Zhuxi Jiang
Nonparametric Topic Modeling with Neural Inference
Jun 18, 2018


Abstract:This work focuses on combining nonparametric topic models with Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes (AEVB). Specifically, we first propose iTM-VAE, where the topics are treated as trainable parameters and the document-specific topic proportions are obtained by a stick-breaking construction. The inference of iTM-VAE is modeled by neural networks such that it can be computed in a simple feed-forward manner. We also describe how to introduce a hyper-prior into iTM-VAE so as to model the uncertainty of the prior parameter. Actually, the hyper-prior technique is quite general and we show that it can be applied to other AEVB based models to alleviate the {\it collapse-to-prior} problem elegantly. Moreover, we also propose HiTM-VAE, where the document-specific topic distributions are generated in a hierarchical manner. HiTM-VAE is even more flexible and can generate topic distributions with better variability. Experimental results on 20News and Reuters RCV1-V2 datasets show that the proposed models outperform the state-of-the-art baselines significantly. The advantages of the hyper-prior technique and the hierarchical model construction are also confirmed by experiments.
Variational Deep Embedding: An Unsupervised and Generative Approach to Clustering
Jun 28, 2017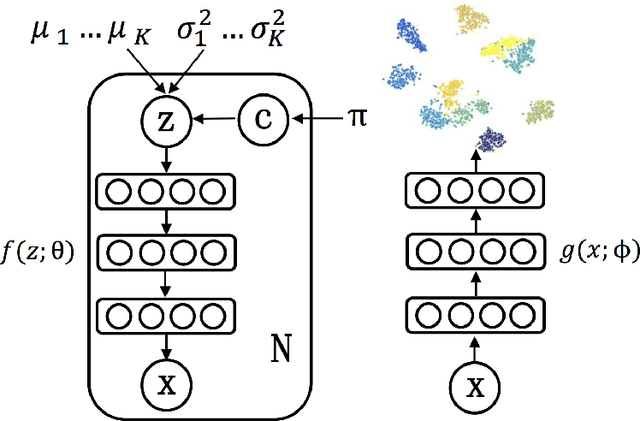
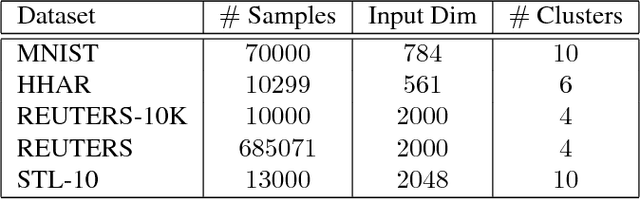
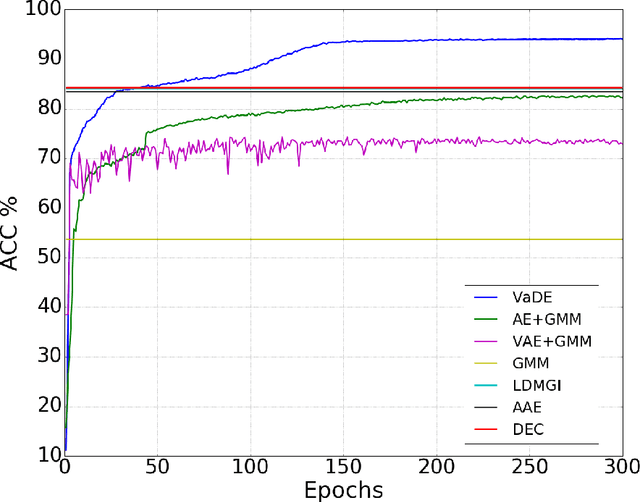
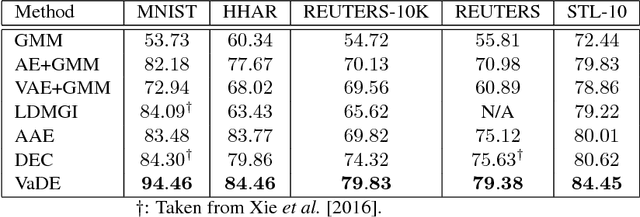
Abstract:Clustering is among the most fundamental tasks in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, we propose Variational Deep Embedding (VaDE), a novel unsupervised generative clustering approach within the framework of Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE). Specifically, VaDE models the data generative procedure with a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and a deep neural network (DNN): 1) the GMM picks a cluster; 2) from which a latent embedding is generated; 3) then the DNN decodes the latent embedding into observables. Inference in VaDE is done in a variational way: a different DNN is used to encode observables to latent embeddings, so that the evidence lower bound (ELBO) can be optimized using Stochastic Gradient Variational Bayes (SGVB) estimator and the reparameterization trick. Quantitative comparisons with strong baselines are included in this paper, and experimental results show that VaDE significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art clustering methods on 4 benchmarks from various modalities. Moreover, by VaDE's generative nature, we show its capability of generating highly realistic samples for any specified cluster, without using supervised information during training. Lastly, VaDE is a flexible and extensible framework for unsupervised generative clustering, more general mixture models than GMM can be easily plugged in.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge