Zhongle Ren
DI3CL: Contrastive Learning With Dynamic Instances and Contour Consistency for SAR Land-Cover Classification Foundation Model
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Although significant advances have been achieved in SAR land-cover classification, recent methods remain predominantly focused on supervised learning, which relies heavily on extensive labeled datasets. This dependency not only limits scalability and generalization but also restricts adaptability to diverse application scenarios. In this paper, a general-purpose foundation model for SAR land-cover classification is developed, serving as a robust cornerstone to accelerate the development and deployment of various downstream models. Specifically, a Dynamic Instance and Contour Consistency Contrastive Learning (DI3CL) pre-training framework is presented, which incorporates a Dynamic Instance (DI) module and a Contour Consistency (CC) module. DI module enhances global contextual awareness by enforcing local consistency across different views of the same region. CC module leverages shallow feature maps to guide the model to focus on the geometric contours of SAR land-cover objects, thereby improving structural discrimination. Additionally, to enhance robustness and generalization during pre-training, a large-scale and diverse dataset named SARSense, comprising 460,532 SAR images, is constructed to enable the model to capture comprehensive and representative features. To evaluate the generalization capability of our foundation model, we conducted extensive experiments across a variety of SAR land-cover classification tasks, including SAR land-cover mapping, water body detection, and road extraction. The results consistently demonstrate that the proposed DI3CL outperforms existing methods. Our code and pre-trained weights are publicly available at: https://github.com/SARpre-train/DI3CL.
Pixel DAG-Recurrent Neural Network for Spectral-Spatial Hyperspectral Image Classification
Jun 09, 2019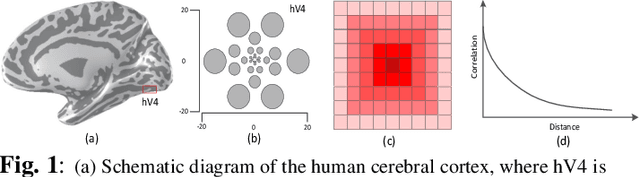
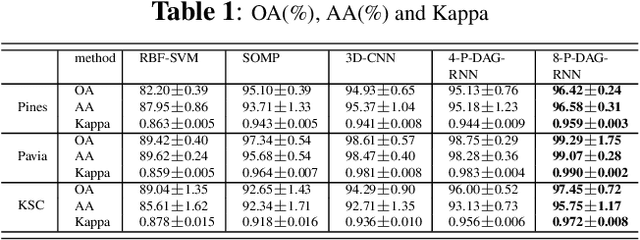
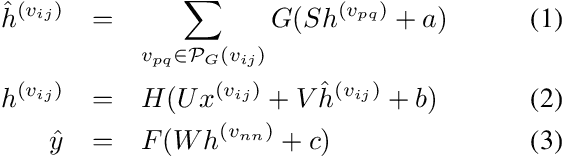
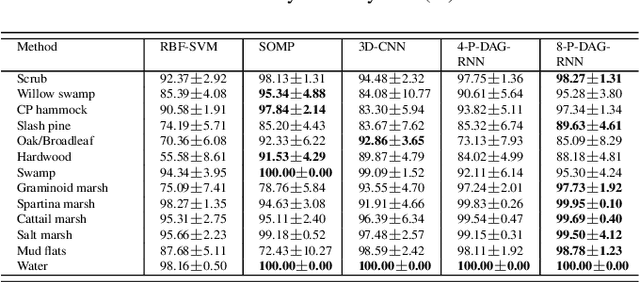
Abstract:Exploiting rich spatial and spectral features contributes to improve the classification accuracy of hyperspectral images (HSIs). In this paper, based on the mechanism of the population receptive field (pRF) in human visual cortex, we further utilize the spatial correlation of pixels in images and propose pixel directed acyclic graph recurrent neural network (Pixel DAG-RNN) to extract and apply spectral-spatial features for HSIs classification. In our model, an undirected cyclic graph (UCG) is used to represent the relevance connectivity of pixels in an image patch, and four DAGs are used to approximate the spatial relationship of UCGs. In order to avoid overfitting, weight sharing and dropout are adopted. The higher classification performance of our model on HSIs classification has been verified by experiments on three benchmark data sets.
Modified Diversity of Class Probability Estimation Co-training for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Sep 05, 2018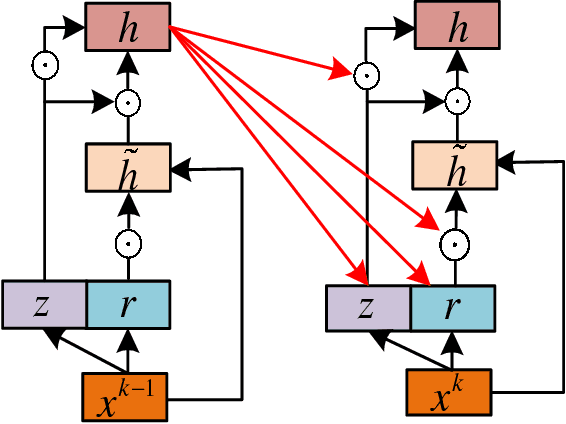
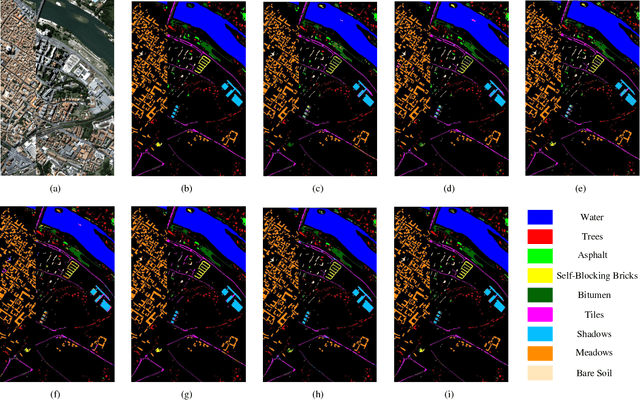
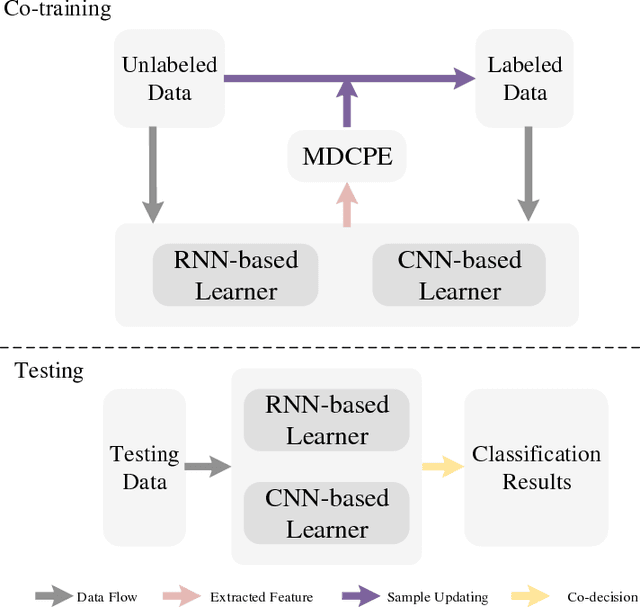
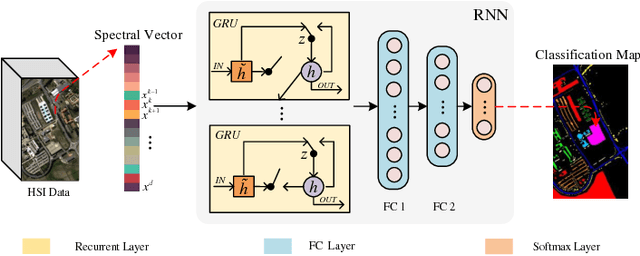
Abstract:Due to the limited amount and imbalanced classes of labeled training data, the conventional supervised learning can not ensure the discrimination of the learned feature for hyperspectral image (HSI) classification. In this paper, we propose a modified diversity of class probability estimation (MDCPE) with two deep neural networks to learn spectral-spatial feature for HSI classification. In co-training phase, recurrent neural network (RNN) and convolutional neural network (CNN) are utilized as two learners to extract features from labeled and unlabeled data. Based on the extracted features, MDCPE selects most credible samples to update initial labeled data by combining k-means clustering with the traditional diversity of class probability estimation (DCPE) co-training. In this way, MDCPE can keep new labeled data class-balanced and extract discriminative features for both the minority and majority classes. During testing process, classification results are acquired by co-decision of the two learners. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed semi-supervised co-training method can make full use of unlabeled information to enhance generality of the learners and achieve favorable accuracies on all three widely used data sets: Salinas, Pavia University and Pavia Center.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge