Zhigang Zhao
A Supervised Information Enhanced Multi-Granularity Contrastive Learning Framework for EEG Based Emotion Recognition
May 12, 2024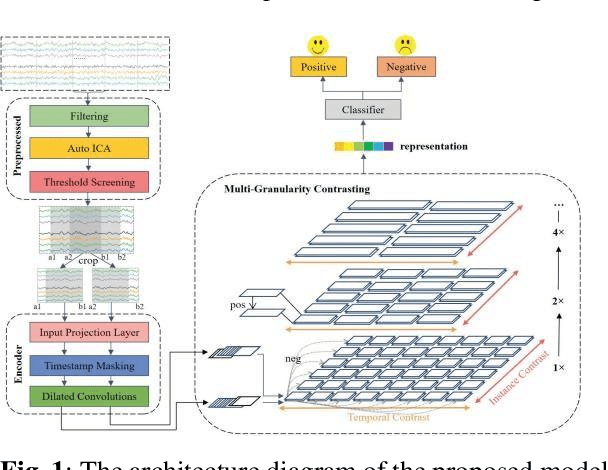
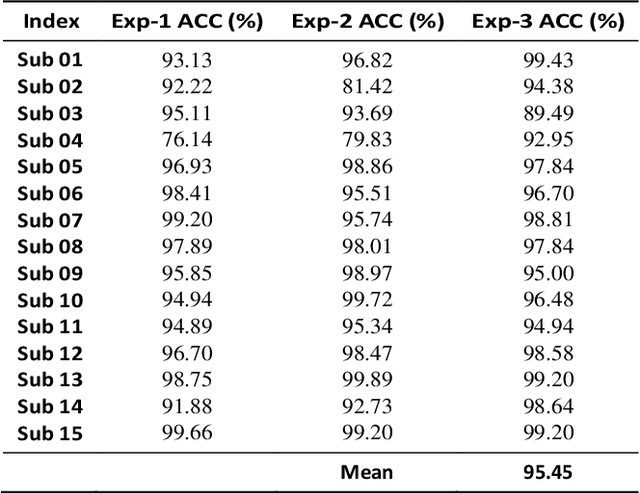
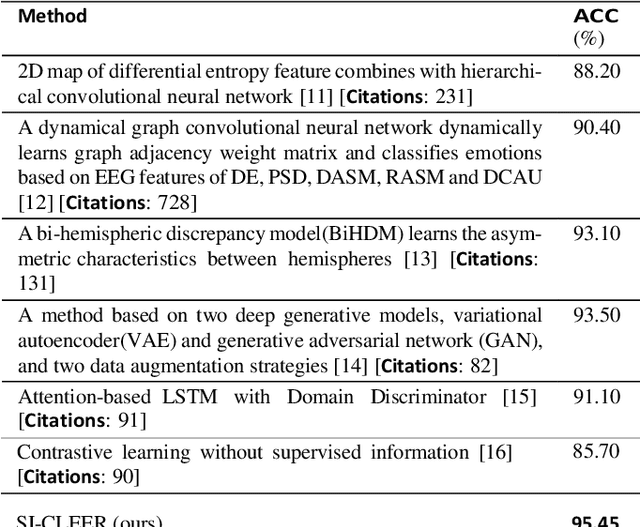
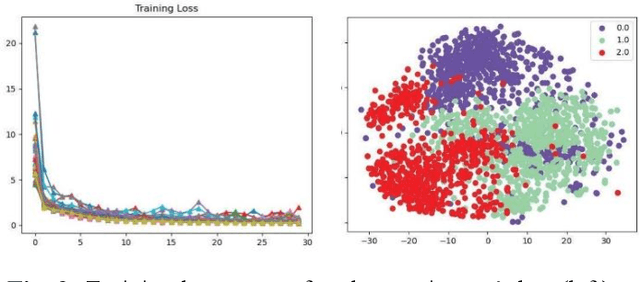
Abstract:This study introduces a novel Supervised Info-enhanced Contrastive Learning framework for EEG based Emotion Recognition (SICLEER). SI-CLEER employs multi-granularity contrastive learning to create robust EEG contextual representations, potentiallyn improving emotion recognition effectiveness. Unlike existing methods solely guided by classification loss, we propose a joint learning model combining self-supervised contrastive learning loss and supervised classification loss. This model optimizes both loss functions, capturing subtle EEG signal differences specific to emotion detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate SI-CLEER's robustness and superior accuracy on the SEED dataset compared to state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, we analyze electrode performance, highlighting the significance of central frontal and temporal brain region EEGs in emotion detection. This study offers an universally applicable approach with potential benefits for diverse EEG classification tasks.
HDDGAN: A Heterogeneous Dual-Discriminator Generative Adversarial Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Apr 24, 2024

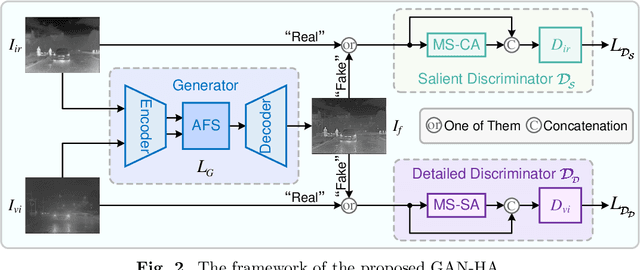

Abstract:Infrared and visible image fusion (IVIF) aims to preserve thermal radiation information from infrared images while integrating texture details from visible images, enabling the capture of important features and hidden details of subjects in complex scenes and disturbed environments. Consequently, IVIF offers distinct advantages in practical applications such as video surveillance, night navigation, and target recognition. However, prevailing methods often face challenges in simultaneously capturing thermal region features and detailed information due to the disparate characteristics of infrared and visible images. Consequently, fusion outcomes frequently entail a compromise between thermal target area information and texture details. In this study, we introduce a novel heterogeneous dual-discriminator generative adversarial network (HDDGAN) to address this issue. Specifically, the generator is structured as a multi-scale skip-connected structure, facilitating the extraction of essential features from different source images. To enhance the information representation ability of the fusion result, an attention mechanism is employed to construct the information fusion layer within the generator, leveraging the disparities between the source images. Moreover, recognizing the distinct learning requirements of information in infrared and visible images, we design two discriminators with differing structures. This approach aims to guide the model to learn salient information from infrared images while simultaneously capturing detailed information from visible images. Extensive experiments conducted on various public datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed HDDGAN over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) algorithms, highlighting its enhanced potential for practical applications.
EEG based Emotion Recognition: A Tutorial and Review
Mar 16, 2022



Abstract:Emotion recognition technology through analyzing the EEG signal is currently an essential concept in Artificial Intelligence and holds great potential in emotional health care, human-computer interaction, multimedia content recommendation, etc. Though there have been several works devoted to reviewing EEG-based emotion recognition, the content of these reviews needs to be updated. In addition, those works are either fragmented in content or only focus on specific techniques adopted in this area but neglect the holistic perspective of the entire technical routes. Hence, in this paper, we review from the perspective of researchers who try to take the first step on this topic. We review the recent representative works in the EEG-based emotion recognition research and provide a tutorial to guide the researchers to start from the beginning. The scientific basis of EEG-based emotion recognition in the psychological and physiological levels is introduced. Further, we categorize these reviewed works into different technical routes and illustrate the theoretical basis and the research motivation, which will help the readers better understand why those techniques are studied and employed. At last, existing challenges and future investigations are also discussed in this paper, which guides the researchers to decide potential future research directions.
Fast LLMMSE filter for low-dose CT imaging
Mar 23, 2019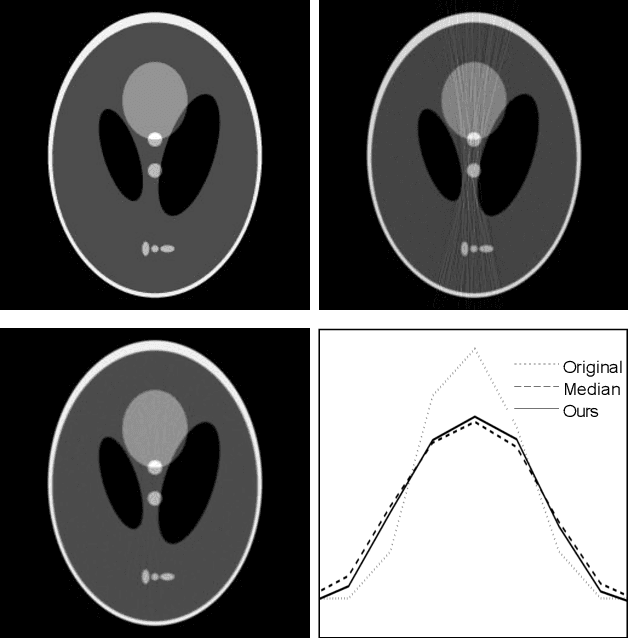
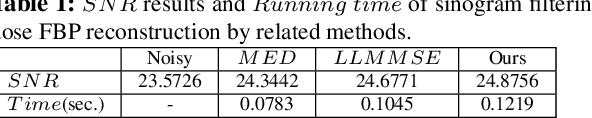
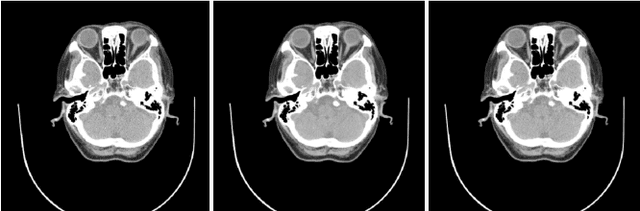
Abstract:Low-dose X-ray CT technology is one of important directions of current research and development of medical imaging equipment. A fast algorithm of blockwise sinogram filtering is presented for realtime low-dose CT imaging. A nonstationary Gaussian noise model of low-dose sinogram data is proposed in the low-mA (tube current) CT protocol. Then, according to the linear minimum mean square error principle, an adaptive blockwise algorithm is built to filter contaminated sinogram data caused by photon starvation. A moving sum technique is used to speed the algorithm into a linear time one, regardless of the block size and thedata range. The proposedfast filtering givesa better performance in noise reduction and detail preservation in the reconstructed images,which is verified in experiments on simulated and real data compared with some related filtering methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge