Bangsheng Tang
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Efficient Speculative Decoding for Llama at Scale: Challenges and Solutions
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding is a standard method for accelerating the inference speed of large language models. However, scaling it for production environments poses several engineering challenges, including efficiently implementing different operations (e.g., tree attention and multi-round speculative decoding) on GPU. In this paper, we detail the training and inference optimization techniques that we have implemented to enable EAGLE-based speculative decoding at a production scale for Llama models. With these changes, we achieve a new state-of-the-art inference latency for Llama models. For example, Llama4 Maverick decodes at a speed of about 4 ms per token (with a batch size of one) on 8 NVIDIA H100 GPUs, which is 10% faster than the previously best known method. Furthermore, for EAGLE-based speculative decoding, our optimizations enable us to achieve a speed-up for large batch sizes between 1.4x and 2.0x at production scale.
Context Parallelism for Scalable Million-Token Inference
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:We present context parallelism for long-context large language model inference, which achieves near-linear scaling for long-context prefill latency with up to 128 H100 GPUs across 16 nodes. Particularly, our method achieves 1M context prefill with Llama3 405B model in 77s (93% parallelization efficiency, 63% FLOPS utilization) and 128K context prefill in 3.8s. We develop two lossless exact ring attention variants: pass-KV and pass-Q to cover a wide range of use cases with the state-of-the-art performance: full prefill, persistent KV prefill and decode. Benchmarks on H100 GPU hosts inter-connected with RDMA and TCP both show similar scalability for long-context prefill, demonstrating that our method scales well using common commercial data center with medium-to-low inter-host bandwidth.
Variational Deep Embedding: An Unsupervised and Generative Approach to Clustering
Jun 28, 2017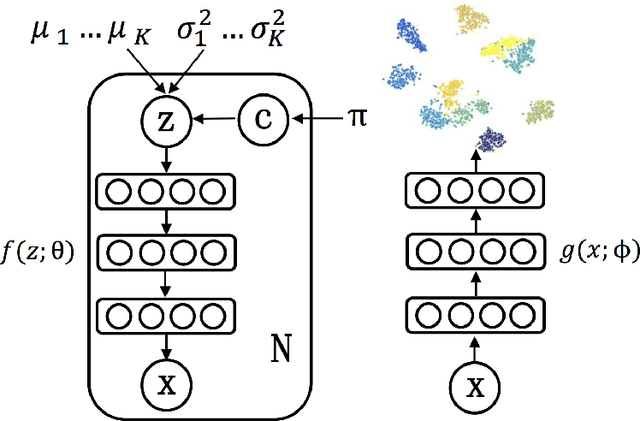
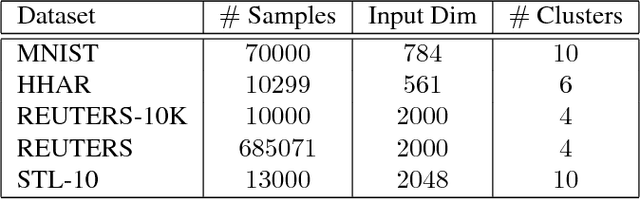
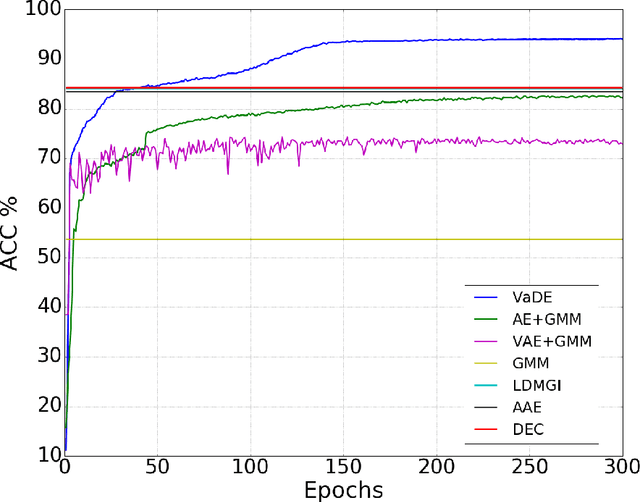
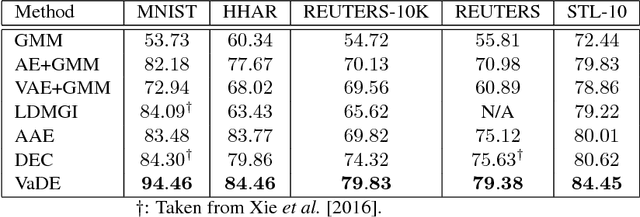
Abstract:Clustering is among the most fundamental tasks in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, we propose Variational Deep Embedding (VaDE), a novel unsupervised generative clustering approach within the framework of Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE). Specifically, VaDE models the data generative procedure with a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and a deep neural network (DNN): 1) the GMM picks a cluster; 2) from which a latent embedding is generated; 3) then the DNN decodes the latent embedding into observables. Inference in VaDE is done in a variational way: a different DNN is used to encode observables to latent embeddings, so that the evidence lower bound (ELBO) can be optimized using Stochastic Gradient Variational Bayes (SGVB) estimator and the reparameterization trick. Quantitative comparisons with strong baselines are included in this paper, and experimental results show that VaDE significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art clustering methods on 4 benchmarks from various modalities. Moreover, by VaDE's generative nature, we show its capability of generating highly realistic samples for any specified cluster, without using supervised information during training. Lastly, VaDE is a flexible and extensible framework for unsupervised generative clustering, more general mixture models than GMM can be easily plugged in.
A Neural Autoregressive Approach to Collaborative Filtering
May 31, 2016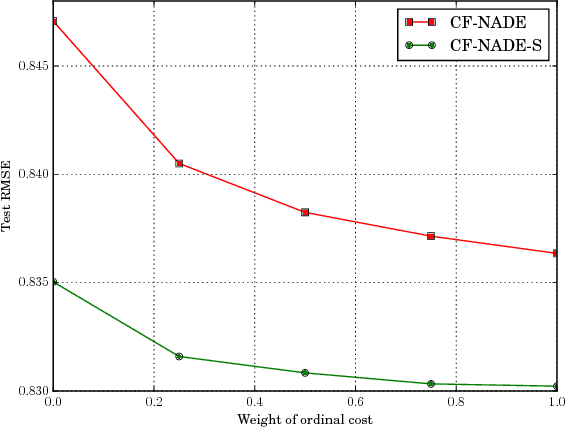
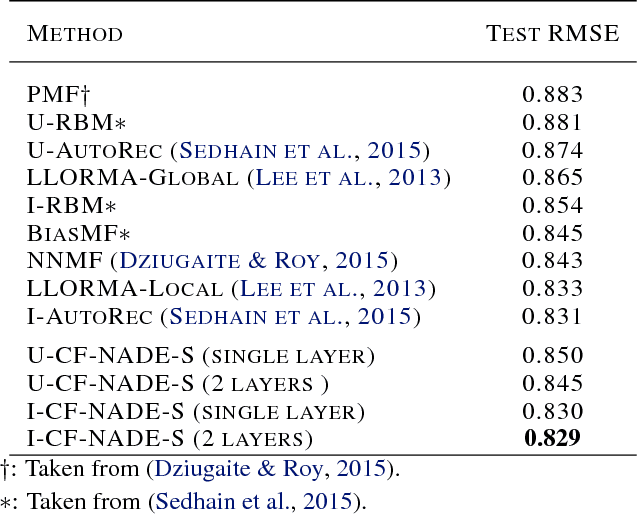
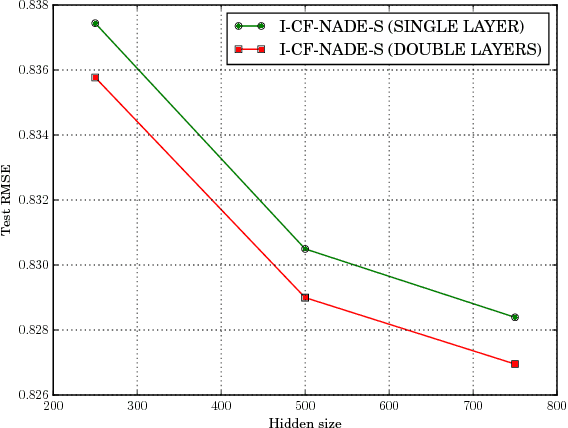
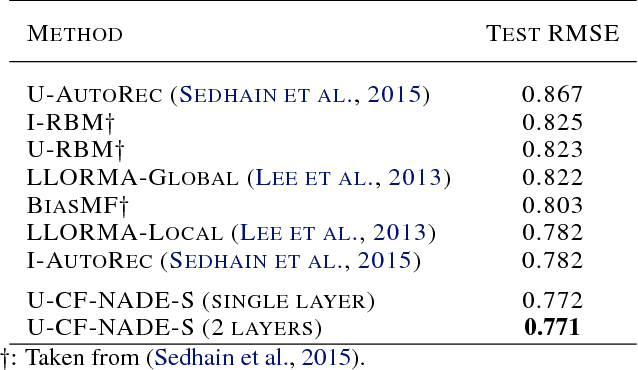
Abstract:This paper proposes CF-NADE, a neural autoregressive architecture for collaborative filtering (CF) tasks, which is inspired by the Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) based CF model and the Neural Autoregressive Distribution Estimator (NADE). We first describe the basic CF-NADE model for CF tasks. Then we propose to improve the model by sharing parameters between different ratings. A factored version of CF-NADE is also proposed for better scalability. Furthermore, we take the ordinal nature of the preferences into consideration and propose an ordinal cost to optimize CF-NADE, which shows superior performance. Finally, CF-NADE can be extended to a deep model, with only moderately increased computational complexity. Experimental results show that CF-NADE with a single hidden layer beats all previous state-of-the-art methods on MovieLens 1M, MovieLens 10M, and Netflix datasets, and adding more hidden layers can further improve the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge