Zhaohui Liang
Robustness and Resilience Evaluation of Eco-Driving Strategies at Signalized Intersections
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Eco-driving strategies have demonstrated substantial potential for improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions, especially at signalized intersections. However, evaluations of eco-driving methods typically rely on simplified simulation or experimental conditions, where certain assumptions are made to manage complexity and experimental control. This study introduces a unified framework to evaluate eco-driving strategies through the lens of two complementary criteria: control robustness and environmental resilience. We define formal indicators that quantify performance degradation caused by internal execution variability and external environmental disturbances, respectively. These indicators are then applied to assess multiple eco-driving controllers through real-world vehicle experiments. The results reveal key tradeoffs between tracking accuracy and adaptability, showing that optimization-based controllers offer more consistent performance across varying disturbance levels, while analytical controllers may perform comparably under nominal conditions but exhibit greater sensitivity to execution and timing variability.
CATS-V2V: A Real-World Vehicle-to-Vehicle Cooperative Perception Dataset with Complex Adverse Traffic Scenarios
Nov 14, 2025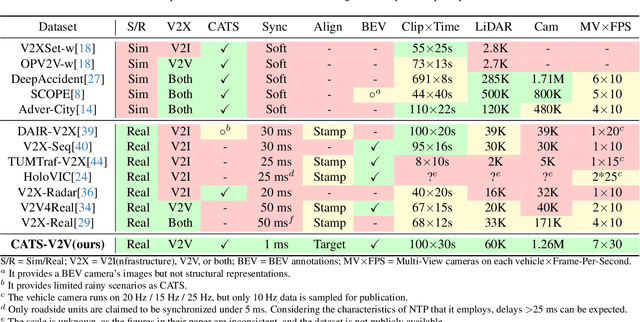

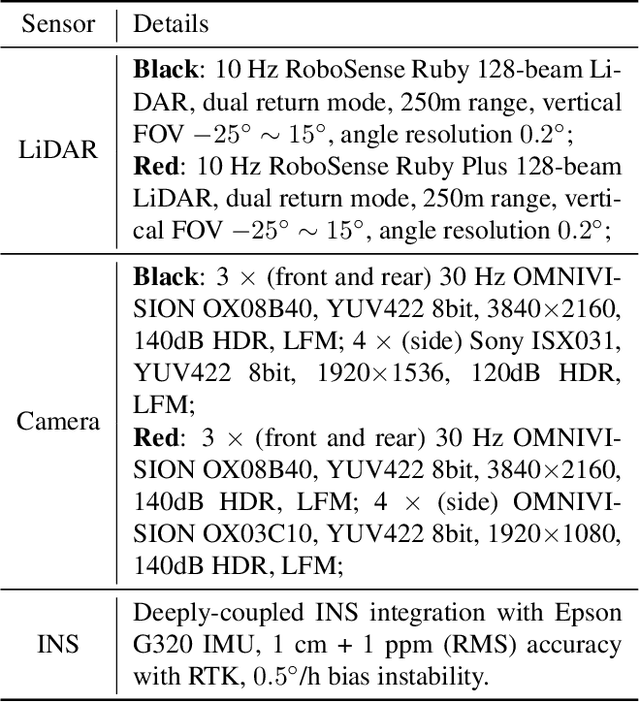
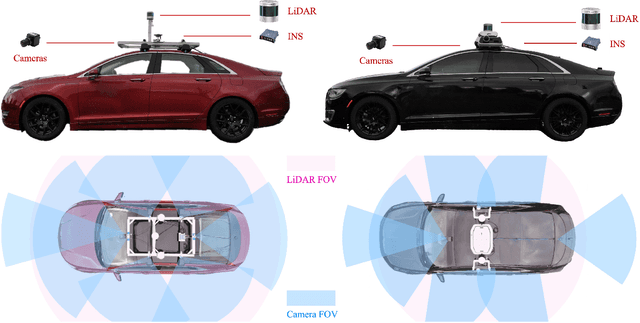
Abstract:Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) cooperative perception has great potential to enhance autonomous driving performance by overcoming perception limitations in complex adverse traffic scenarios (CATS). Meanwhile, data serves as the fundamental infrastructure for modern autonomous driving AI. However, due to stringent data collection requirements, existing datasets focus primarily on ordinary traffic scenarios, constraining the benefits of cooperative perception. To address this challenge, we introduce CATS-V2V, the first-of-its-kind real-world dataset for V2V cooperative perception under complex adverse traffic scenarios. The dataset was collected by two hardware time-synchronized vehicles, covering 10 weather and lighting conditions across 10 diverse locations. The 100-clip dataset includes 60K frames of 10 Hz LiDAR point clouds and 1.26M multi-view 30 Hz camera images, along with 750K anonymized yet high-precision RTK-fixed GNSS and IMU records. Correspondingly, we provide time-consistent 3D bounding box annotations for objects, as well as static scenes to construct a 4D BEV representation. On this basis, we propose a target-based temporal alignment method, ensuring that all objects are precisely aligned across all sensor modalities. We hope that CATS-V2V, the largest-scale, most supportive, and highest-quality dataset of its kind to date, will benefit the autonomous driving community in related tasks.
An Advanced Microscopic Energy Consumption Model for Automated Vehicle:Development, Calibration, Verification
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:The automated vehicle (AV) equipped with the Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is expected to reduce the fuel consumption for the intelligent transportation system. This paper presents the Advanced ACC-Micro (AA-Micro) model, a new energy consumption model based on micro trajectory data, calibrated and verified by empirical data. Utilizing a commercial AV equipped with the ACC system as the test platform, experiments were conducted at the Columbus 151 Speedway, capturing data from multiple ACC and Human-Driven (HV) test runs. The calibrated AA-Micro model integrates features from traditional energy consumption models and demonstrates superior goodness of fit, achieving an impressive 90% accuracy in predicting ACC system energy consumption without overfitting. A comprehensive statistical evaluation of the AA-Micro model's applicability and adaptability in predicting energy consumption and vehicle trajectories indicated strong model consistency and reliability for ACC vehicles, evidenced by minimal variance in RMSE values and uniform RSS distributions. Conversely, significant discrepancies were observed when applying the model to HV data, underscoring the necessity for specialized models to accurately predict energy consumption for HV and ACC systems, potentially due to their distinct energy consumption characteristics.
Uncovering the effects of model initialization on deep model generalization: A study with adult and pediatric Chest X-ray images
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Model initialization techniques are vital for improving the performance and reliability of deep learning models in medical computer vision applications. While much literature exists on non-medical images, the impacts on medical images, particularly chest X-rays (CXRs) are less understood. Addressing this gap, our study explores three deep model initialization techniques: Cold-start, Warm-start, and Shrink and Perturb start, focusing on adult and pediatric populations. We specifically focus on scenarios with periodically arriving data for training, thereby embracing the real-world scenarios of ongoing data influx and the need for model updates. We evaluate these models for generalizability against external adult and pediatric CXR datasets. We also propose novel ensemble methods: F-score-weighted Sequential Least-Squares Quadratic Programming (F-SLSQP) and Attention-Guided Ensembles with Learnable Fuzzy Softmax to aggregate weight parameters from multiple models to capitalize on their collective knowledge and complementary representations. We perform statistical significance tests with 95% confidence intervals and p-values to analyze model performance. Our evaluations indicate models initialized with ImageNet-pre-trained weights demonstrate superior generalizability over randomly initialized counterparts, contradicting some findings for non-medical images. Notably, ImageNet-pretrained models exhibit consistent performance during internal and external testing across different training scenarios. Weight-level ensembles of these models show significantly higher recall (p<0.05) during testing compared to individual models. Thus, our study accentuates the benefits of ImageNet-pretrained weight initialization, especially when used with weight-level ensembles, for creating robust and generalizable deep learning solutions.
Semantically Redundant Training Data Removal and Deep Model Classification Performance: A Study with Chest X-rays
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has demonstrated its innate capacity to independently learn hierarchical features from complex and multi-dimensional data. A common understanding is that its performance scales up with the amount of training data. Another data attribute is the inherent variety. It follows, therefore, that semantic redundancy, which is the presence of similar or repetitive information, would tend to lower performance and limit generalizability to unseen data. In medical imaging data, semantic redundancy can occur due to the presence of multiple images that have highly similar presentations for the disease of interest. Further, the common use of augmentation methods to generate variety in DL training may be limiting performance when applied to semantically redundant data. We propose an entropy-based sample scoring approach to identify and remove semantically redundant training data. We demonstrate using the publicly available NIH chest X-ray dataset that the model trained on the resulting informative subset of training data significantly outperforms the model trained on the full training set, during both internal (recall: 0.7164 vs 0.6597, p<0.05) and external testing (recall: 0.3185 vs 0.2589, p<0.05). Our findings emphasize the importance of information-oriented training sample selection as opposed to the conventional practice of using all available training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge