Yuchi Huang
Interactive Generative Adversarial Networks for Facial Expression Generation in Dyadic Interactions
Jan 30, 2018


Abstract:A social interaction is a social exchange between two or more individuals,where individuals modify and adjust their behaviors in response to their interaction partners. Our social interactions are one of most fundamental aspects of our lives and can profoundly affect our mood, both positively and negatively. With growing interest in virtual reality and avatar-mediated interactions,it is desirable to make these interactions natural and human like to promote positive effect in the interactions and applications such as intelligent tutoring systems, automated interview systems and e-learning. In this paper, we propose a method to generate facial behaviors for an agent. These behaviors include facial expressions and head pose and they are generated considering the users affective state. Our models learn semantically meaningful representations of the face and generate appropriate and temporally smooth facial behaviors in dyadic interactions.
Iterated Support Vector Machines for Distance Metric Learning
Feb 02, 2015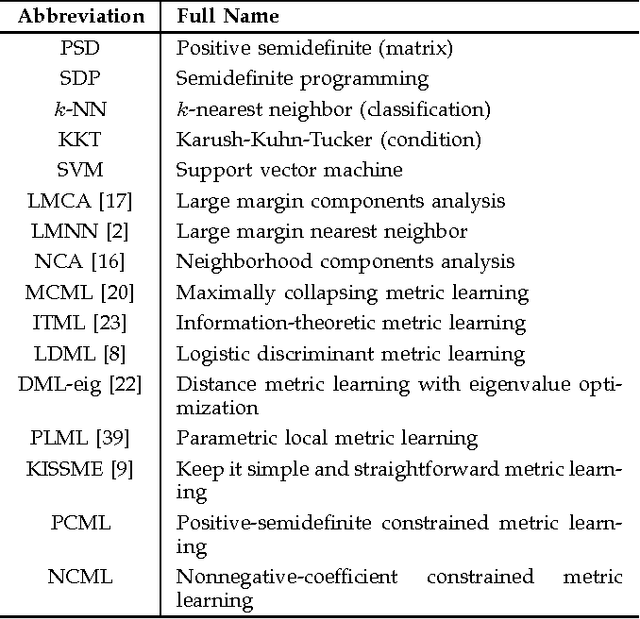
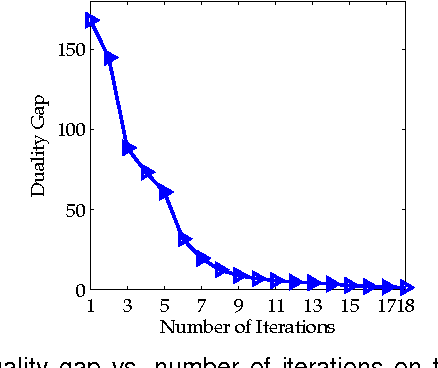
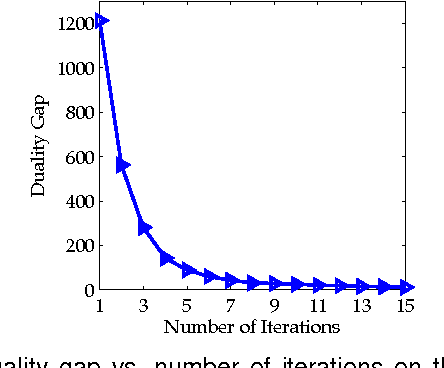
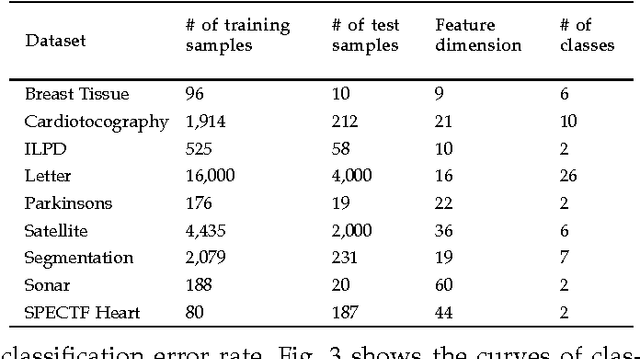
Abstract:Distance metric learning aims to learn from the given training data a valid distance metric, with which the similarity between data samples can be more effectively evaluated for classification. Metric learning is often formulated as a convex or nonconvex optimization problem, while many existing metric learning algorithms become inefficient for large scale problems. In this paper, we formulate metric learning as a kernel classification problem, and solve it by iterated training of support vector machines (SVM). The new formulation is easy to implement, efficient in training, and tractable for large-scale problems. Two novel metric learning models, namely Positive-semidefinite Constrained Metric Learning (PCML) and Nonnegative-coefficient Constrained Metric Learning (NCML), are developed. Both PCML and NCML can guarantee the global optimality of their solutions. Experimental results on UCI dataset classification, handwritten digit recognition, face verification and person re-identification demonstrate that the proposed metric learning methods achieve higher classification accuracy than state-of-the-art methods and they are significantly more efficient in training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge