Zhibo Qu
Meta-Policy Reflexion: Reusable Reflective Memory and Rule Admissibility for Resource-Efficient LLM Agent
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM) agents achieve impressive single-task performance but commonly exhibit repeated failures, inefficient exploration, and limited cross-task adaptability. Existing reflective strategies (e.g., Reflexion, ReAct) improve per-episode behavior but typically produce ephemeral, task-specific traces that are not reused across tasks. Reinforcement-learning based alternatives can produce transferable policies but require substantial parameter updates and compute. In this work we introduce Meta-Policy Reflexion (MPR): a hybrid framework that consolidates LLM-generated reflections into a structured, predicate-like Meta-Policy Memory (MPM) and applies that memory at inference time through two complementary mechanisms soft memory-guided decoding and hard rule admissibility checks(HAC). MPR (i) externalizes reusable corrective knowledge without model weight updates, (ii) enforces domain constraints to reduce unsafe or invalid actions, and (iii) retains the adaptability of language-based reflection. We formalize the MPM representation, present algorithms for update and decoding, and validate the approach in a text-based agent environment following the experimental protocol described in the provided implementation (AlfWorld-based). Empirical results reported in the supplied material indicate consistent gains in execution accuracy and robustness when compared to Reflexion baselines; rule admissibility further improves stability. We analyze mechanisms that explain these gains, discuss scalability and failure modes, and outline future directions for multimodal and multi?agent extensions.
Reflection-Enhanced Meta-Optimization Integrating TextGrad-style Prompt Optimization with Memory-Driven Self-Evolution
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in prompt optimization, exemplified by methods such as TextGrad, enable automatic, gradient-like refinement of textual prompts to enhance the performance of large language models (LLMs) on specific downstream tasks. However, current approaches are typically stateless and operate independently across optimization runs, lacking mechanisms to preserve and leverage historical optimization experience. Furthermore, they are susceptible to overfitting, often yielding prompt updates that generalize poorly beyond the immediate task context. To address these limitations, we propose Reflection-Enhanced Meta-Optimization (REMO), a novel framework that integrates (1) a memory-augmented Reflection Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) module - structured as a "mistake notebook" and (2) a Self-Adaptive Optimizer, implemented via an LLM-driven meta-controller that synthesizes epoch-level reflective insights to iteratively improve system-level prompting strategies. This architecture enables not only local, fine-grained prompt tuning akin to TextGrad, but also the systematic accumulation and reuse of cross-run optimization knowledge, thereby supporting continual improvement over time. We instantiate the REMO framework using Qwen3-32B in standard inference mode - without explicit chain-of-thought prompting - and evaluate its efficacy on the GSM8K benchmark for mathematical reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to a TextGrad baseline, REMO achieves more stable and robust generalization, albeit at the cost of increased computational overhead. We provide a detailed exposition of the algorithmic design, conduct a qualitative and quantitative analysis of optimization dynamics, and present a comprehensive ablation study to elucidate the contributions of each component.
UAV Cognitive Semantic Communications Enabled by Knowledge Graph for Robust Object Detection
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are widely used for object detection. However, the existing UAV-based object detection systems are subject to severe challenges, namely, their limited computation, energy and communication resources, which limits the achievable detection performance. To overcome these challenges, a UAV cognitive semantic communication system is proposed by exploiting a knowledge graph. Moreover, we design a multi-scale codec for semantic compression to reduce data transmission volume while guaranteeing detection performance. Considering the complexity and dynamicity of UAV communication scenarios, a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) adaptive module with robust channel adaptation capability is introduced. Furthermore, an object detection scheme is proposed by exploiting the knowledge graph to overcome channel noise interference and compression distortion. Simulation results conducted on the practical aerial image dataset demonstrate that our proposed semantic communication system outperforms benchmark systems in terms of detection accuracy, communication robustness, and computation efficiency, especially in dealing with low bandwidth compression ratios and low SNR regimes.
Knowledge Graph Driven UAV Cognitive Semantic Communication Systems for Efficient Object Detection
Jan 25, 2024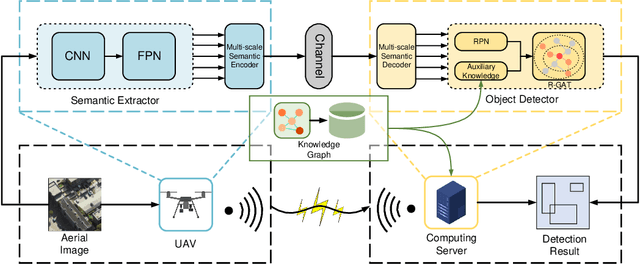
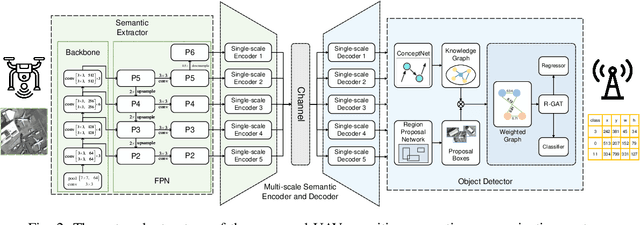
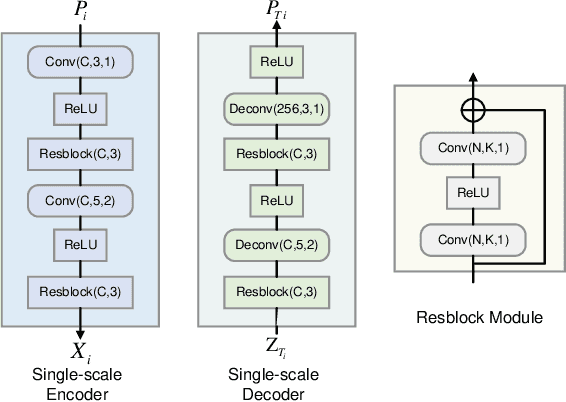
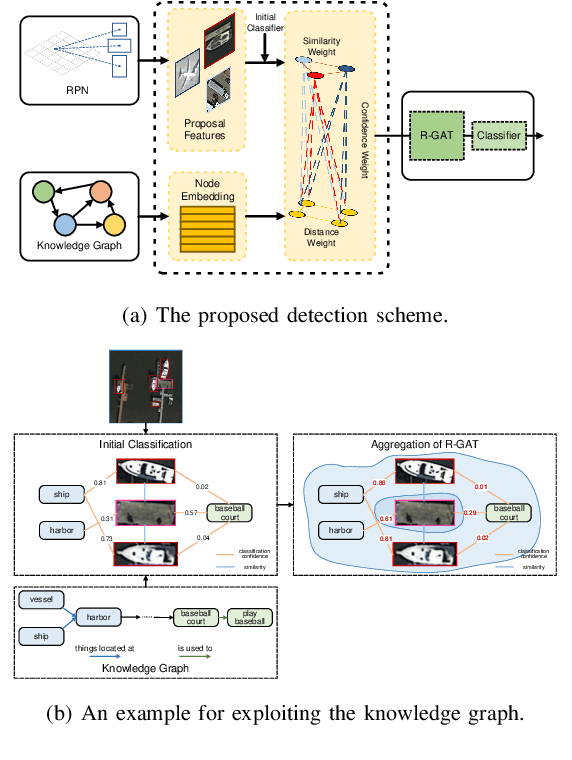
Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are widely used for object detection. However, the existing UAV-based object detection systems are subject to the serious challenge, namely, the finite computation, energy and communication resources, which limits the achievable detection performance. In order to overcome this challenge, a UAV cognitive semantic communication system is proposed by exploiting knowledge graph. Moreover, a multi-scale compression network is designed for semantic compression to reduce data transmission volume while guaranteeing the detection performance. Furthermore, an object detection scheme is proposed by using the knowledge graph to overcome channel noise interference and compression distortion. Simulation results conducted on the practical aerial image dataset demonstrate that compared to the benchmark systems, our proposed system has superior detection accuracy, communication robustness and computation efficiency even under high compression rates and low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge