Zhiyuan Yin
Codebook-Centric Deep Hashing: End-to-End Joint Learning of Semantic Hash Centers and Neural Hash Function
Nov 15, 2025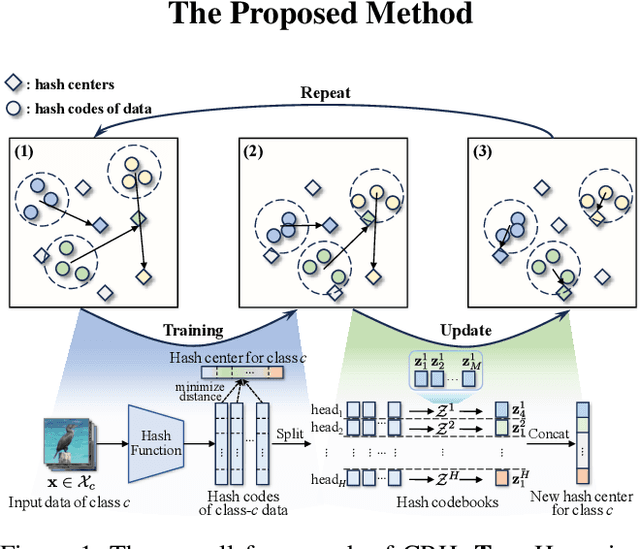
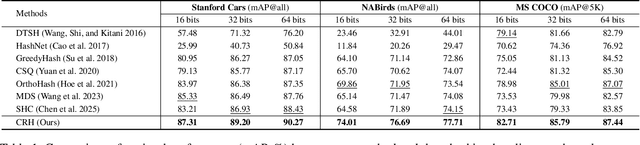

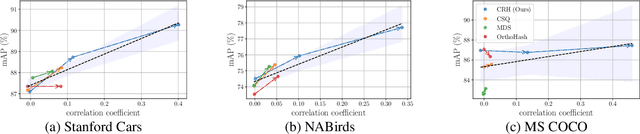
Abstract:Hash center-based deep hashing methods improve upon pairwise or triplet-based approaches by assigning fixed hash centers to each class as learning targets, thereby avoiding the inefficiency of local similarity optimization. However, random center initialization often disregards inter-class semantic relationships. While existing two-stage methods mitigate this by first refining hash centers with semantics and then training the hash function, they introduce additional complexity, computational overhead, and suboptimal performance due to stage-wise discrepancies. To address these limitations, we propose $\textbf{Center-Reassigned Hashing (CRH)}$, an end-to-end framework that $\textbf{dynamically reassigns hash centers}$ from a preset codebook while jointly optimizing the hash function. Unlike previous methods, CRH adapts hash centers to the data distribution $\textbf{without explicit center optimization phases}$, enabling seamless integration of semantic relationships into the learning process. Furthermore, $\textbf{a multi-head mechanism}$ enhances the representational capacity of hash centers, capturing richer semantic structures. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate that CRH learns semantically meaningful hash centers and outperforms state-of-the-art deep hashing methods in retrieval tasks.
INFELM: In-depth Fairness Evaluation of Large Text-To-Image Models
Jan 07, 2025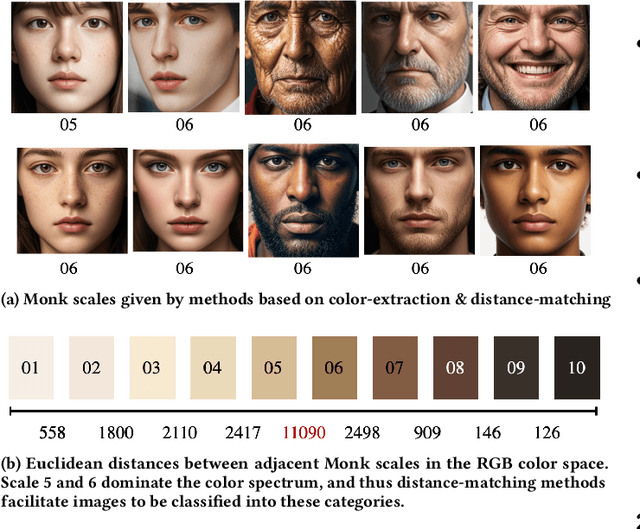

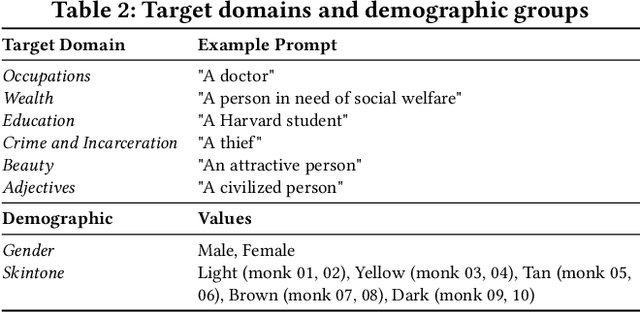
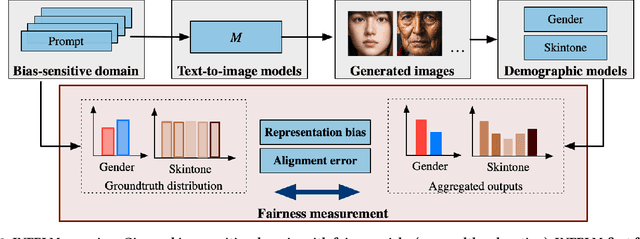
Abstract:The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) and large vision models (LVMs) have propelled the evolution of multi-modal AI systems, which have demonstrated the remarkable potential for industrial applications by emulating human-like cognition. However, they also pose significant ethical challenges, including amplifying harmful content and reinforcing societal biases. For instance, biases in some industrial image generation models highlighted the urgent need for robust fairness assessments. Most existing evaluation frameworks focus on the comprehensiveness of various aspects of the models, but they exhibit critical limitations, including insufficient attention to content generation alignment and social bias-sensitive domains. More importantly, their reliance on pixel-detection techniques is prone to inaccuracies. To address these issues, this paper presents INFELM, an in-depth fairness evaluation on widely-used text-to-image models. Our key contributions are: (1) an advanced skintone classifier incorporating facial topology and refined skin pixel representation to enhance classification precision by at least 16.04%, (2) a bias-sensitive content alignment measurement for understanding societal impacts, (3) a generalizable representation bias evaluation for diverse demographic groups, and (4) extensive experiments analyzing large-scale text-to-image model outputs across six social-bias-sensitive domains. We find that existing models in the study generally do not meet the empirical fairness criteria, and representation bias is generally more pronounced than alignment errors. INFELM establishes a robust benchmark for fairness assessment, supporting the development of multi-modal AI systems that align with ethical and human-centric principles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge