Zhiyao Yang
Weakly Supervised Fine-grained Span-Level Framework for Chinese Radiology Report Quality Assurance
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Quality Assurance (QA) for radiology reports refers to judging whether the junior reports (written by junior doctors) are qualified. The QA scores of one junior report are given by the senior doctor(s) after reviewing the image and junior report. This process requires intensive labor costs for senior doctors. Additionally, the QA scores may be inaccurate for reasons like diagnosis bias, the ability of senior doctors, and so on. To address this issue, we propose a Span-level Quality Assurance EvaluaTOR (Sqator) to mark QA scores automatically. Unlike the common document-level semantic comparison method, we try to analyze the semantic difference by exploring more fine-grained text spans. Unlike the common document-level semantic comparison method, we try to analyze the semantic difference by exploring more fine-grained text spans. Specifically, Sqator measures QA scores by measuring the importance of revised spans between junior and senior reports, and outputs the final QA scores by merging all revised span scores. We evaluate Sqator using a collection of 12,013 radiology reports. Experimental results show that Sqator can achieve competitive QA scores. Moreover, the importance scores of revised spans can be also consistent with the judgments of senior doctors.
Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis with Explicit Sentiment Augmentations
Dec 18, 2023
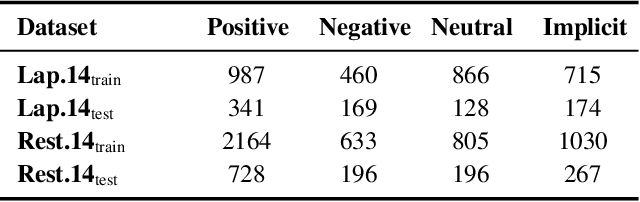

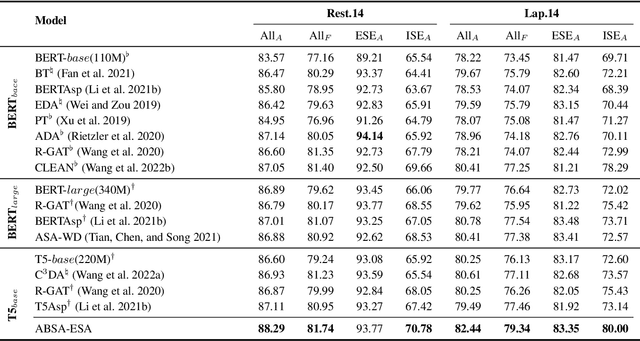
Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA), a fine-grained sentiment classification task, has received much attention recently. Many works investigate sentiment information through opinion words, such as ''good'' and ''bad''. However, implicit sentiment widely exists in the ABSA dataset, which refers to the sentence containing no distinct opinion words but still expresses sentiment to the aspect term. To deal with implicit sentiment, this paper proposes an ABSA method that integrates explicit sentiment augmentations. And we propose an ABSA-specific augmentation method to create such augmentations. Specifically, we post-trains T5 by rule-based data. We employ Syntax Distance Weighting and Unlikelihood Contrastive Regularization in the training procedure to guide the model to generate an explicit sentiment. Meanwhile, we utilize the Constrained Beam Search to ensure the augmentation sentence contains the aspect terms. We test ABSA-ESA on two of the most popular benchmarks of ABSA. The results show that ABSA-ESA outperforms the SOTA baselines on implicit and explicit sentiment accuracy.
Unsupervised Sentence Representation Learning with Frequency-induced Adversarial Tuning and Incomplete Sentence Filtering
May 15, 2023



Abstract:Pre-trained Language Model (PLM) is nowadays the mainstay of Unsupervised Sentence Representation Learning (USRL). However, PLMs are sensitive to the frequency information of words from their pre-training corpora, resulting in anisotropic embedding space, where the embeddings of high-frequency words are clustered but those of low-frequency words disperse sparsely. This anisotropic phenomenon results in two problems of similarity bias and information bias, lowering the quality of sentence embeddings. To solve the problems, we fine-tune PLMs by leveraging the frequency information of words and propose a novel USRL framework, namely Sentence Representation Learning with Frequency-induced Adversarial tuning and Incomplete sentence filtering (SLT-FAI). We calculate the word frequencies over the pre-training corpora of PLMs and assign words thresholding frequency labels. With them, (1) we incorporate a similarity discriminator used to distinguish the embeddings of high-frequency and low-frequency words, and adversarially tune the PLM with it, enabling to achieve uniformly frequency-invariant embedding space; and (2) we propose a novel incomplete sentence detection task, where we incorporate an information discriminator to distinguish the embeddings of original sentences and incomplete sentences by randomly masking several low-frequency words, enabling to emphasize the more informative low-frequency words. Our SLT-FAI is a flexible and plug-and-play framework, and it can be integrated with existing USRL techniques. We evaluate SLT-FAI with various backbones on benchmark datasets. Empirical results indicate that SLT-FAI can be superior to the existing USRL baselines. Our code is released in \url{https://github.com/wangbing1416/SLT-FAI}.
Variational Wasserstein Barycenters with c-Cyclical Monotonicity
Oct 22, 2021
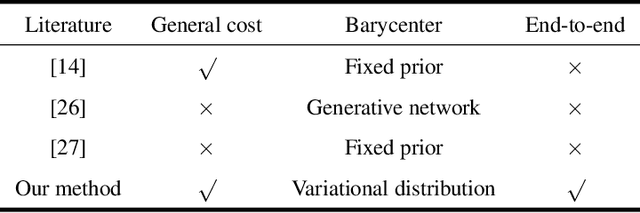
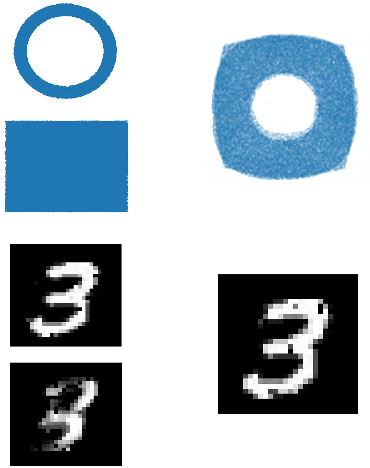
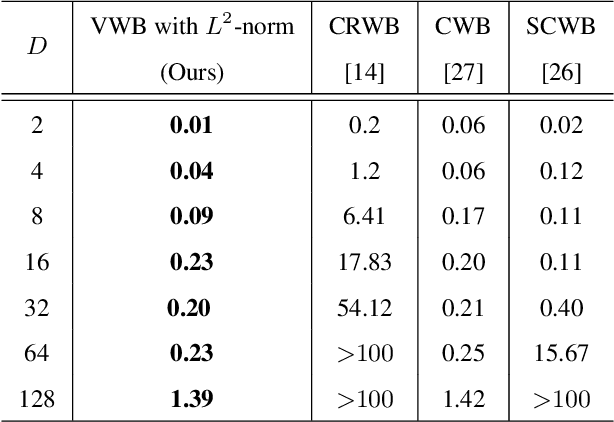
Abstract:Wasserstein barycenter, built on the theory of optimal transport, provides a powerful framework to aggregate probability distributions, and it has increasingly attracted great attention within the machine learning community. However, it suffers from severe computational burden, especially for high dimensional and continuous settings. To this end, we develop a novel continuous approximation method for the Wasserstein barycenters problem given sample access to the input distributions. The basic idea is to introduce a variational distribution as the approximation of the true continuous barycenter, so as to frame the barycenters computation problem as an optimization problem, where parameters of the variational distribution adjust the proxy distribution to be similar to the barycenter. Leveraging the variational distribution, we construct a tractable dual formulation for the regularized Wasserstein barycenter problem with c-cyclical monotonicity, which can be efficiently solved by stochastic optimization. We provide theoretical analysis on convergence and demonstrate the practical effectiveness of our method on real applications of subset posterior aggregation and synthetic data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge