Zhida Feng
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
ERNIE-ViLG 2.0: Improving Text-to-Image Diffusion Model with Knowledge-Enhanced Mixture-of-Denoising-Experts
Oct 27, 2022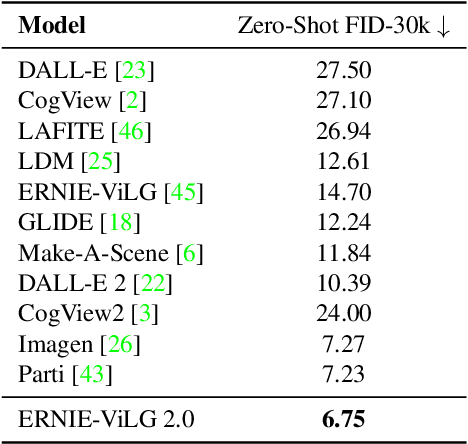
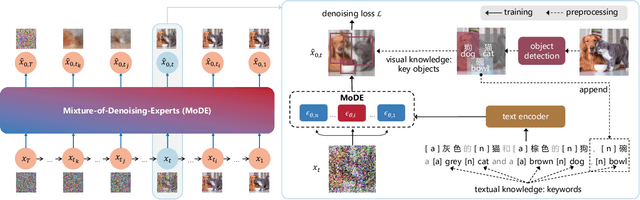
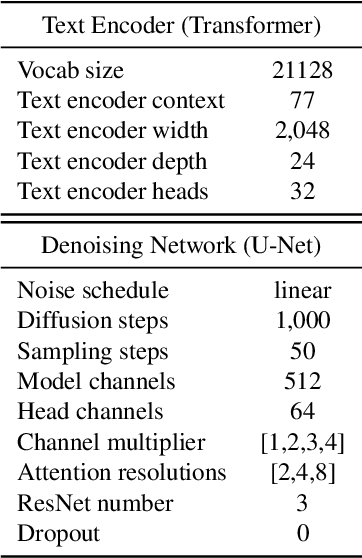
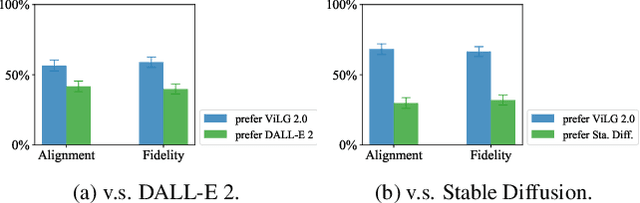
Abstract:Recent progress in diffusion models has revolutionized the popular technology of text-to-image generation. While existing approaches could produce photorealistic high-resolution images with text conditions, there are still several open problems to be solved, which limits the further improvement of image fidelity and text relevancy. In this paper, we propose ERNIE-ViLG 2.0, a large-scale Chinese text-to-image diffusion model, which progressively upgrades the quality of generated images~by: (1) incorporating fine-grained textual and visual knowledge of key elements in the scene, and (2) utilizing different denoising experts at different denoising stages. With the proposed mechanisms, ERNIE-ViLG 2.0 not only achieves the state-of-the-art on MS-COCO with zero-shot FID score of 6.75, but also significantly outperforms recent models in terms of image fidelity and image-text alignment, with side-by-side human evaluation on the bilingual prompt set ViLG-300.
ERNIE-SPARSE: Learning Hierarchical Efficient Transformer Through Regularized Self-Attention
Mar 23, 2022



Abstract:Sparse Transformer has recently attracted a lot of attention since the ability for reducing the quadratic dependency on the sequence length. We argue that two factors, information bottleneck sensitivity and inconsistency between different attention topologies, could affect the performance of the Sparse Transformer. This paper proposes a well-designed model named ERNIE-Sparse. It consists of two distinctive parts: (i) Hierarchical Sparse Transformer (HST) to sequentially unify local and global information. (ii) Self-Attention Regularization (SAR) method, a novel regularization designed to minimize the distance for transformers with different attention topologies. To evaluate the effectiveness of ERNIE-Sparse, we perform extensive evaluations. Firstly, we perform experiments on a multi-modal long sequence modeling task benchmark, Long Range Arena (LRA). Experimental results demonstrate that ERNIE-Sparse significantly outperforms a variety of strong baseline methods including the dense attention and other efficient sparse attention methods and achieves improvements by 2.77% (57.78% vs. 55.01%). Secondly, to further show the effectiveness of our method, we pretrain ERNIE-Sparse and verified it on 3 text classification and 2 QA downstream tasks, achieve improvements on classification benchmark by 0.83% (92.46% vs. 91.63%), on QA benchmark by 3.24% (74.67% vs. 71.43%). Experimental results continue to demonstrate its superior performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge