Zhicheng Zhou
Data Trajectory Alignment for LLM Domain Adaptation: A Two-Phase Synthesis Framework for Telecommunications Mathematics
Nov 10, 2025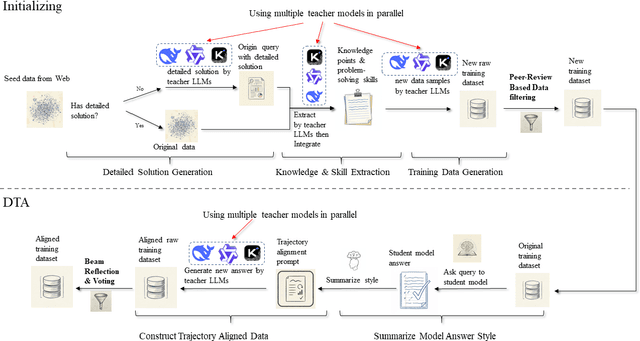


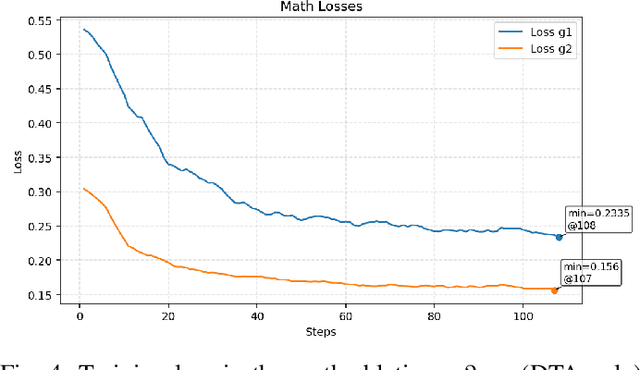
Abstract:General-purpose large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in verticals such as telecommunications, where adaptation is hindered by scarce, low-information-density corpora and tight mobile/edge constraints. We propose Data Trajectory Alignment (DTA), a two-phase, model-agnostic data curation framework that treats solution processes - not only final answers - as first-class supervision. Phase I (Initializing) synthesizes diverse, high-coverage candidates using an ensemble of strong teachers. Phase II (DTA) rewrites teacher solutions to align intermediate steps and presentation style with the target student's inductive biases and then performs signal-aware exemplar selection via agreement checks and reflection-based judging. Instantiated on telecommunications mathematics (e.g., link budgets, SNR/AMC selection, and power-control feasibility), DTA yields state-of-the-art (SOTA) accuracy on TELEMATH without enabling explicit "thinking" modes: 72.45% pass@1, surpassing distilled-only training by +17.65 points and outperforming a strong baseline (Qwen3-32B with thinking enabled) by +2.94 points. Token-shift analyses indicate that DTA concentrates gains on logical-structural discourse markers rather than merely amplifying domain nouns, indicating improved reasoning scaffolding. Under edge-like inference settings, DTA improves efficiency by reducing reliance on multi-sample voting and disabling expensive reasoning heuristics, cutting energy per output token by ~42% versus Qwen3-32B (thinking mode enabled) and end-to-end latency by ~60% versus Qwen3-32B (thinking mode disabled). These results demonstrate that aligning how solutions are produced enables compact, high-yield supervision that is effective for both accuracy and efficiency, offering a practical recipe for domain adaptation in low-resource verticals beyond telecom.
A Novel Optimized Asynchronous Federated Learning Framework
Nov 18, 2021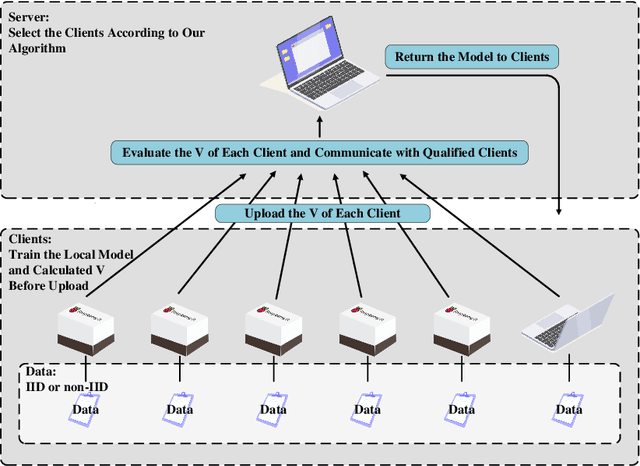
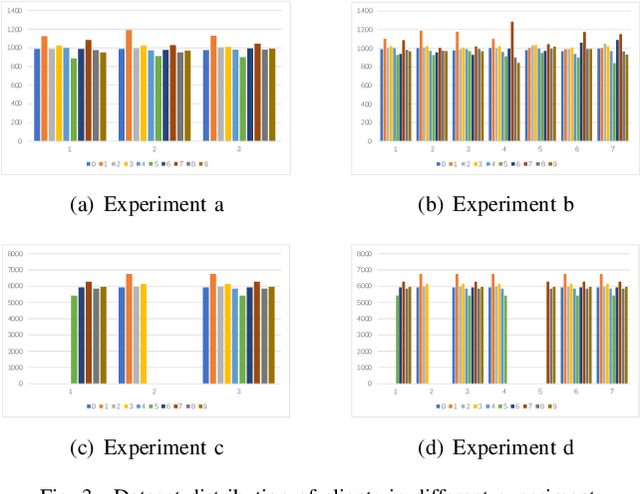
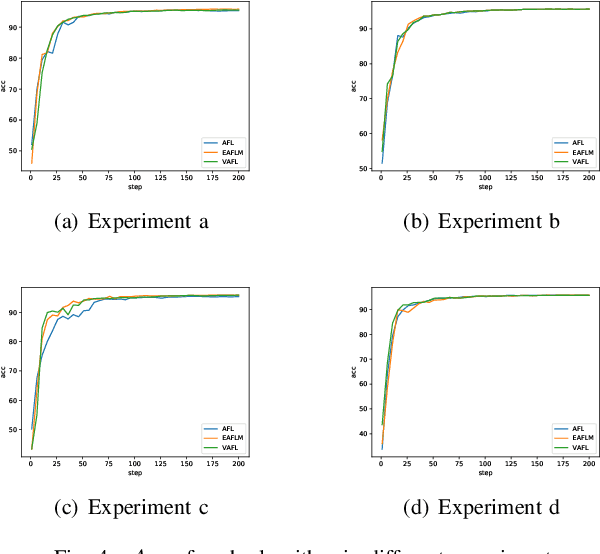
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) since proposed has been applied in many fields, such as credit assessment, medical, etc. Because of the difference in the network or computing resource, the clients may not update their gradients at the same time that may take a lot of time to wait or idle. That's why Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) method is needed. The main bottleneck in AFL is communication. How to find a balance between the model performance and the communication cost is a challenge in AFL. This paper proposed a novel AFL framework VAFL. And we verified the performance of the algorithm through sufficient experiments. The experiments show that VAFL can reduce the communication times about 51.02\% with 48.23\% average communication compression rate and allow the model to be converged faster. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/RobAI-Lab/VAFL}
NDT-Transformer: Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Localisation using the Normal Distribution Transform Representation
Mar 23, 2021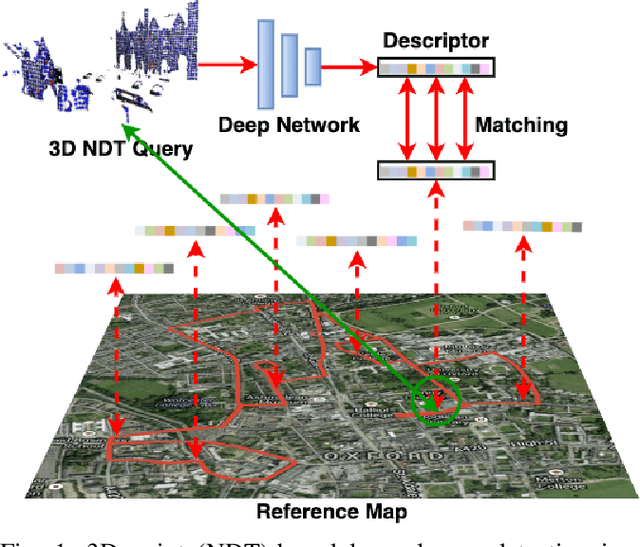
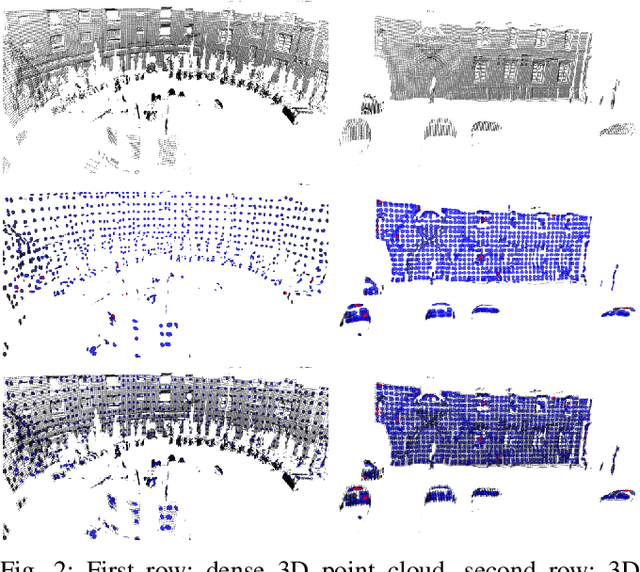
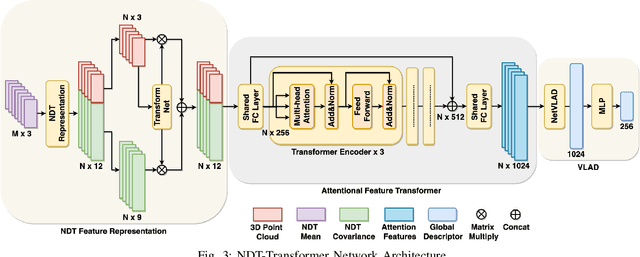
Abstract:3D point cloud-based place recognition is highly demanded by autonomous driving in GPS-challenged environments and serves as an essential component (i.e. loop-closure detection) in lidar-based SLAM systems. This paper proposes a novel approach, named NDT-Transformer, for realtime and large-scale place recognition using 3D point clouds. Specifically, a 3D Normal Distribution Transform (NDT) representation is employed to condense the raw, dense 3D point cloud as probabilistic distributions (NDT cells) to provide the geometrical shape description. Then a novel NDT-Transformer network learns a global descriptor from a set of 3D NDT cell representations. Benefiting from the NDT representation and NDT-Transformer network, the learned global descriptors are enriched with both geometrical and contextual information. Finally, descriptor retrieval is achieved using a query-database for place recognition. Compared to the state-of-the-art methods, the proposed approach achieves an improvement of 7.52% on average top 1 recall and 2.73% on average top 1% recall on the Oxford Robotcar benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge