Yunzhong He
Agentic Rubrics as Contextual Verifiers for SWE Agents
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Verification is critical for improving agents: it provides the reward signal for Reinforcement Learning and enables inference-time gains through Test-Time Scaling (TTS). Despite its importance, verification in software engineering (SWE) agent settings often relies on code execution, which can be difficult to scale due to environment setup overhead. Scalable alternatives such as patch classifiers and heuristic methods exist, but they are less grounded in codebase context and harder to interpret. To this end, we explore Agentic Rubrics: an expert agent interacts with the repository to create a context-grounded rubric checklist, and candidate patches are then scored against it without requiring test execution. On SWE-Bench Verified under parallel TTS evaluation, Agentic Rubrics achieve a score of 54.2% on Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B and 40.6% on Qwen3-32B, with at least a +3.5 percentage-point gain over the strongest baseline in our comparison set. We further analyze rubric behavior, showing that rubric scores are consistent with ground-truth tests while also flagging issues that tests do not capture. Our ablations show that agentic context gathering is essential for producing codebase-specific, unambiguous criteria. Together, these results suggest that Agentic Rubrics provide an efficient, scalable, and granular verification signal for SWE agents.
Audio MultiChallenge: A Multi-Turn Evaluation of Spoken Dialogue Systems on Natural Human Interaction
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) spoken dialogue systems are increasingly replacing cascaded pipelines for voice-based human-AI interaction, processing raw audio directly without intermediate transcription. Existing benchmarks primarily evaluate these models on synthetic speech and single-turn tasks, leaving realistic multi-turn conversational ability underexplored. We introduce Audio MultiChallenge, an open-source benchmark to evaluate E2E spoken dialogue systems under natural multi-turn interaction patterns. Building on the text-based MultiChallenge framework, which evaluates Inference Memory, Instruction Retention, and Self Coherence, we introduce a new axis Voice Editing that tests robustness to mid-utterance speech repairs and backtracking. We further augment each axis to the audio modality, such as introducing Audio-Cue challenges for Inference Memory that require recalling ambient sounds and paralinguistic signals beyond semantic content. We curate 452 conversations from 47 speakers with 1,712 instance-specific rubrics through a hybrid audio-native agentic and human-in-the-loop pipeline that exposes model failures at scale while preserving natural disfluencies found in unscripted human speech. Our evaluation of proprietary and open-source models reveals that even frontier models struggle on our benchmark, with Gemini 3 Pro Preview (Thinking), our highest-performing model achieving a 54.65% pass rate. Error analysis shows that models fail most often on our new axes and that Self Coherence degrades with longer audio context. These failures reflect difficulty of tracking edits, audio cues, and long-range context in natural spoken dialogue. Audio MultiChallenge provides a reproducible testbed to quantify them and drive improvements in audio-native multi-turn interaction capability.
PRBench: Large-Scale Expert Rubrics for Evaluating High-Stakes Professional Reasoning
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Frontier model progress is often measured by academic benchmarks, which offer a limited view of performance in real-world professional contexts. Existing evaluations often fail to assess open-ended, economically consequential tasks in high-stakes domains like Legal and Finance, where practical returns are paramount. To address this, we introduce Professional Reasoning Bench (PRBench), a realistic, open-ended, and difficult benchmark of real-world problems in Finance and Law. We open-source its 1,100 expert-authored tasks and 19,356 expert-curated criteria, making it, to our knowledge, the largest public, rubric-based benchmark for both legal and finance domains. We recruit 182 qualified professionals, holding JDs, CFAs, or 6+ years of experience, who contributed tasks inspired by their actual workflows. This process yields significant diversity, with tasks spanning 114 countries and 47 US jurisdictions. Our expert-curated rubrics are validated through a rigorous quality pipeline, including independent expert validation. Subsequent evaluation of 20 leading models reveals substantial room for improvement, with top scores of only 0.39 (Finance) and 0.37 (Legal) on our Hard subsets. We further catalog associated economic impacts of the prompts and analyze performance using human-annotated rubric categories. Our analysis shows that models with similar overall scores can diverge significantly on specific capabilities. Common failure modes include inaccurate judgments, a lack of process transparency and incomplete reasoning, highlighting critical gaps in their reliability for professional adoption.
Beyond Seeing: Evaluating Multimodal LLMs on Tool-Enabled Image Perception, Transformation, and Reasoning
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are increasingly applied in real-world scenarios where user-provided images are often imperfect, requiring active image manipulations such as cropping, editing, or enhancement to uncover salient visual cues. Beyond static visual perception, MLLMs must also think with images: dynamically transforming visual content and integrating it with other tools to solve complex tasks. However, this shift from treating vision as passive context to a manipulable cognitive workspace remains underexplored. Most existing benchmarks still follow a think about images paradigm, where images are regarded as static inputs. To address this gap, we introduce IRIS, an Interactive Reasoning with Images and Systems that evaluates MLLMs' ability to perceive, transform, and reason across complex visual-textual tasks under the think with images paradigm. IRIS comprises 1,204 challenging, open-ended vision tasks (603 single-turn, 601 multi-turn) spanning across five diverse domains, each paired with detailed rubrics to enable systematic evaluation. Our evaluation shows that current MLLMs struggle with tasks requiring effective integration of vision and general-purpose tools. Even the strongest model (GPT-5-think) reaches only 18.68% pass rate. We further observe divergent tool-use behaviors, with OpenAI models benefiting from diverse image manipulations while Gemini-2.5-pro shows no improvement. By introducing the first benchmark centered on think with images, IRIS offers critical insights for advancing visual intelligence in MLLMs.
Online Rubrics Elicitation from Pairwise Comparisons
Oct 08, 2025
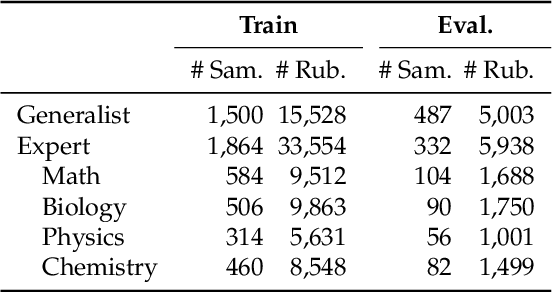
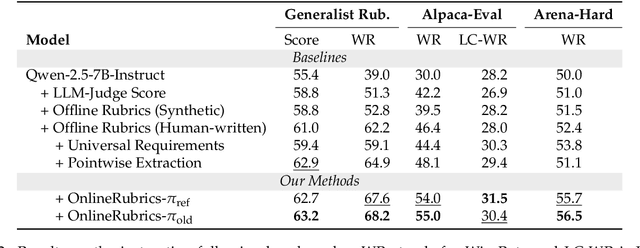
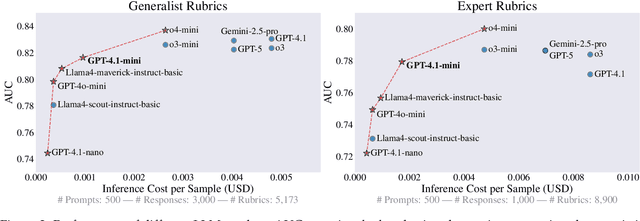
Abstract:Rubrics provide a flexible way to train LLMs on open-ended long-form answers where verifiable rewards are not applicable and human preferences provide coarse signals. Prior work shows that reinforcement learning with rubric-based rewards leads to consistent gains in LLM post-training. Most existing approaches rely on rubrics that remain static over the course of training. Such static rubrics, however, are vulnerable to reward-hacking type behaviors and fail to capture emergent desiderata that arise during training. We introduce Online Rubrics Elicitation (OnlineRubrics), a method that dynamically curates evaluation criteria in an online manner through pairwise comparisons of responses from current and reference policies. This online process enables continuous identification and mitigation of errors as training proceeds. Empirically, this approach yields consistent improvements of up to 8% over training exclusively with static rubrics across AlpacaEval, GPQA, ArenaHard as well as the validation sets of expert questions and rubrics. We qualitatively analyze the elicited criteria and identify prominent themes such as transparency, practicality, organization, and reasoning.
Auto-GPT for Online Decision Making: Benchmarks and Additional Opinions
Jun 04, 2023Abstract:Auto-GPT is an autonomous agent that leverages recent advancements in adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) for decision-making tasks. While there has been a growing interest in Auto-GPT stypled agents, questions remain regarding the effectiveness and flexibility of Auto-GPT in solving real-world decision-making tasks. Its limited capability for real-world engagement and the absence of benchmarks contribute to these uncertainties. In this paper, we present a comprehensive benchmark study of Auto-GPT styled agents in decision-making tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. Our aim is to gain deeper insights into this problem and understand the adaptability of GPT-based agents. We compare the performance of popular LLMs such as GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Claude, and Vicuna in Auto-GPT styled decision-making tasks. Furthermore, we introduce the Additional Opinions algorithm, an easy and effective method that incorporates supervised/imitation-based learners into the Auto-GPT scheme. This approach enables lightweight supervised learning without requiring fine-tuning of the foundational LLMs. We demonstrate through careful baseline comparisons and ablation studies that the Additional Opinions algorithm significantly enhances performance in online decision-making benchmarks, including WebShop and ALFWorld.
HierCat: Hierarchical Query Categorization from Weakly Supervised Data at Facebook Marketplace
Feb 22, 2023Abstract:Query categorization at customer-to-customer e-commerce platforms like Facebook Marketplace is challenging due to the vagueness of search intent, noise in real-world data, and imbalanced training data across languages. Its deployment also needs to consider challenges in scalability and downstream integration in order to translate modeling advances into better search result relevance. In this paper we present HierCat, the query categorization system at Facebook Marketplace. HierCat addresses these challenges by leveraging multi-task pre-training of dual-encoder architectures with a hierarchical inference step to effectively learn from weakly supervised training data mined from searcher engagement. We show that HierCat not only outperforms popular methods in offline experiments, but also leads to 1.4% improvement in NDCG and 4.3% increase in searcher engagement at Facebook Marketplace Search in online A/B testing.
Que2Engage: Embedding-based Retrieval for Relevant and Engaging Products at Facebook Marketplace
Feb 21, 2023Abstract:Embedding-based Retrieval (EBR) in e-commerce search is a powerful search retrieval technique to address semantic matches between search queries and products. However, commercial search engines like Facebook Marketplace Search are complex multi-stage systems optimized for multiple business objectives. At Facebook Marketplace, search retrieval focuses on matching search queries with relevant products, while search ranking puts more emphasis on contextual signals to up-rank the more engaging products. As a result, the end-to-end searcher experience is a function of both relevance and engagement, and the interaction between different stages of the system. This presents challenges to EBR systems in order to optimize for better searcher experiences. In this paper we presents Que2Engage, a search EBR system built towards bridging the gap between retrieval and ranking for end-to-end optimizations. Que2Engage takes a multimodal & multitask approach to infuse contextual information into the retrieval stage and to balance different business objectives. We show the effectiveness of our approach via a multitask evaluation framework and thorough baseline comparisons and ablation studies. Que2Engage is deployed on Facebook Marketplace Search and shows significant improvements in searcher engagement in two weeks of A/B testing.
A Social Search Model for Large Scale Social Networks
May 09, 2020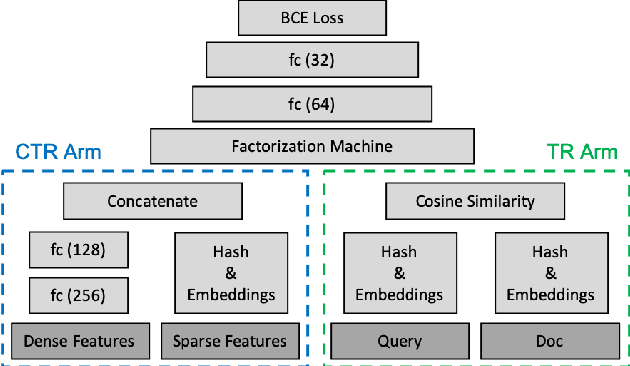

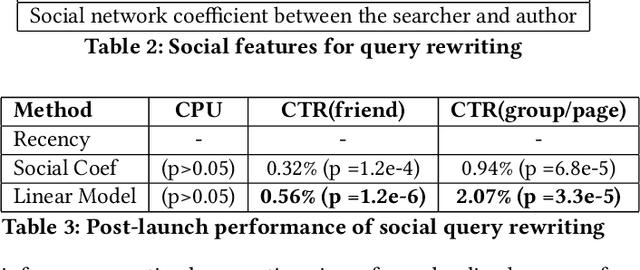
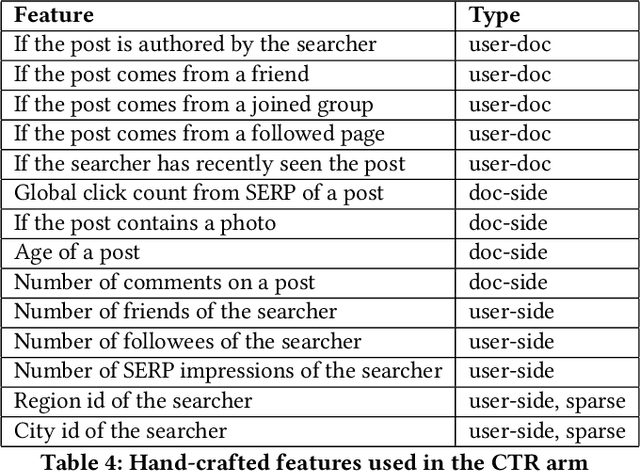
Abstract:With the rise of social networks, information on the internet is no longer solely organized by web pages. Rather, content is generated and shared among users and organized around their social relations on social networks. This presents new challenges to information retrieval systems. On a social network search system, the generation of result sets not only needs to consider keyword matches, like a traditional web search engine does, but it also needs to take into account the searcher's social connections and the content's visibility settings. Besides, search ranking should be able to handle both textual relevance and the rich social interaction signals from the social network. In this paper, we present our solution to these two challenges by first introducing a social retrieval mechanism, and then investigate novel deep neural networks for the ranking problem. The retrieval system treats social connections as indexing terms, and generates meaningful results sets by biasing towards close social connections in a constrained optimization fashion. The result set is then ranked by a deep neural network that handles textual and social relevance in a two-tower approach, in which personalization and textual relevance are addressed jointly. The retrieval mechanism is deployed on Facebook and is helping billions of users finding postings from their connections efficiently. Based on the postings being retrieved, we evaluate our two-tower neutral network, and examine the importance of personalization and textual signals in the ranking problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge