Zeping Sui
MIMO-AFDM Outperforms MIMO-OFDM in the Face of Hardware Impairments
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The impact of both multiplicative and additive hardware impairments (HWIs) on multiple-input multiple-output affine frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-AFDM) systems is investigated. For small-scale MIMO-AFDM systems, a tight bit error rate (BER) upper bound associated with the maximum likelihood (ML) detector is derived. By contrast, for large-scale systems, a closed-form BER approximation associated with the linear minimum mean squared error (LMMSE) detector is presented, including realistic imperfect channel estimation scenarios. Our first key observation is that the full diversity order of a hardware-impaired AFDM system remains unaffected, which is a unique advantage. Furthermore, our analysis shows that 1) the BER results derived accurately predict the simulated ML performance in moderate-to-high signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), while the theoretical BER curve of the LMMSE detector closely matches that of the Monte-Carlo based one. 2) MIMO-AFDM is more resilient to multiplicative distortions, such as phase noise and carrier frequency offset, compared to its orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) counterparts. This is attributed to its inherent chirp signal characteristics; 3) MIMO-AFDM consistently achieves superior BER performance compared to conventional MIMO-OFDM systems under the same additive HWI conditions, as well as different velocity values. The latter is because MIMO-AFDM is also resilient to the additional inter-carrier interference (ICI) imposed by the nonlinear distortions of additive HWIs. In a nutshell, compared to OFDM, AFDM demonstrates stronger ICI resilience and achieves the maximum full diversity attainable gain even under HWIs, thanks to its intrinsic chirp signalling structure as well as to the beneficial spreading effect of the discrete affine Fourier transform.
Error Rate Analysis and Low-Complexity Receiver Design for Zero-Padded AFDM
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:This paper studies the error rate performance and low-complexity receiver design for zero-padded affine frequency division multiplexing (ZP-AFDM) systems. By exploiting the unique ZP-aided lower triangular structure of the time domain (TD) channel matrix, we propose {a novel low-complexity} minimum mean square error (MMSE) detector and {a} maximum ratio combining-based TD (MRC-TD) detector. Furthermore, the theoretical bit error rate (BER) {performance} of both MMSE and maximum likelihood detectors {is} analyzed. Simulation results demonstrate {that} the proposed detectors can achieve identical BER performance to that of {the conventional MMSE detector based on matrix inversion} while {enjoying significantly reduced complexity.}
Optimal Real-time Communication in 6G Ultra-Massive V2X Mobile Networks
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a novel cooperative vehicular communication algorithm tailored for future 6G ultra-massive vehicle-to-everything (V2X) networks leveraging integrated space-air-ground communication systems. Specifically, we address the challenge of real-time information exchange among rapidly moving vehicles. We demonstrate the existence of an upper bound on channel capacity given a fixed number of relays, and propose a low-complexity relay selection heuristic algorithm. Simulation results verify that our proposed algorithm achieves superior channel capacities compared to existing cooperative vehicular communication approaches.
Energy Detection over Composite $κ-μ$ Shadowed Fading Channels with Inverse Gaussian Distribution in Ultra mMTC Networks
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the characteristics of energy detection (ED) over composite $\kappa$-$\mu$ shadowed fading channels in ultra machine-type communication (mMTC) networks. We have derived the closed-form expressions of the probability density function (PDF) of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) based on the Inverse Gaussian (\emph{IG}) distribution. By adopting novel integration and mathematical transformation techniques, we derive a truncation-based closed-form expression for the average detection probability for the first time. It can be observed from our simulations that the number of propagation paths has a more pronounced effect on average detection probability compared to average SNR, which is in contrast to earlier studies that focus on device-to-device networks. It suggests that for 6G mMTC network design, we should consider enhancing transmitter-receiver placement and antenna alignment strategies, rather than relying solely on increasing the device-to-device average SNR.
Generalized Tensor-Aided Channel Estimation for Hardware Impaired Device Identification
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the joint generalized channel estimation and device identification problem in Internet of Things (IoT) networks {under multipath propagation}. To fully utilize the received signal, we decompose the generalized channel into three components: transmitter hardware characteristics, path gains, and angles of arrival. By modelling the received signals as parallel factor (PARAFAC) tensors, we develop alternating least squares (ALS)-based algorithms to simultaneously estimate the generalized channels and identify the transmitters. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme outperforms {both Khatri-Rao Factorization (KRF) and the conventional least squares (LS) method} in terms of channel estimation accuracy and achieves performance close to the derived Cramer-Rao lower bound.
Ambiguity-Free Broadband DOA Estimation Relying on Parameterized Time-Frequency Transform
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:An ambiguity-free direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation scheme is proposed for sparse uniform linear arrays under low signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and non-stationary broadband signals. First, for achieving better DOA estimation performance at low SNRs while using non-stationary signals compared to the conventional frequency-difference (FD) paradigms, we propose parameterized time-frequency transform-based FD processing. Then, the unambiguous compressive FD beamforming is conceived to compensate the resolution loss induced by difference operation. Finally, we further derive a coarse-to-fine histogram statistics scheme to alleviate the perturbation in compressive FD beamforming with good DOA estimation accuracy. Simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed algorithm regarding robustness, resolution, and DOA estimation accuracy.
Generalized Spatial Modulation Aided Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:Generalized spatial modulation-aided affine frequency division multiplexing (GSM-AFDM) is conceived for reliable multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communications over doubly selective channels. We commence by proposing several low-complexity detectors for large-scale GSM-AFDM systems. Specifically, we introduce the linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) equalizer-based maximum likelihood detector (LMMSE-MLD). By exploiting the GSM properties, we then derive the LMMSE-based transmit-antenna activation pattern (TAP) check-based log-likelihood ratio detector (LMMSE-TC-LLRD). In addition, we propose a pair of new detectors, namely the greedy residual check detector (GRCD) and the reduced space check detector (RSCD). We also derive a bit error rate (BER) upper-bound by considering the MLD. Our simulation results demonstrate that 1) the BER upper bound derived is tight for moderate to high signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), 2) the proposed GSM-AFDM achieves lower BER than its conventional counterparts, and 3) the conceived detectors strike a compelling trade-off between the BER and complexity.
Performance Analysis and Optimization of STAR-RIS-Aided Cell-Free Massive MIMO Systems Relying on Imperfect Hardware
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS)-aided cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (CF-mMIMO) systems are investigated under spatially correlated fading channels using realistic imperfect hardware. Specifically, the transceiver distortions, \textcolor{black}{time-varying phase noise, and RIS phase shift errors} are considered. Upon considering imperfect hardware and pilot contamination, we derive a linear minimum mean-square error (MMSE) criterion-based cascaded channel estimator. Moreover, a closed-form expression of the downlink ergodic spectral efficiency (SE) is derived based on maximum ratio (MR) based transmit precoding and channel statistics, where both a finite number of access points (APs) and STAR-RIS elements as well as imperfect hardware are considered. Furthermore, by exploiting the ergodic signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios (SINRs) among user equipment (UE), a max-min fairness problem is formulated for the joint optimization of the passive transmitting and reflecting beamforming (BF) at the STAR-RIS as well as of the power control coefficients. An alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is proposed for solving the resultant problems, where iterative adaptive particle swarm optimization (APSO) and bisection methods are proposed for circumventing the non-convexity of the RIS passive BF and the quasi-concave power control sub-problems, respectively. Our simulation results illustrate that the STAR-RIS-aided CF-mMIMO system attains higher SE than its RIS-aided counterpart. The performance of different hardware parameters is also evaluated. Additionally, it is demonstrated that the SE of the worst UE can be significantly improved by exploiting the proposed AO-based algorithm compared to conventional solutions associated with random passive BF and equal-power scenarios.
Multi-bit Distributed Detection of Sparse Stochastic Signals over Error-Prone Reporting Channels
Nov 06, 2024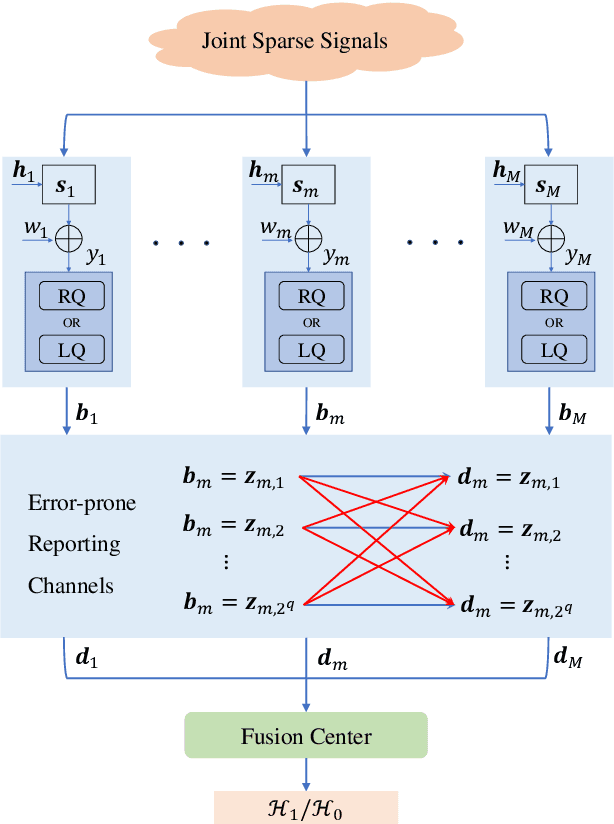

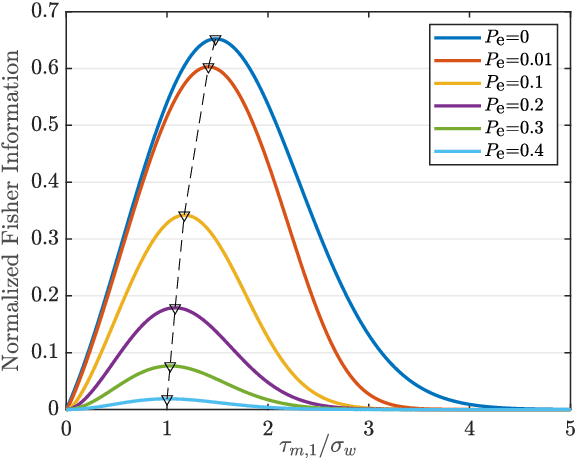
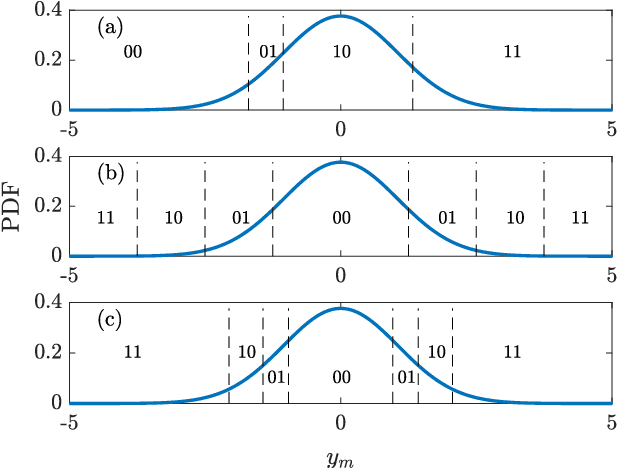
Abstract:We consider a distributed detection problem within a wireless sensor network (WSN), where a substantial number of sensors cooperate to detect the existence of sparse stochastic signals. To achieve a trade-off between detection performance and system constraints, multi-bit quantizers are employed at local sensors. Then, two quantization strategies, namely raw quantization (RQ) and likelihood ratio quantization (LQ), are examined. The multi-bit quantized signals undergo encoding into binary codewords and are subsequently transmitted to the fusion center via error-prone reporting channels. Upon exploiting the locally most powerful test (LMPT) strategy, we devise two multi-bit LMPT detectors in which quantized raw observations and local likelihood ratios are fused respectively. Moreover, the asymptotic detection performance of the proposed quantized detectors is analyzed, and closed-form expressions for the detection and false alarm probabilities are derived. Furthermore, the multi-bit quantizer design criterion, considering both RQ and LQ, is then proposed to achieve near-optimal asymptotic performance for our proposed detectors. The normalized Fisher information and asymptotic relative efficiency are derived, serving as tools to analyze and compensate for the loss of information introduced by the quantization. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed detectors, especially in scenarios with low signal-to-noise ratios and poor channel conditions.
RIS-Assisted Cell-Free Massive MIMO Relying on Reflection Pattern Modulation
Aug 10, 2024Abstract:We propose reflection pattern modulation-aided reconfigurable intelligent surface (RPM-RIS)-assisted cell-free massive multiple-input-multiple-output (CF-mMIMO) schemes for green uplink transmission. In our RPM-RIS-assisted CF-mMIMO system, extra information is conveyed by the indices of the active RIS blocks, exploiting the joint benefits of both RIS-assisted CF-mMIMO transmission and RPM. Since only part of the RIS blocks are active, our proposed architecture strikes a flexible energy \emph{vs.} spectral efficiency (SE) trade-off. We commence with introducing the system model by considering spatially correlated channels. Moreover, we conceive a channel estimation scheme subject to the linear minimum mean-square error (MMSE) constraint, yielding sufficient information for the subsequent signal processing steps. Then, upon exploiting a so-called large-scale fading decoding (LSFD) scheme, the uplink signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) is derived based on the RIS ON/OFF statistics, where both maximum ratio (MR) and local minimum mean-square error (L-MMSE) combiners are considered. By invoking the MR combiner, the closed-form expression of the uplink SE is formulated based only on the channel statistics. Furthermore, we derive the total energy efficiency (EE) of our proposed RPM-RIS-assisted CF-mMIMO system. Additionally, we propose a chaotic sequence-based adaptive particle swarm optimization (CSA-PSO) algorithm to maximize the total EE by designing the RIS phase shifts. Finally, our simulation results demonstrate that the proposed RPM-RIS-assisted CF-mMIMO architecture strikes an attractive SE \emph{vs.} EE trade-off, while the CSA-PSO algorithm is capable of attaining a significant EE performance gain compared to conventional solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge