Yuning Xing
Reward Prediction Error Prioritisation in Experience Replay: The RPE-PER Method
Jan 30, 2025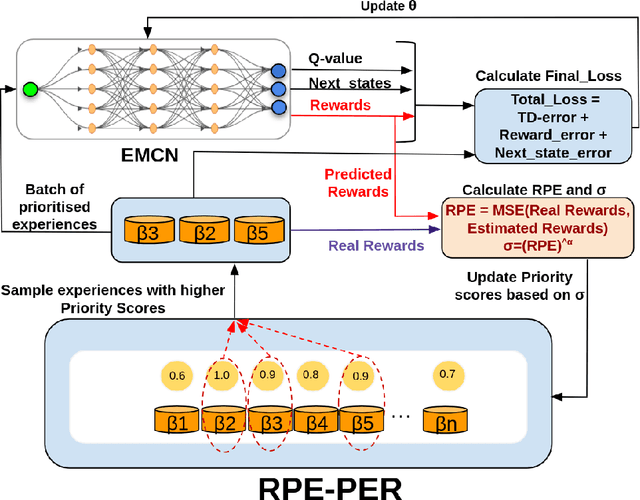
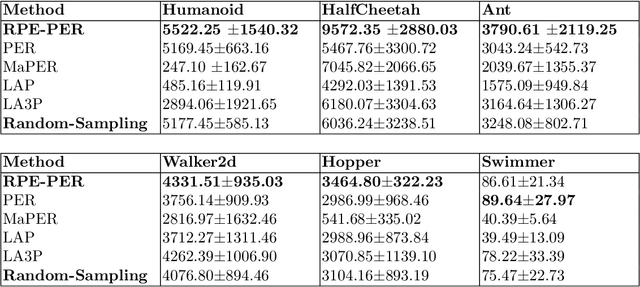
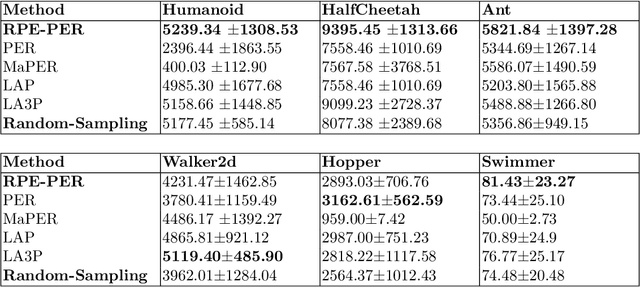
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning algorithms aim to learn optimal control strategies through iterative interactions with an environment. A critical element in this process is the experience replay buffer, which stores past experiences, allowing the algorithm to learn from a diverse range of interactions rather than just the most recent ones. This buffer is especially essential in dynamic environments with limited experiences. However, efficiently selecting high-value experiences to accelerate training remains a challenge. Drawing inspiration from the role of reward prediction errors (RPEs) in biological systems, where they are essential for adaptive behaviour and learning, we introduce Reward Predictive Error Prioritised Experience Replay (RPE-PER). This novel approach prioritises experiences in the buffer based on RPEs. Our method employs a critic network, EMCN, that predicts rewards in addition to the Q-values produced by standard critic networks. The discrepancy between these predicted and actual rewards is computed as RPE and utilised as a signal for experience prioritisation. Experimental evaluations across various continuous control tasks demonstrate RPE-PER's effectiveness in enhancing the learning speed and performance of off-policy actor-critic algorithms compared to baseline approaches.
Benchmarking Reinforcement Learning Methods for Dexterous Robotic Manipulation with a Three-Fingered Gripper
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) training is predominantly conducted in cost-effective and controlled simulation environments. However, the transfer of these trained models to real-world tasks often presents unavoidable challenges. This research explores the direct training of RL algorithms in controlled yet realistic real-world settings for the execution of dexterous manipulation. The benchmarking results of three RL algorithms trained on intricate in-hand manipulation tasks within practical real-world contexts are presented. Our study not only demonstrates the practicality of RL training in authentic real-world scenarios, facilitating direct real-world applications, but also provides insights into the associated challenges and considerations. Additionally, our experiences with the employed experimental methods are shared, with the aim of empowering and engaging fellow researchers and practitioners in this dynamic field of robotics.
Image-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning with Intrinsically Motivated Stimuli: On the Execution of Complex Robotic Tasks
Jul 31, 2024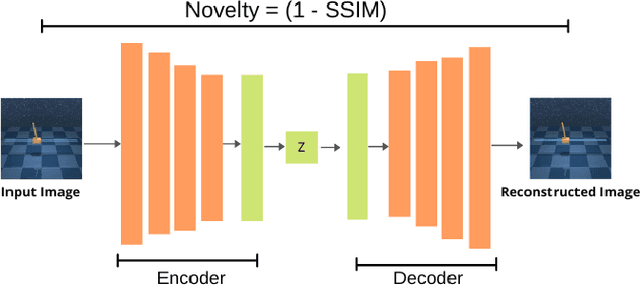
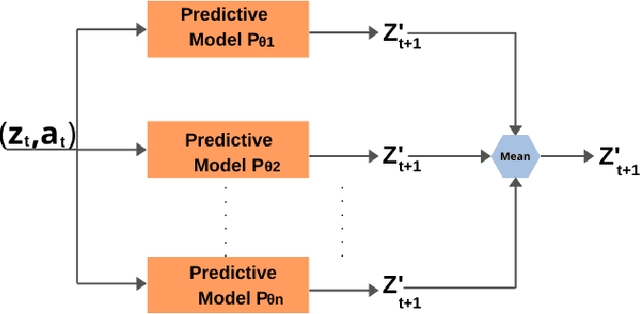
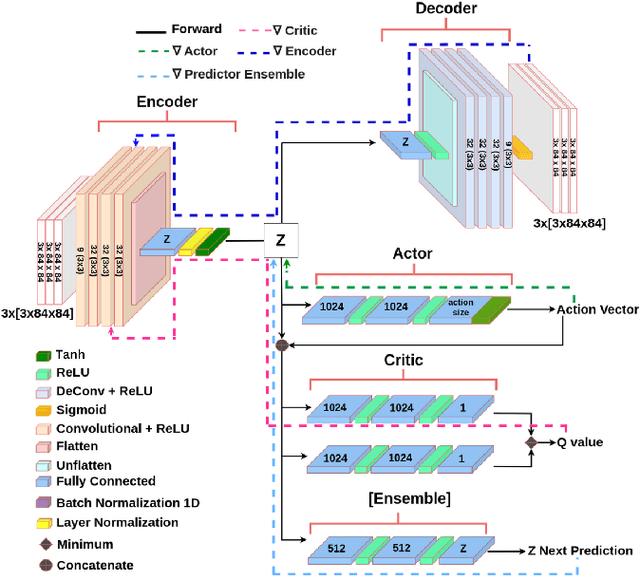
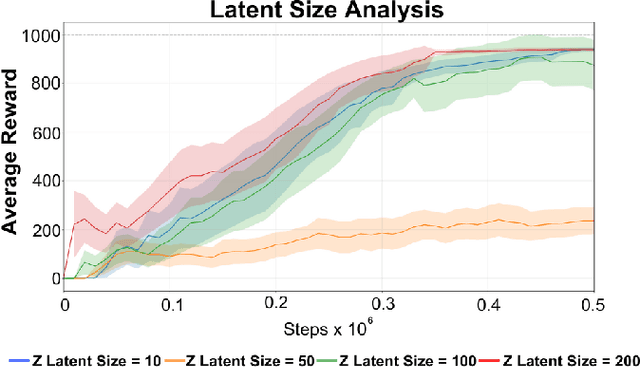
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been widely used to solve tasks where the environment consistently provides a dense reward value. However, in real-world scenarios, rewards can often be poorly defined or sparse. Auxiliary signals are indispensable for discovering efficient exploration strategies and aiding the learning process. In this work, inspired by intrinsic motivation theory, we postulate that the intrinsic stimuli of novelty and surprise can assist in improving exploration in complex, sparsely rewarded environments. We introduce a novel sample-efficient method able to learn directly from pixels, an image-based extension of TD3 with an autoencoder called \textit{NaSA-TD3}. The experiments demonstrate that NaSA-TD3 is easy to train and an efficient method for tackling complex continuous-control robotic tasks, both in simulated environments and real-world settings. NaSA-TD3 outperforms existing state-of-the-art RL image-based methods in terms of final performance without requiring pre-trained models or human demonstrations.
Look how they have grown: Non-destructive Leaf Detection and Size Estimation of Tomato Plants for 3D Growth Monitoring
Apr 07, 2023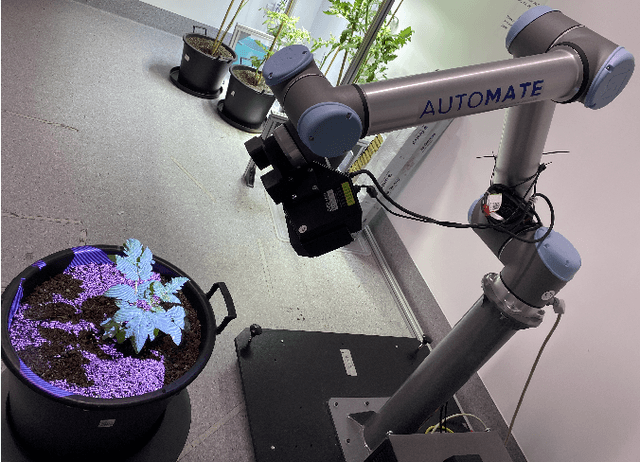
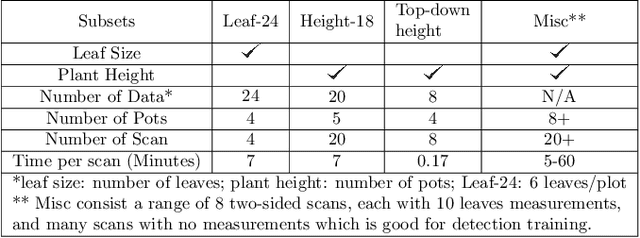
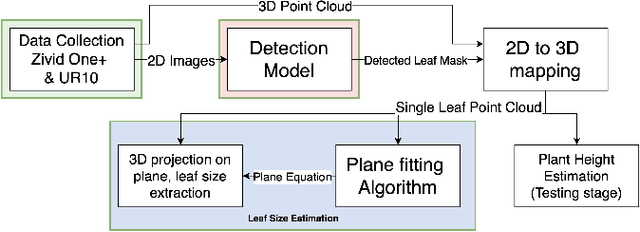
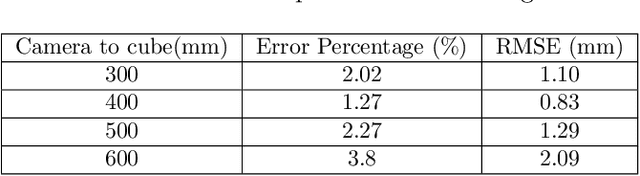
Abstract:Smart farming is a growing field as technology advances. Plant characteristics are crucial indicators for monitoring plant growth. Research has been done to estimate characteristics like leaf area index, leaf disease, and plant height. However, few methods have been applied to non-destructive measurements of leaf size. In this paper, an automated non-destructive imaged-based measuring system is presented, which uses 2D and 3D data obtained using a Zivid 3D camera, creating 3D virtual representations (digital twins) of the tomato plants. Leaves are detected from corresponding 2D RGB images and mapped to their 3D point cloud using the detected leaf masks, which then pass the leaf point cloud to the plane fitting algorithm to extract the leaf size to provide data for growth monitoring. The performance of the measurement platform has been measured through a comprehensive trial on real-world tomato plants with quantified performance metrics compared to ground truth measurements. Three tomato leaf and height datasets (including 50+ 3D point cloud files of tomato plants) were collected and open-sourced in this project. The proposed leaf size estimation method demonstrates an RMSE value of 4.47mm and an R^2 value of 0.87. The overall measurement system (leaf detection and size estimation algorithms combine) delivers an RMSE value of 8.13mm and an R^2 value of 0.899.
* 10 Pages, 10 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge