Zhenqi Zhao
The WMDP Benchmark: Measuring and Reducing Malicious Use With Unlearning
Mar 06, 2024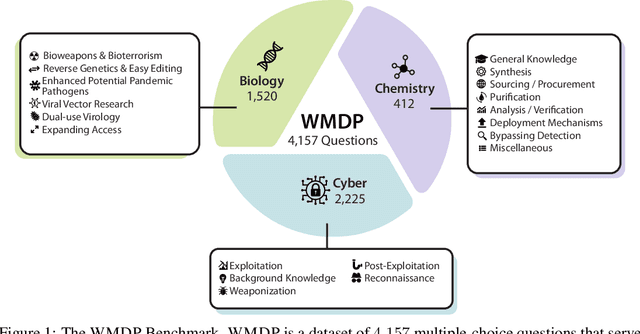
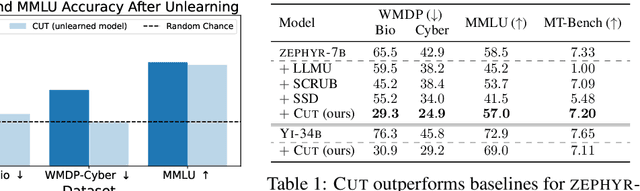
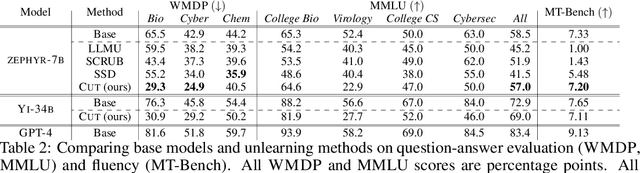
Abstract:The White House Executive Order on Artificial Intelligence highlights the risks of large language models (LLMs) empowering malicious actors in developing biological, cyber, and chemical weapons. To measure these risks of malicious use, government institutions and major AI labs are developing evaluations for hazardous capabilities in LLMs. However, current evaluations are private, preventing further research into mitigating risk. Furthermore, they focus on only a few, highly specific pathways for malicious use. To fill these gaps, we publicly release the Weapons of Mass Destruction Proxy (WMDP) benchmark, a dataset of 4,157 multiple-choice questions that serve as a proxy measurement of hazardous knowledge in biosecurity, cybersecurity, and chemical security. WMDP was developed by a consortium of academics and technical consultants, and was stringently filtered to eliminate sensitive information prior to public release. WMDP serves two roles: first, as an evaluation for hazardous knowledge in LLMs, and second, as a benchmark for unlearning methods to remove such hazardous knowledge. To guide progress on unlearning, we develop CUT, a state-of-the-art unlearning method based on controlling model representations. CUT reduces model performance on WMDP while maintaining general capabilities in areas such as biology and computer science, suggesting that unlearning may be a concrete path towards reducing malicious use from LLMs. We release our benchmark and code publicly at https://wmdp.ai
MP2: A Momentum Contrast Approach for Recommendation with Pointwise and Pairwise Learning
Apr 18, 2022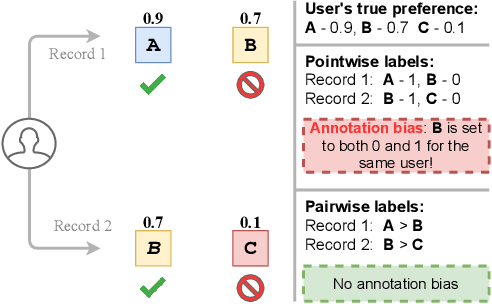
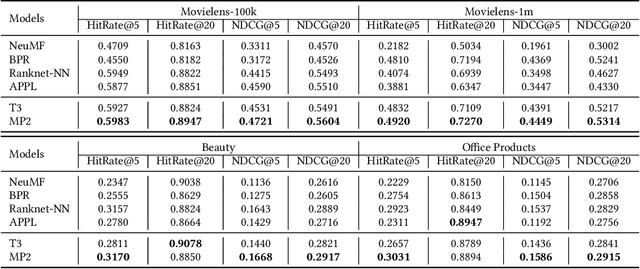
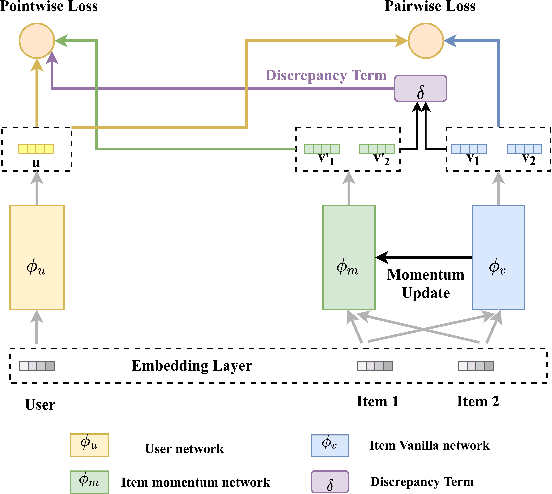
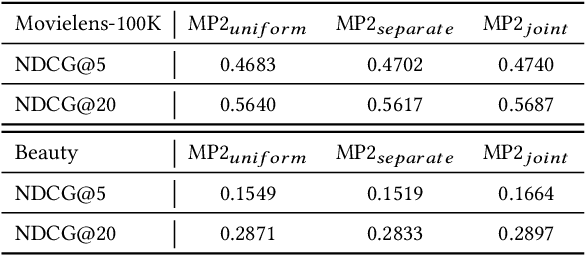
Abstract:Binary pointwise labels (aka implicit feedback) are heavily leveraged by deep learning based recommendation algorithms nowadays. In this paper we discuss the limited expressiveness of these labels may fail to accommodate varying degrees of user preference, and thus lead to conflicts during model training, which we call annotation bias. To solve this issue, we find the soft-labeling property of pairwise labels could be utilized to alleviate the bias of pointwise labels. To this end, we propose a momentum contrast framework (MP2) that combines pointwise and pairwise learning for recommendation. MP2 has a three-tower network structure: one user network and two item networks. The two item networks are used for computing pointwise and pairwise loss respectively. To alleviate the influence of the annotation bias, we perform a momentum update to ensure a consistent item representation. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method against state-of-the-art recommendation algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge