Zichao Lin
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
SuperInfer: SLO-Aware Rotary Scheduling and Memory Management for LLM Inference on Superchips
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) serving faces a fundamental tension between stringent latency Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and limited GPU memory capacity. When high request rates exhaust the KV cache budget, existing LLM inference systems often suffer severe head-of-line (HOL) blocking. While prior work explored PCIe-based offloading, these approaches cannot sustain responsiveness under high request rates, often failing to meet tight Time-To-First-Token (TTFT) and Time-Between-Tokens (TBT) SLOs. We present SuperInfer, a high-performance LLM inference system designed for emerging Superchips (e.g., NVIDIA GH200) with tightly coupled GPU-CPU architecture via NVLink-C2C. SuperInfer introduces RotaSched, the first proactive, SLO-aware rotary scheduler that rotates requests to maintain responsiveness on Superchips, and DuplexKV, an optimized rotation engine that enables full-duplex transfer over NVLink-C2C. Evaluations on GH200 using various models and datasets show that SuperInfer improves TTFT SLO attainment rates by up to 74.7% while maintaining comparable TBT and throughput compared to state-of-the-art systems, demonstrating that SLO-aware scheduling and memory co-design unlocks the full potential of Superchips for responsive LLM serving.
Knowledge Graph Enhanced Relation Extraction Datasets
Oct 19, 2022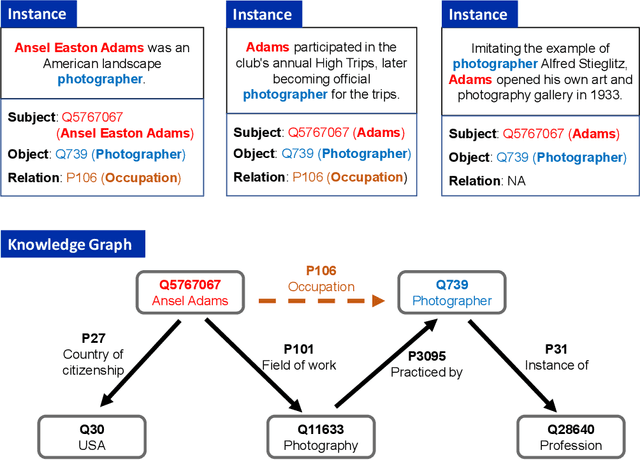


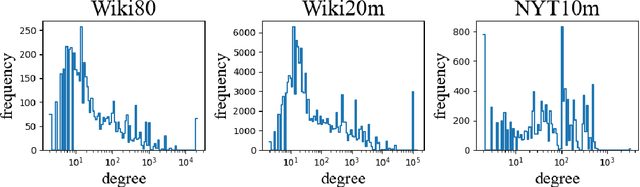
Abstract:Knowledge-enhanced methods that take advantage of auxiliary knowledge graphs recently emerged in relation extraction, and they surpass traditional text-based relation extraction methods. However, there are no unified public benchmarks that currently involve evidence sentences and knowledge graphs for knowledge-enhanced relation extraction. To combat these issues, we propose KGRED, a knowledge graph enhanced relation extraction dataset with features as follows: (1) the benchmarks are based on widely-used distantly supervised relation extraction datasets; (2) we refine these existing datasets to improve the data quality, and we also construct auxiliary knowledge graphs for these existing datasets through entity linking to support knowledge-enhanced relation extraction tasks; (3) with the new benchmarks we curated, we build baselines in two popular relation extraction settings including sentence-level and bag-level relation extraction, and we also make comparisons among the latest knowledge-enhanced relation extraction methods. KGRED provides high-quality relation extraction datasets with auxiliary knowledge graphs for evaluating the performance of knowledge-enhanced relation extraction methods. Meanwhile, our experiments on KGRED reveal the influence of knowledge graph information on relation extraction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge