Zhixian Xie
RoDiF: Robust Direct Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Policies with Corrupted Human Feedback
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Diffusion policies are a powerful paradigm for robotic control, but fine-tuning them with human preferences is fundamentally challenged by the multi-step structure of the denoising process. To overcome this, we introduce a Unified Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation that coherently integrates the diffusion denoising chain with environmental dynamics, enabling reward-free Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for diffusion policies. Building on this formulation, we propose RoDiF (Robust Direct Fine-Tuning), a method that explicitly addresses corrupted human preferences. RoDiF reinterprets the DPO objective through a geometric hypothesis-cutting perspective and employs a conservative cutting strategy to achieve robustness without assuming any specific noise distribution. Extensive experiments on long-horizon manipulation tasks show that RoDiF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, effectively steering pretrained diffusion policies of diverse architectures to human-preferred modes, while maintaining strong performance even under 30% corrupted preference labels.
Where to Touch, How to Contact: Hierarchical RL-MPC Framework for Geometry-Aware Long-Horizon Dexterous Manipulation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:A key challenge in contact-rich dexterous manipulation is the need to jointly reason over geometry, kinematic constraints, and intricate, nonsmooth contact dynamics. End-to-end visuomotor policies bypass this structure, but often require large amounts of data, transfer poorly from simulation to reality, and generalize weakly across tasks/embodiments. We address those limitations by leveraging a simple insight: dexterous manipulation is inherently hierarchical - at a high level, a robot decides where to touch (geometry) and move the object (kinematics); at a low level it determines how to realize that plan through contact dynamics. Building on this insight, we propose a hierarchical RL--MPC framework in which a high-level reinforcement learning (RL) policy predicts a contact intention, a novel object-centric interface that specifies (i) an object-surface contact location and (ii) a post-contact object-level subgoal pose. Conditioned on this contact intention, a low-level contact-implicit model predictive control (MPC) optimizes local contact modes and replans with contact dynamics to generate robot actions that robustly drive the object toward each subgoal. We evaluate the framework on non-prehensile tasks, including geometry-generalized pushing and object 3D reorientation. It achieves near-100% success with substantially reduced data (10x less than end-to-end baselines), highly robust performance, and zero-shot sim-to-real transfer.
TwinTrack: Bridging Vision and Contact Physics for Real-Time Tracking of Unknown Dynamic Objects
May 28, 2025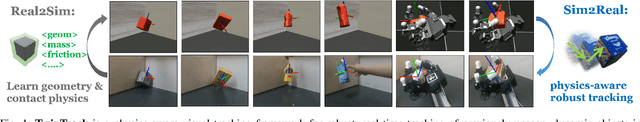
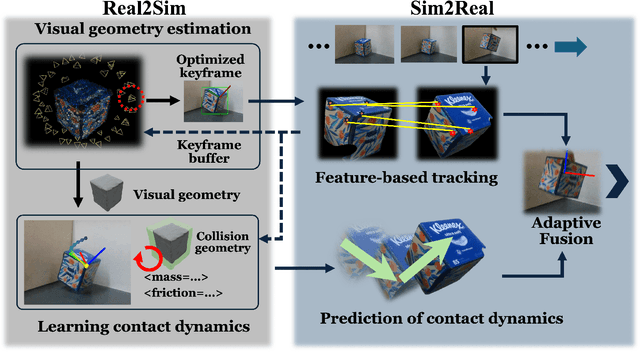
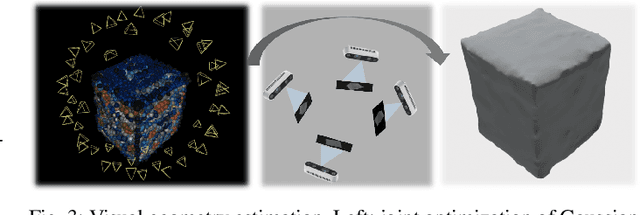
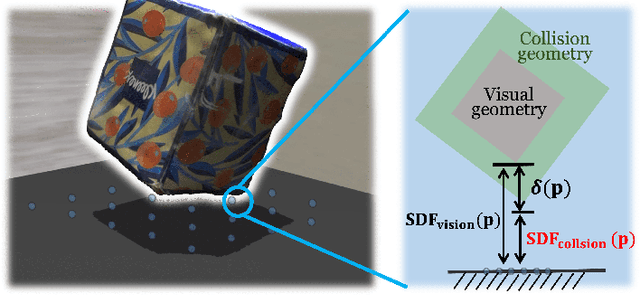
Abstract:Real-time tracking of previously unseen, highly dynamic objects in contact-rich environments -- such as during dexterous in-hand manipulation -- remains a significant challenge. Purely vision-based tracking often suffers from heavy occlusions due to the frequent contact interactions and motion blur caused by abrupt motion during contact impacts. We propose TwinTrack, a physics-aware visual tracking framework that enables robust and real-time 6-DoF pose tracking of unknown dynamic objects in a contact-rich scene by leveraging the contact physics of the observed scene. At the core of TwinTrack is an integration of Real2Sim and Sim2Real. In Real2Sim, we combine the complementary strengths of vision and contact physics to estimate object's collision geometry and physical properties: object's geometry is first reconstructed from vision, then updated along with other physical parameters from contact dynamics for physical accuracy. In Sim2Real, robust pose estimation of the object is achieved by adaptive fusion between visual tracking and prediction of the learned contact physics. TwinTrack is built on a GPU-accelerated, deeply customized physics engine to ensure real-time performance. We evaluate our method on two contact-rich scenarios: object falling with rich contact impacts against the environment, and contact-rich in-hand manipulation. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to baseline methods, TwinTrack achieves significantly more robust, accurate, and real-time 6-DoF tracking in these challenging scenarios, with tracking speed exceeding 20 Hz. Project page: https://irislab.tech/TwinTrack-webpage/
Robust Reward Alignment via Hypothesis Space Batch Cutting
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Reward design for reinforcement learning and optimal control agents is challenging. Preference-based alignment addresses this by enabling agents to learn rewards from ranked trajectory pairs provided by humans. However, existing methods often struggle from poor robustness to unknown false human preferences. In this work, we propose a robust and efficient reward alignment method based on a novel and geometrically interpretable perspective: hypothesis space batched cutting. Our method iteratively refines the reward hypothesis space through "cuts" based on batches of human preferences. Within each batch, human preferences, queried based on disagreement, are grouped using a voting function to determine the appropriate cut, ensuring a bounded human query complexity. To handle unknown erroneous preferences, we introduce a conservative cutting method within each batch, preventing erroneous human preferences from making overly aggressive cuts to the hypothesis space. This guarantees provable robustness against false preferences. We evaluate our method in a model predictive control setting across diverse tasks, including DM-Control, dexterous in-hand manipulation, and locomotion. The results demonstrate that our framework achieves comparable or superior performance to state-of-the-art methods in error-free settings while significantly outperforming existing method when handling high percentage of erroneous human preferences.
Language-Model-Assisted Bi-Level Programming for Reward Learning from Internet Videos
Oct 11, 2024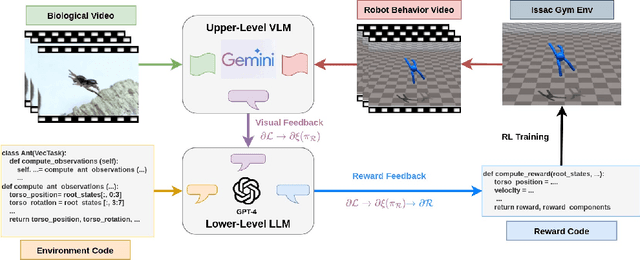



Abstract:Learning from Demonstrations, particularly from biological experts like humans and animals, often encounters significant data acquisition challenges. While recent approaches leverage internet videos for learning, they require complex, task-specific pipelines to extract and retarget motion data for the agent. In this work, we introduce a language-model-assisted bi-level programming framework that enables a reinforcement learning agent to directly learn its reward from internet videos, bypassing dedicated data preparation. The framework includes two levels: an upper level where a vision-language model (VLM) provides feedback by comparing the learner's behavior with expert videos, and a lower level where a large language model (LLM) translates this feedback into reward updates. The VLM and LLM collaborate within this bi-level framework, using a "chain rule" approach to derive a valid search direction for reward learning. We validate the method for reward learning from YouTube videos, and the results have shown that the proposed method enables efficient reward design from expert videos of biological agents for complex behavior synthesis.
Safe MPC Alignment with Human Directional Feedback
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:In safety-critical robot planning or control, manually specifying safety constraints or learning them from demonstrations can be challenging. In this paper, we propose a certifiable alignment method for a robot to learn a safety constraint in its model predictive control (MPC) policy with human online directional feedback. To our knowledge, it is the first method to learn safety constraints from human feedback. The proposed method is based on an empirical observation: human directional feedback, when available, tends to guide the robot toward safer regions. The method only requires the direction of human feedback to update the learning hypothesis space. It is certifiable, providing an upper bound on the total number of human feedback in the case of successful learning of safety constraints, or declaring the misspecification of the hypothesis space, i.e., the true implicit safety constraint cannot be found within the specified hypothesis space. We evaluated the proposed method using numerical examples and user studies in two developed simulation games. Additionally, we implemented and tested the proposed method on a real-world Franka robot arm performing mobile water-pouring tasks in a user study. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate the efficacy and efficiency of our method, showing that it enables a robot to successfully learn safety constraints with a small handful (tens) of human directional corrections.
DialogXL: All-in-One XLNet for Multi-Party Conversation Emotion Recognition
Dec 16, 2020
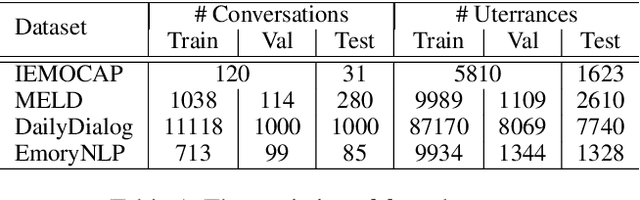

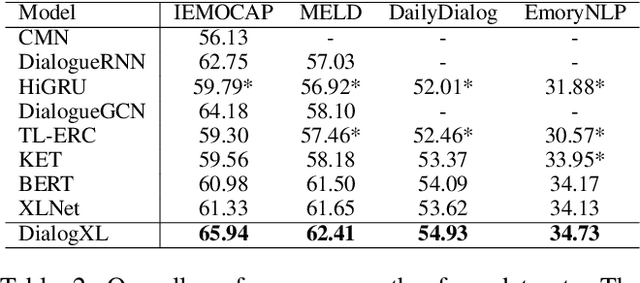
Abstract:This paper presents our pioneering effort for emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) with pre-trained language models. Unlike regular documents, conversational utterances appear alternately from different parties and are usually organized as hierarchical structures in previous work. Such structures are not conducive to the application of pre-trained language models such as XLNet. To address this issue, we propose an all-in-one XLNet model, namely DialogXL, with enhanced memory to store longer historical context and dialog-aware self-attention to deal with the multi-party structures. Specifically, we first modify the recurrence mechanism of XLNet from segment-level to utterance-level in order to better model the conversational data. Second, we introduce dialog-aware self-attention in replacement of the vanilla self-attention in XLNet to capture useful intra- and inter-speaker dependencies. Extensive experiments are conducted on four ERC benchmarks with mainstream models presented for comparison. The experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms the baselines on all the datasets. Several other experiments such as ablation study and error analysis are also conducted and the results confirm the role of the critical modules of DialogXL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge