Pixel DAG-Recurrent Neural Network for Spectral-Spatial Hyperspectral Image Classification
Paper and Code
Jun 09, 2019
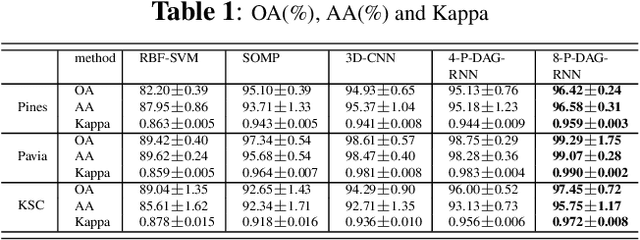
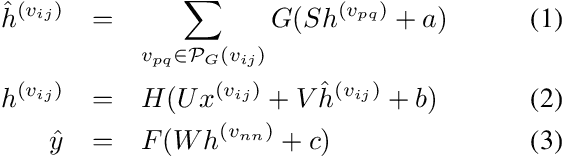
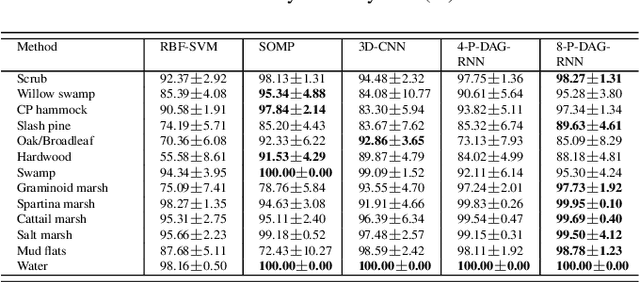
Exploiting rich spatial and spectral features contributes to improve the classification accuracy of hyperspectral images (HSIs). In this paper, based on the mechanism of the population receptive field (pRF) in human visual cortex, we further utilize the spatial correlation of pixels in images and propose pixel directed acyclic graph recurrent neural network (Pixel DAG-RNN) to extract and apply spectral-spatial features for HSIs classification. In our model, an undirected cyclic graph (UCG) is used to represent the relevance connectivity of pixels in an image patch, and four DAGs are used to approximate the spatial relationship of UCGs. In order to avoid overfitting, weight sharing and dropout are adopted. The higher classification performance of our model on HSIs classification has been verified by experiments on three benchmark data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge