Yukai Xu
BicKD: Bilateral Contrastive Knowledge Distillation
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is a machine learning framework that transfers knowledge from a teacher model to a student model. The vanilla KD proposed by Hinton et al. has been the dominant approach in logit-based distillation and demonstrates compelling performance. However, it only performs sample-wise probability alignment between teacher and student's predictions, lacking an mechanism for class-wise comparison. Besides, vanilla KD imposes no structural constraint on the probability space. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective methodology, bilateral contrastive knowledge distillation (BicKD). This approach introduces a novel bilateral contrastive loss, which intensifies the orthogonality among different class generalization spaces while preserving consistency within the same class. The bilateral formulation enables explicit comparison of both sample-wise and class-wise prediction patterns between teacher and student. By emphasizing probabilistic orthogonality, BicKD further regularizes the geometric structure of the predictive distribution. Extensive experiments show that our BicKD method enhances knowledge transfer, and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art knowledge distillation techniques across various model architectures and benchmarks.
PAD-FT: A Lightweight Defense for Backdoor Attacks via Data Purification and Fine-Tuning
Sep 18, 2024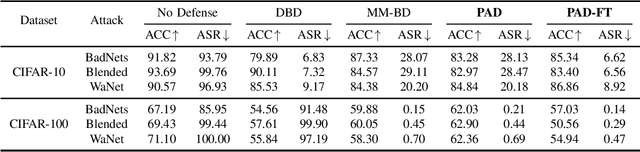
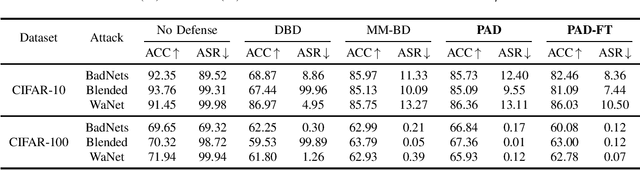
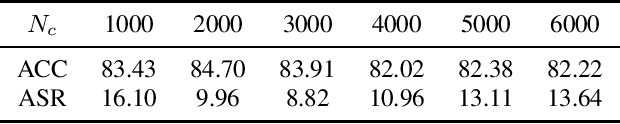
Abstract:Backdoor attacks pose a significant threat to deep neural networks, particularly as recent advancements have led to increasingly subtle implantation, making the defense more challenging. Existing defense mechanisms typically rely on an additional clean dataset as a standard reference and involve retraining an auxiliary model or fine-tuning the entire victim model. However, these approaches are often computationally expensive and not always feasible in practical applications. In this paper, we propose a novel and lightweight defense mechanism, termed PAD-FT, that does not require an additional clean dataset and fine-tunes only a very small part of the model to disinfect the victim model. To achieve this, our approach first introduces a simple data purification process to identify and select the most-likely clean data from the poisoned training dataset. The self-purified clean dataset is then used for activation clipping and fine-tuning only the last classification layer of the victim model. By integrating data purification, activation clipping, and classifier fine-tuning, our mechanism PAD-FT demonstrates superior effectiveness across multiple backdoor attack methods and datasets, as confirmed through extensive experimental evaluation.
Privacy-Preserving Heterogeneous Federated Learning for Sensitive Healthcare Data
Jun 15, 2024


Abstract:In the realm of healthcare where decentralized facilities are prevalent, machine learning faces two major challenges concerning the protection of data and models. The data-level challenge concerns the data privacy leakage when centralizing data with sensitive personal information. While the model-level challenge arises from the heterogeneity of local models, which need to be collaboratively trained while ensuring their confidentiality to address intellectual property concerns. To tackle these challenges, we propose a new framework termed Abstention-Aware Federated Voting (AAFV) that can collaboratively and confidentially train heterogeneous local models while simultaneously protecting the data privacy. This is achieved by integrating a novel abstention-aware voting mechanism and a differential privacy mechanism onto local models' predictions. In particular, the proposed abstention-aware voting mechanism exploits a threshold-based abstention method to select high-confidence votes from heterogeneous local models, which not only enhances the learning utility but also protects model confidentiality. Furthermore, we implement AAFV on two practical prediction tasks of diabetes and in-hospital patient mortality. The experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and confidentiality of AAFV in testing accuracy and privacy protection.
DivTOD: Unleashing the Power of LLMs for Diversifying Task-Oriented Dialogue Representations
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:Language models pre-trained on general text have achieved impressive results in diverse fields. Yet, the distinct linguistic characteristics of task-oriented dialogues (TOD) compared to general text limit the practical utility of existing language models. Current task-oriented dialogue pre-training methods overlook the one-to-many property of conversations, where multiple responses can be appropriate given the same conversation context. In this paper, we propose a novel dialogue pre-training model called DivTOD, which collaborates with LLMs to learn diverse task-oriented dialogue representations. DivTOD guides LLMs in transferring diverse knowledge to smaller models while removing domain knowledge that contradicts task-oriented dialogues. Experiments show that our model outperforms strong TOD baselines on various downstream dialogue tasks and learns the intrinsic diversity of task-oriented dialogues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge