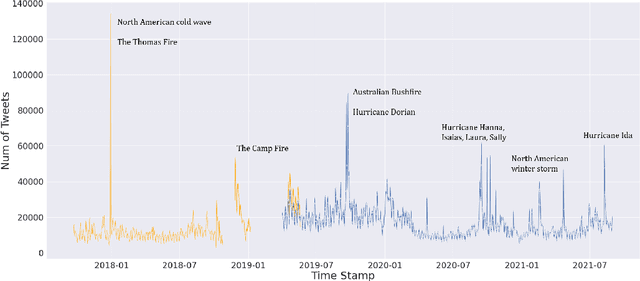
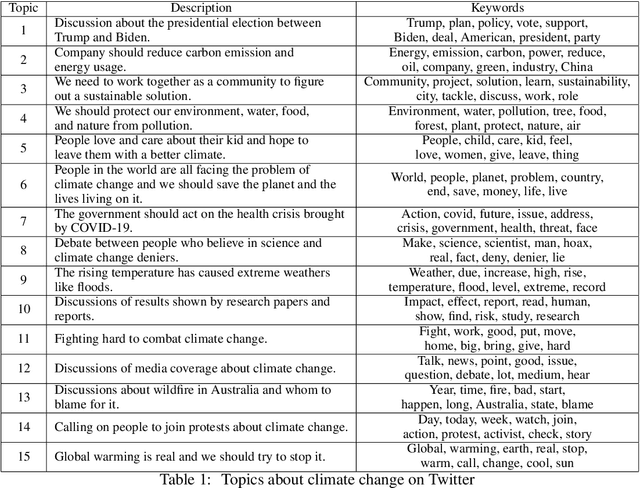
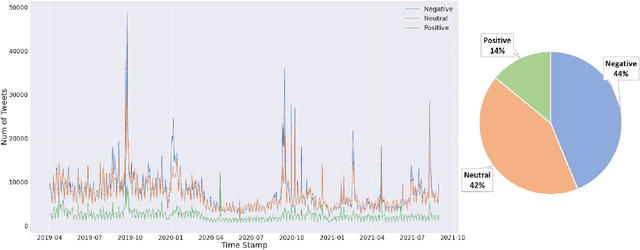
Abstract:Nowadays social media platforms such as Twitter provide a great opportunity to understand public opinion of climate change compared to traditional survey methods. In this paper, we constructed a massive climate change Twitter dataset and conducted comprehensive analysis using machine learning. By conducting topic modeling and natural language processing, we show the relationship between the number of tweets about climate change and major climate events; the common topics people discuss climate change; and the trend of sentiment. Our dataset was published on Kaggle (\url{https://www.kaggle.com/leonshangguan/climate-change-tweets-ids-until-aug-2021}) and can be used in further research.
Learning to Aggregate and Refine Noisy Labels for Visual Sentiment Analysis
Sep 15, 2021



Abstract:Visual sentiment analysis has received increasing attention in recent years. However, the quality of the dataset is a concern because the sentiment labels are crowd-sourcing, subjective, and prone to mistakes. This poses a severe threat to the data-driven models including the deep neural networks which would generalize poorly on the testing cases if they are trained to over-fit the samples with noisy sentiment labels. Inspired by the recent progress on learning with noisy labels, we propose a robust learning method to perform robust visual sentiment analysis. Our method relies on an external memory to aggregate and filter noisy labels during training and thus can prevent the model from overfitting the noisy cases. The memory is composed of the prototypes with corresponding labels, both of which can be updated online. We establish a benchmark for visual sentiment analysis with label noise using publicly available datasets. The experiment results of the proposed benchmark settings comprehensively show the effectiveness of our method.
NTIRE 2021 Multi-modal Aerial View Object Classification Challenge
Jul 02, 2021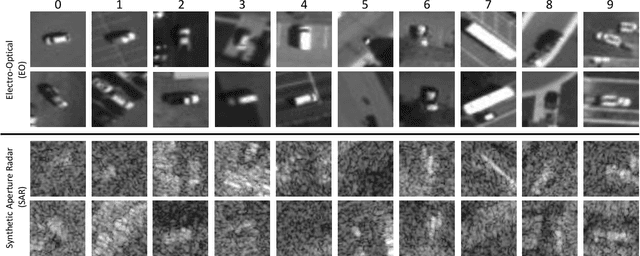
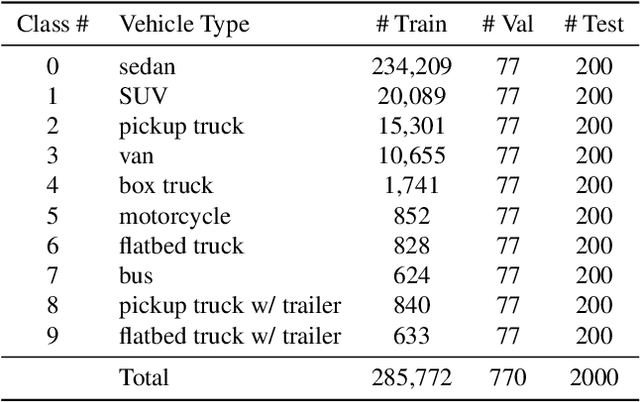
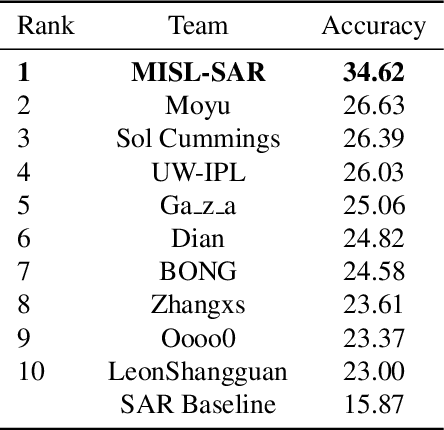
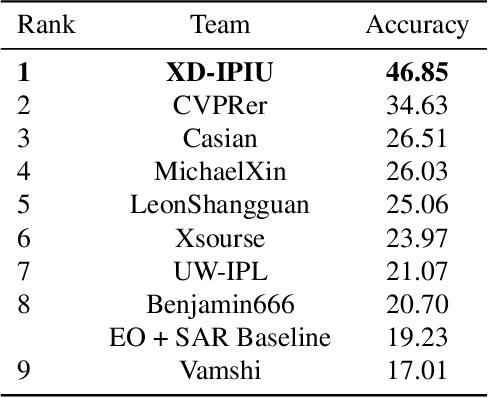
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the first Challenge on Multi-modal Aerial View Object Classification (MAVOC) in conjunction with the NTIRE 2021 workshop at CVPR. This challenge is composed of two different tracks using EO andSAR imagery. Both EO and SAR sensors possess different advantages and drawbacks. The purpose of this competition is to analyze how to use both sets of sensory information in complementary ways. We discuss the top methods submitted for this competition and evaluate their results on our blind test set. Our challenge results show significant improvement of more than 15% accuracy from our current baselines for each track of the competition
* 10 pages, 1 figure. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge