Chaitanya Kulkarni
NEMO-4-PAYPAL: Leveraging NVIDIA's Nemo Framework for empowering PayPal's Commerce Agent
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:We present the development and optimization of PayPal's Commerce Agent, powered by NEMO-4-PAYPAL, a multi-agent system designed to revolutionize agentic commerce on the PayPal platform. Through our strategic partnership with NVIDIA, we leveraged the NeMo Framework for LLM model fine-tuning to enhance agent performance. Specifically, we optimized the Search and Discovery agent by replacing our base model with a fine-tuned Nemotron small language model (SLM). We conducted comprehensive experiments using the llama3.1-nemotron-nano-8B-v1 architecture, training LoRA-based models through systematic hyperparameter sweeps across learning rates, optimizers (Adam, AdamW), cosine annealing schedules, and LoRA ranks. Our contributions include: (1) the first application of NVIDIA's NeMo Framework to commerce-specific agent optimization, (2) LLM powered fine-tuning strategy for retrieval-focused commerce tasks, (3) demonstration of significant improvements in latency and cost while maintaining agent quality, and (4) a scalable framework for multi-agent system optimization in production e-commerce environments. Our results demonstrate that the fine-tuned Nemotron SLM effectively resolves the key performance issue in the retrieval component, which represents over 50\% of total agent response time, while maintaining or enhancing overall system performance.
HierCat: Hierarchical Query Categorization from Weakly Supervised Data at Facebook Marketplace
Feb 22, 2023Abstract:Query categorization at customer-to-customer e-commerce platforms like Facebook Marketplace is challenging due to the vagueness of search intent, noise in real-world data, and imbalanced training data across languages. Its deployment also needs to consider challenges in scalability and downstream integration in order to translate modeling advances into better search result relevance. In this paper we present HierCat, the query categorization system at Facebook Marketplace. HierCat addresses these challenges by leveraging multi-task pre-training of dual-encoder architectures with a hierarchical inference step to effectively learn from weakly supervised training data mined from searcher engagement. We show that HierCat not only outperforms popular methods in offline experiments, but also leads to 1.4% improvement in NDCG and 4.3% increase in searcher engagement at Facebook Marketplace Search in online A/B testing.
Min-similarity association rules for identifying past comorbidities of recurrent ED and inpatient patients
Oct 26, 2021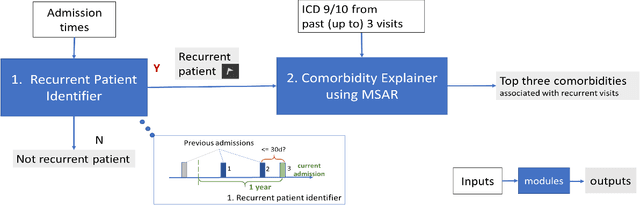
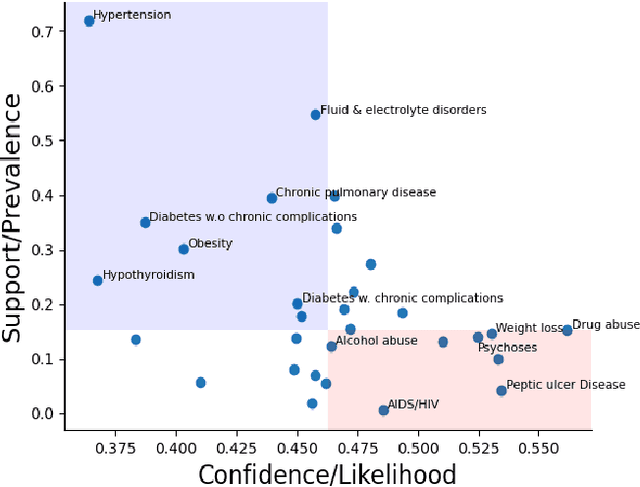
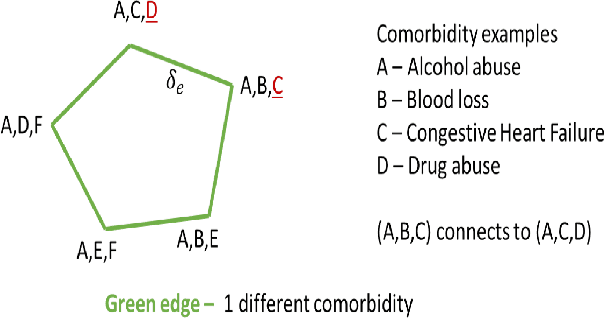
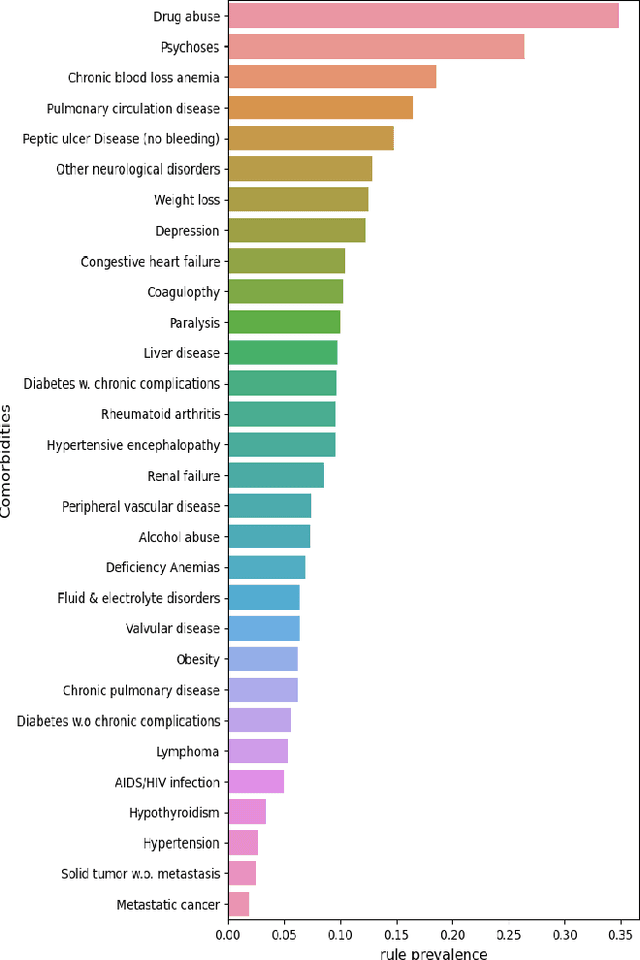
Abstract:In the hospital setting, a small percentage of recurrent frequent patients contribute to a disproportional amount of healthcare resource usage. Moreover, in many of these cases, patient outcomes can be greatly improved by reducing reoccurring visits, especially when they are associated with substance abuse, mental health, and medical factors that could be improved by social-behavioral interventions, outpatient or preventative care. To address this, we developed a computationally efficient and interpretable framework that both identifies recurrent patients with high utilization and determines which comorbidities contribute most to their recurrent visits. Specifically, we present a novel algorithm, called the minimum similarity association rules (MSAR), balancing confidence-support trade-off, to determine the conditions most associated with reoccurring Emergency department (ED) and inpatient visits. We validate MSAR on a large Electric Health Record (EHR) dataset. Part of the solution is deployed in Philips product Patient Flow Capacity Suite (PFCS).
An Annotated Corpus for Machine Reading of Instructions in Wet Lab Protocols
May 01, 2018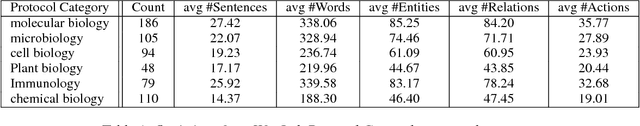
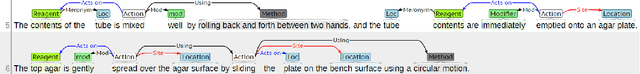

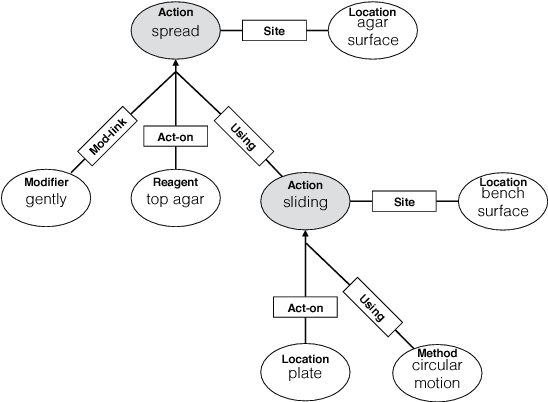
Abstract:We describe an effort to annotate a corpus of natural language instructions consisting of 622 wet lab protocols to facilitate automatic or semi-automatic conversion of protocols into a machine-readable format and benefit biological research. Experimental results demonstrate the utility of our corpus for developing machine learning approaches to shallow semantic parsing of instructional texts. We make our annotated Wet Lab Protocol Corpus available to the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge