Zeyan Liu
IDMap: A Pseudo-Speaker Generator Framework Based on Speaker Identity Index to Vector Mapping
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Facilitated by the speech generation framework that disentangles speech into content, speaker, and prosody, voice anonymization is accomplished by substituting the original speaker embedding vector with that of a pseudo-speaker. In this framework, the pseudo-speaker generation forms a fundamental challenge. Current pseudo-speaker generation methods demonstrate limitations in the uniqueness of pseudo-speakers, consequently restricting their effectiveness in voice privacy protection. Besides, existing model-based methods suffer from heavy computation costs. Especially, in the large-scale scenario where a huge number of pseudo-speakers are generated, the limitations of uniqueness and computational inefficiency become more significant. To this end, this paper proposes a framework for pseudo-speaker generation, which establishes a mapping from speaker identity index to speaker vector in the feedforward architecture, termed IDMap. Specifically, the framework is specified into two models: IDMap-MLP and IDMap-Diff. Experiments were conducted on both small- and large-scale evaluation datasets. Small-scale evaluations on the LibriSpeech dataset validated the effectiveness of the proposed IDMap framework in enhancing the uniqueness of pseudo-speakers, thereby improving voice privacy protection, while at a reduced computational cost. Large-scale evaluations on the MLS and Common Voice datasets further justified the superiority of the IDMap framework regarding the stability of the voice privacy protection capability as the number of pseudo-speakers increased. Audio samples and open-source code can be found in https://github.com/VoicePrivacy/IDMap.
Pinhole Effect on Linkability and Dispersion in Speaker Anonymization
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Speaker anonymization aims to conceal speaker-specific attributes in speech signals, making the anonymized speech unlinkable to the original speaker identity. Recent approaches achieve this by disentangling speech into content and speaker components, replacing the latter with pseudo speakers. The anonymized speech can be mapped either to a common pseudo speaker shared across utterances or to distinct pseudo speakers unique to each utterance. This paper investigates the impact of these mapping strategies on three key dimensions: speaker linkability, dispersion in the anonymized speaker space, and de-identification from the original identity. Our findings show that using distinct pseudo speakers increases speaker dispersion and reduces linkability compared to common pseudo-speaker mapping, thereby enhancing privacy preservation. These observations are interpreted through the proposed pinhole effect, a conceptual framework introduced to explain the relationship between mapping strategies and anonymization performance. The hypothesis is validated through empirical evaluation.
Two Birds with One Stone: Multi-Task Detection and Attribution of LLM-Generated Text
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-4 and Llama, have demonstrated remarkable abilities in generating natural language. However, they also pose security and integrity challenges. Existing countermeasures primarily focus on distinguishing AI-generated content from human-written text, with most solutions tailored for English. Meanwhile, authorship attribution--determining which specific LLM produced a given text--has received comparatively little attention despite its importance in forensic analysis. In this paper, we present DA-MTL, a multi-task learning framework that simultaneously addresses both text detection and authorship attribution. We evaluate DA-MTL on nine datasets and four backbone models, demonstrating its strong performance across multiple languages and LLM sources. Our framework captures each task's unique characteristics and shares insights between them, which boosts performance in both tasks. Additionally, we conduct a thorough analysis of cross-modal and cross-lingual patterns and assess the framework's robustness against adversarial obfuscation techniques. Our findings offer valuable insights into LLM behavior and the generalization of both detection and authorship attribution.
Exploring Audio-Visual Information Fusion for Sound Event Localization and Detection In Low-Resource Realistic Scenarios
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:This study presents an audio-visual information fusion approach to sound event localization and detection (SELD) in low-resource scenarios. We aim at utilizing audio and video modality information through cross-modal learning and multi-modal fusion. First, we propose a cross-modal teacher-student learning (TSL) framework to transfer information from an audio-only teacher model, trained on a rich collection of audio data with multiple data augmentation techniques, to an audio-visual student model trained with only a limited set of multi-modal data. Next, we propose a two-stage audio-visual fusion strategy, consisting of an early feature fusion and a late video-guided decision fusion to exploit synergies between audio and video modalities. Finally, we introduce an innovative video pixel swapping (VPS) technique to extend an audio channel swapping (ACS) method to an audio-visual joint augmentation. Evaluation results on the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) 2023 Challenge data set demonstrate significant improvements in SELD performances. Furthermore, our submission to the SELD task of the DCASE 2023 Challenge ranks first place by effectively integrating the proposed techniques into a model ensemble.
The Adversarial AI-Art: Understanding, Generation, Detection, and Benchmarking
Apr 22, 2024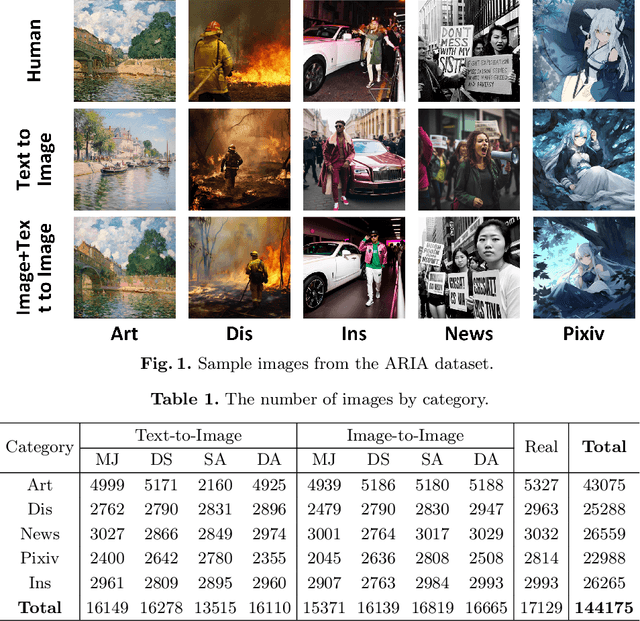
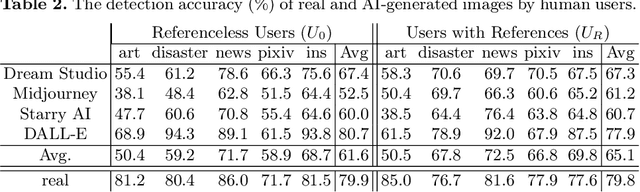
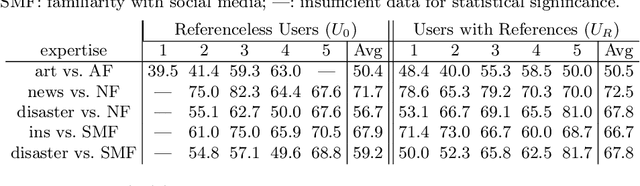
Abstract:Generative AI models can produce high-quality images based on text prompts. The generated images often appear indistinguishable from images generated by conventional optical photography devices or created by human artists (i.e., real images). While the outstanding performance of such generative models is generally well received, security concerns arise. For instance, such image generators could be used to facilitate fraud or scam schemes, generate and spread misinformation, or produce fabricated artworks. In this paper, we present a systematic attempt at understanding and detecting AI-generated images (AI-art) in adversarial scenarios. First, we collect and share a dataset of real images and their corresponding artificial counterparts generated by four popular AI image generators. The dataset, named ARIA, contains over 140K images in five categories: artworks (painting), social media images, news photos, disaster scenes, and anime pictures. This dataset can be used as a foundation to support future research on adversarial AI-art. Next, we present a user study that employs the ARIA dataset to evaluate if real-world users can distinguish with or without reference images. In a benchmarking study, we further evaluate if state-of-the-art open-source and commercial AI image detectors can effectively identify the images in the ARIA dataset. Finally, we present a ResNet-50 classifier and evaluate its accuracy and transferability on the ARIA dataset.
Check Me If You Can: Detecting ChatGPT-Generated Academic Writing using CheckGPT
Jun 07, 2023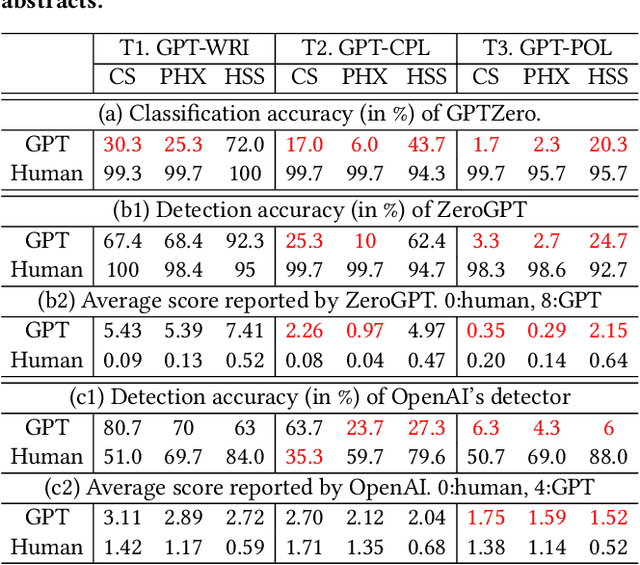

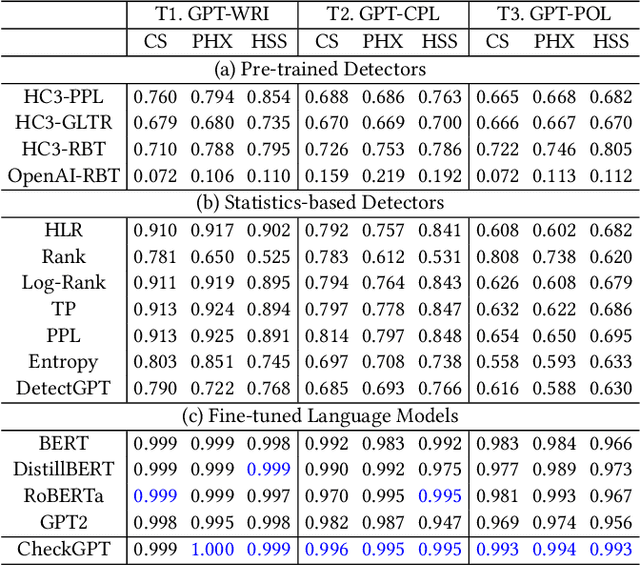
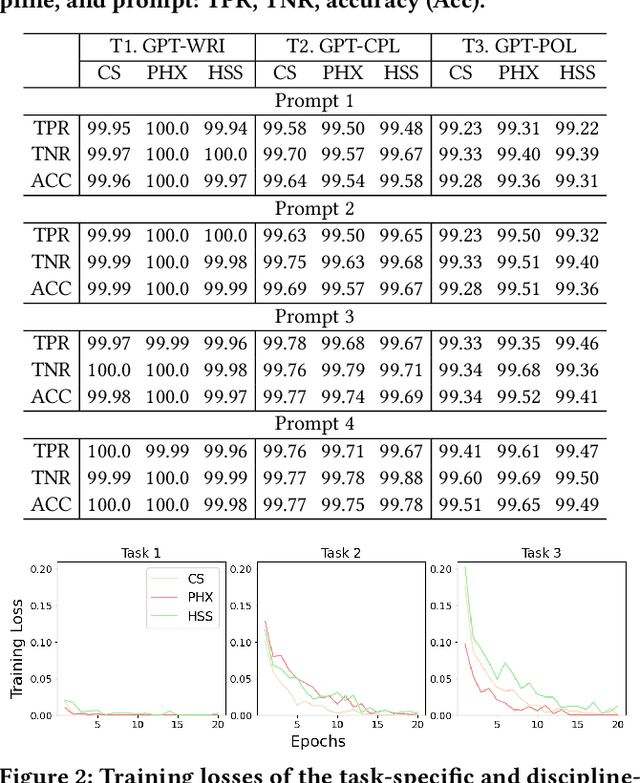
Abstract:With ChatGPT under the spotlight, utilizing large language models (LLMs) for academic writing has drawn a significant amount of discussions and concerns in the community. While substantial research efforts have been stimulated for detecting LLM-Generated Content (LLM-content), most of the attempts are still in the early stage of exploration. In this paper, we present a holistic investigation of detecting LLM-generate academic writing, by providing a dataset, evidence, and algorithms, in order to inspire more community effort to address the concern of LLM academic misuse. We first present GPABenchmark, a benchmarking dataset of 600,000 samples of human-written, GPT-written, GPT-completed, and GPT-polished abstracts of research papers in CS, physics, and humanities and social sciences (HSS). We show that existing open-source and commercial GPT detectors provide unsatisfactory performance on GPABenchmark, especially for GPT-polished text. Moreover, through a user study of 150+ participants, we show that it is highly challenging for human users, including experienced faculty members and researchers, to identify GPT-generated abstracts. We then present CheckGPT, a novel LLM-content detector consisting of a general representation module and an attentive-BiLSTM classification module, which is accurate, transferable, and interpretable. Experimental results show that CheckGPT achieves an average classification accuracy of 98% to 99% for the task-specific discipline-specific detectors and the unified detectors. CheckGPT is also highly transferable that, without tuning, it achieves ~90% accuracy in new domains, such as news articles, while a model tuned with approximately 2,000 samples in the target domain achieves ~98% accuracy. Finally, we demonstrate the explainability insights obtained from CheckGPT to reveal the key behaviors of how LLM generates texts.
Hide and Seek: on the Stealthiness of Attacks against Deep Learning Systems
May 31, 2022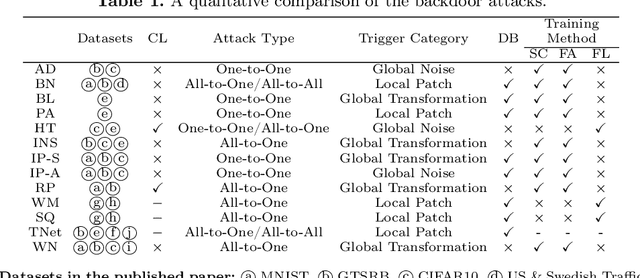
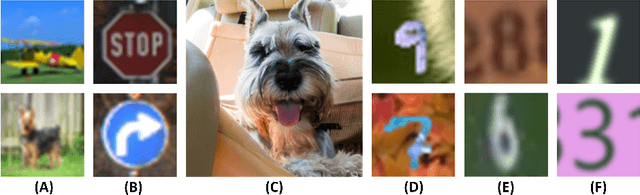
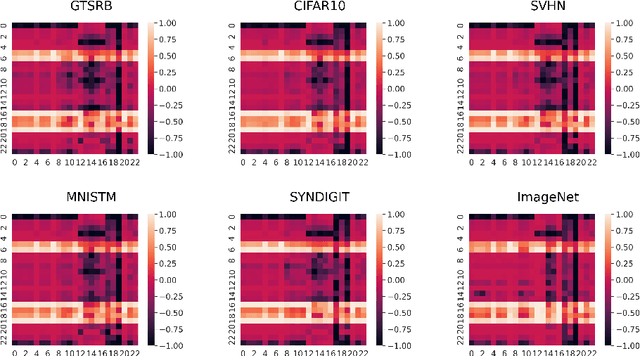
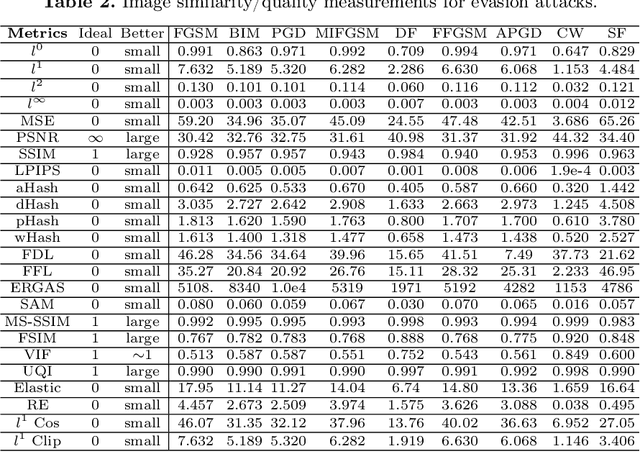
Abstract:With the growing popularity of artificial intelligence and machine learning, a wide spectrum of attacks against deep learning models have been proposed in the literature. Both the evasion attacks and the poisoning attacks attempt to utilize adversarially altered samples to fool the victim model to misclassify the adversarial sample. While such attacks claim to be or are expected to be stealthy, i.e., imperceptible to human eyes, such claims are rarely evaluated. In this paper, we present the first large-scale study on the stealthiness of adversarial samples used in the attacks against deep learning. We have implemented 20 representative adversarial ML attacks on six popular benchmarking datasets. We evaluate the stealthiness of the attack samples using two complementary approaches: (1) a numerical study that adopts 24 metrics for image similarity or quality assessment; and (2) a user study of 3 sets of questionnaires that has collected 20,000+ annotations from 1,000+ responses. Our results show that the majority of the existing attacks introduce nonnegligible perturbations that are not stealthy to human eyes. We further analyze the factors that contribute to attack stealthiness. We further examine the correlation between the numerical analysis and the user studies, and demonstrate that some image quality metrics may provide useful guidance in attack designs, while there is still a significant gap between assessed image quality and visual stealthiness of attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge