Zhihua Tian
Sparse Autoencoder as a Zero-Shot Classifier for Concept Erasing in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in generating high-quality images but also raise people's concerns about generating harmful or misleading content. While extensive approaches have been proposed to erase unwanted concepts without requiring retraining from scratch, they inadvertently degrade performance on normal generation tasks. In this work, we propose Interpret then Deactivate (ItD), a novel framework to enable precise concept removal in T2I diffusion models while preserving overall performance. ItD first employs a sparse autoencoder (SAE) to interpret each concept as a combination of multiple features. By permanently deactivating the specific features associated with target concepts, we repurpose SAE as a zero-shot classifier that identifies whether the input prompt includes target concepts, allowing selective concept erasure in diffusion models. Moreover, we demonstrate that ItD can be easily extended to erase multiple concepts without requiring further training. Comprehensive experiments across celebrity identities, artistic styles, and explicit content demonstrate ItD's effectiveness in eliminating targeted concepts without interfering with normal concept generation. Additionally, ItD is also robust against adversarial prompts designed to circumvent content filters. Code is available at: https://github.com/NANSirun/Interpret-then-deactivate.
Towards Collaborative Anti-Money Laundering Among Financial Institutions
Feb 27, 2025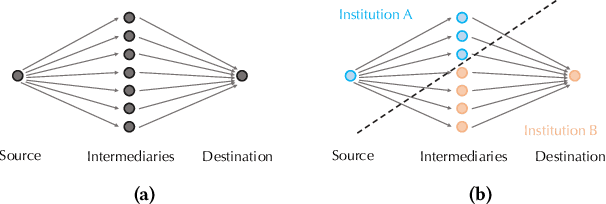
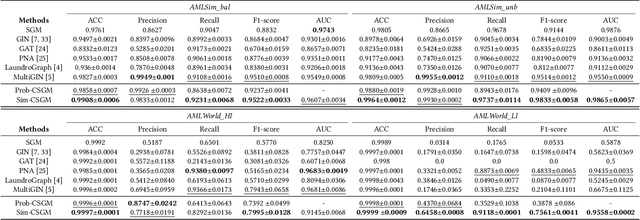
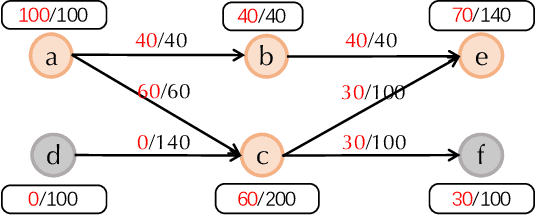
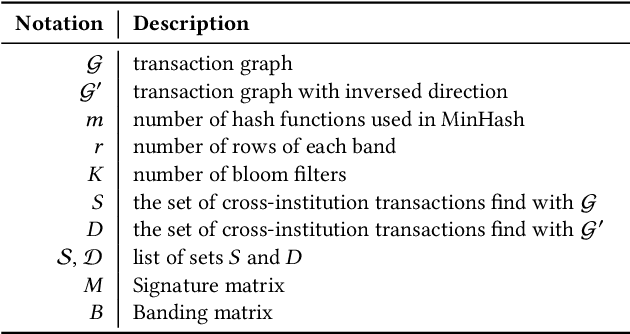
Abstract:Money laundering is the process that intends to legalize the income derived from illicit activities, thus facilitating their entry into the monetary flow of the economy without jeopardizing their source. It is crucial to identify such activities accurately and reliably in order to enforce anti-money laundering (AML). Despite considerable efforts to AML, a large number of such activities still go undetected. Rule-based methods were first introduced and are still widely used in current detection systems. With the rise of machine learning, graph-based learning methods have gained prominence in detecting illicit accounts through the analysis of money transfer graphs. Nevertheless, these methods generally assume that the transaction graph is centralized, whereas in practice, money laundering activities usually span multiple financial institutions. Due to regulatory, legal, commercial, and customer privacy concerns, institutions tend not to share data, restricting their utility in practical usage. In this paper, we propose the first algorithm that supports performing AML over multiple institutions while protecting the security and privacy of local data. To evaluate, we construct Alipay-ECB, a real-world dataset comprising digital transactions from Alipay, the world's largest mobile payment platform, alongside transactions from E-Commerce Bank (ECB). The dataset includes over 200 million accounts and 300 million transactions, covering both intra-institution transactions and those between Alipay and ECB. This makes it the largest real-world transaction graph available for analysis. The experimental results demonstrate that our methods can effectively identify cross-institution money laundering subgroups. Additionally, experiments on synthetic datasets also demonstrate that our method is efficient, requiring only a few minutes on datasets with millions of transactions.
Attributed Graph Clustering in Collaborative Settings
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:Graph clustering is an unsupervised machine learning method that partitions the nodes in a graph into different groups. Despite achieving significant progress in exploiting both attributed and structured data information, graph clustering methods often face practical challenges related to data isolation. Moreover, the absence of collaborative methods for graph clustering limits their effectiveness. In this paper, we propose a collaborative graph clustering framework for attributed graphs, supporting attributed graph clustering over vertically partitioned data with different participants holding distinct features of the same data. Our method leverages a novel technique that reduces the sample space, improving the efficiency of the attributed graph clustering method. Furthermore, we compare our method to its centralized counterpart under a proximity condition, demonstrating that the successful local results of each participant contribute to the overall success of the collaboration. We fully implement our approach and evaluate its utility and efficiency by conducting experiments on four public datasets. The results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable accuracy levels to centralized attributed graph clustering methods. Our collaborative graph clustering framework provides an efficient and effective solution for graph clustering challenges related to data isolation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge