Yuchen Shao
A Study of In-Context-Learning-Based Text-to-SQL Errors
Jan 16, 2025

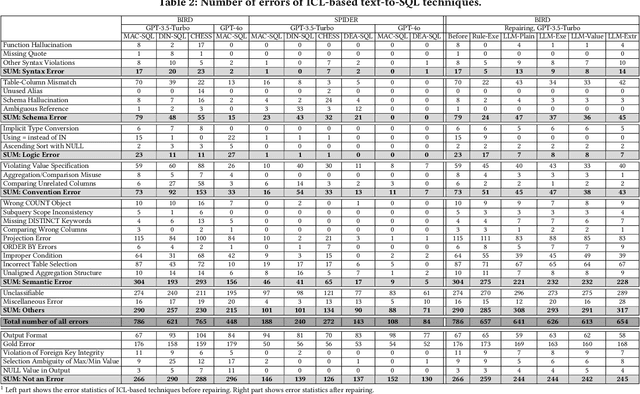
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been adopted to perform text-to-SQL tasks, utilizing their in-context learning (ICL) capability to translate natural language questions into structured query language (SQL). However, such a technique faces correctness problems and requires efficient repairing solutions. In this paper, we conduct the first comprehensive study of text-to-SQL errors. Our study covers four representative ICL-based techniques, five basic repairing methods, two benchmarks, and two LLM settings. We find that text-to-SQL errors are widespread and summarize 29 error types of 7 categories. We also find that existing repairing attempts have limited correctness improvement at the cost of high computational overhead with many mis-repairs. Based on the findings, we propose MapleRepair, a novel text-to-SQL error detection and repairing framework. The evaluation demonstrates that MapleRepair outperforms existing solutions by repairing 13.8% more queries with neglectable mis-repairs and 67.4% less overhead.
Vortex under Ripplet: An Empirical Study of RAG-enabled Applications
Jul 06, 2024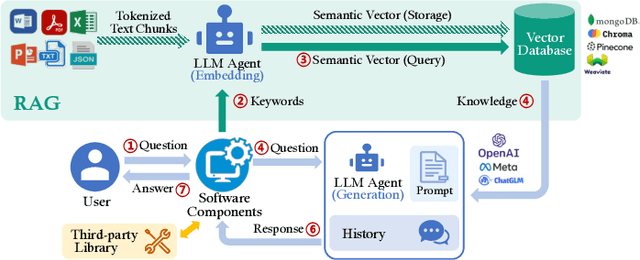
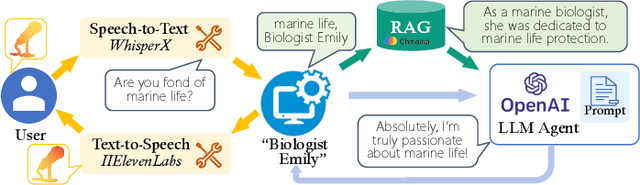

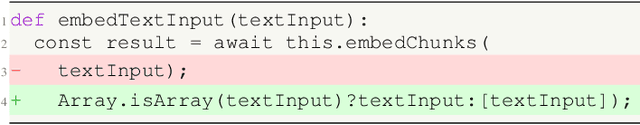
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) enhanced by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) provide effective solutions in various application scenarios. However, developers face challenges in integrating RAG-enhanced LLMs into software systems, due to lack of interface specification, requirements from software context, and complicated system management. In this paper, we manually studied 100 open-source applications that incorporate RAG-enhanced LLMs, and their issue reports. We have found that more than 98% of applications contain multiple integration defects that harm software functionality, efficiency, and security. We have also generalized 19 defect patterns and proposed guidelines to tackle them. We hope this work could aid LLM-enabled software development and motivate future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge