Yuchang Jiang
Not Every Tree Is a Forest: Benchmarking Forest Types from Satellite Remote Sensing
May 03, 2025Abstract:Developing accurate and reliable models for forest types mapping is critical to support efforts for halting deforestation and for biodiversity conservation (such as European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)). This work introduces ForTy, a benchmark for global-scale FORest TYpes mapping using multi-temporal satellite data1. The benchmark comprises 200,000 time series of image patches, each consisting of Sentinel-2, Sentinel-1, climate, and elevation data. Each time series captures variations at monthly or seasonal cadence. Per-pixel annotations, including forest types and other land use classes, support image segmentation tasks. Unlike most existing land use products that often categorize all forest areas into a single class, our benchmark differentiates between three forest types classes: natural forest, planted forest, and tree crops. By leveraging multiple public data sources, we achieve global coverage with this benchmark. We evaluate the forest types dataset using several baseline models, including convolution neural networks and transformer-based models. Additionally, we propose a novel transformer-based model specifically designed to handle multi-modal, multi-temporal satellite data for forest types mapping. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model surpasses the baseline models in performance.
GSR4B: Biomass Map Super-Resolution with Sentinel-1/2 Guidance
Apr 03, 2025

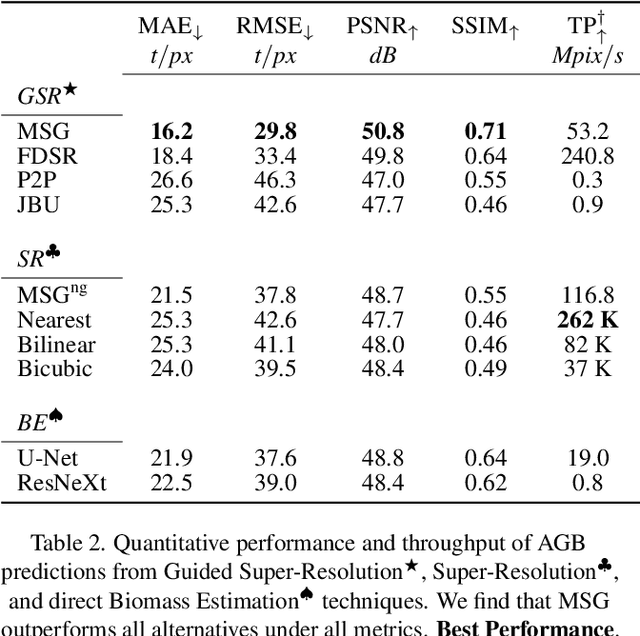

Abstract:Accurate Above-Ground Biomass (AGB) mapping at both large scale and high spatio-temporal resolution is essential for applications ranging from climate modeling to biodiversity assessment, and sustainable supply chain monitoring. At present, fine-grained AGB mapping relies on costly airborne laser scanning acquisition campaigns usually limited to regional scales. Initiatives such as the ESA CCI map attempt to generate global biomass products from diverse spaceborne sensors but at a coarser resolution. To enable global, high-resolution (HR) mapping, several works propose to regress AGB from HR satellite observations such as ESA Sentinel-1/2 images. We propose a novel way to address HR AGB estimation, by leveraging both HR satellite observations and existing low-resolution (LR) biomass products. We cast this problem as Guided Super-Resolution (GSR), aiming at upsampling LR biomass maps (sources) from $100$ to $10$ m resolution, using auxiliary HR co-registered satellite images (guides). We compare super-resolving AGB maps with and without guidance, against direct regression from satellite images, on the public BioMassters dataset. We observe that Multi-Scale Guidance (MSG) outperforms direct regression both for regression ($-780$ t/ha RMSE) and perception ($+2.0$ dB PSNR) metrics, and better captures high-biomass values, without significant computational overhead. Interestingly, unlike the RGB+Depth setting they were originally designed for, our best-performing AGB GSR approaches are those that most preserve the guide image texture. Our results make a strong case for adopting the GSR framework for accurate HR biomass mapping at scale. Our code and model weights are made publicly available (https://github.com/kaankaramanofficial/GSR4B).
Accuracy and Consistency of Space-based Vegetation Height Maps for Forest Dynamics in Alpine Terrain
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Monitoring and understanding forest dynamics is essential for environmental conservation and management. This is why the Swiss National Forest Inventory (NFI) provides countrywide vegetation height maps at a spatial resolution of 0.5 m. Its long update time of 6 years, however, limits the temporal analysis of forest dynamics. This can be improved by using spaceborne remote sensing and deep learning to generate large-scale vegetation height maps in a cost-effective way. In this paper, we present an in-depth analysis of these methods for operational application in Switzerland. We generate annual, countrywide vegetation height maps at a 10-meter ground sampling distance for the years 2017 to 2020 based on Sentinel-2 satellite imagery. In comparison to previous works, we conduct a large-scale and detailed stratified analysis against a precise Airborne Laser Scanning reference dataset. This stratified analysis reveals a close relationship between the model accuracy and the topology, especially slope and aspect. We assess the potential of deep learning-derived height maps for change detection and find that these maps can indicate changes as small as 250 $m^2$. Larger-scale changes caused by a winter storm are detected with an F1-score of 0.77. Our results demonstrate that vegetation height maps computed from satellite imagery with deep learning are a valuable, complementary, cost-effective source of evidence to increase the temporal resolution for national forest assessments.
Mixture of Experts with Uncertainty Voting for Imbalanced Deep Regression Problems
May 24, 2023Abstract:Data imbalance is ubiquitous when applying machine learning to real-world problems, particularly regression problems. If training data are imbalanced, the learning is dominated by the densely covered regions of the target distribution, consequently, the learned regressor tends to exhibit poor performance in sparsely covered regions. Beyond standard measures like over-sampling or re-weighting, there are two main directions to handle learning from imbalanced data. For regression, recent work relies on the continuity of the distribution; whereas for classification there has been a trend to employ mixture-of-expert models and let some ensemble members specialize in predictions for the sparser regions. Here, we adapt the mixture-of-experts approach to the regression setting. A main question when using this approach is how to fuse the predictions from multiple experts into one output. Drawing inspiration from recent work on probabilistic deep learning, we propose to base the fusion on the aleatoric uncertainties of individual experts, thus obviating the need for a separate aggregation module. In our method, dubbed MOUV, each expert predicts not only an output value but also its uncertainty, which in turn serves as a statistically motivated criterion to rely on the right experts. We compare our method with existing alternatives on multiple public benchmarks and show that MOUV consistently outperforms the prior art, while at the same time producing better calibrated uncertainty estimates. Our code is available at link-upon-publication.
Learning a Sensor-invariant Embedding of Satellite Data: A Case Study for Lake Ice Monitoring
Jul 19, 2021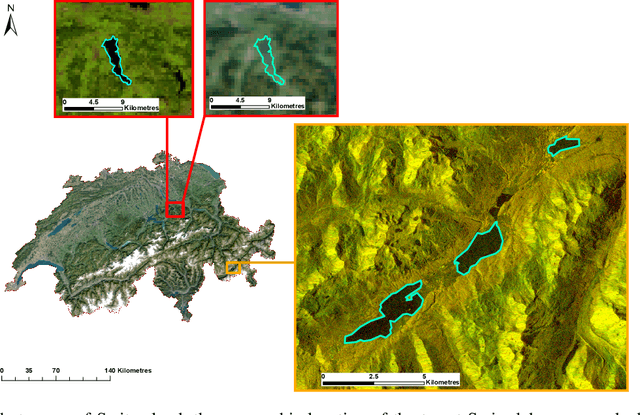
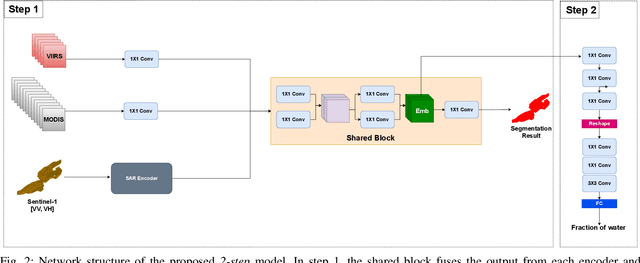
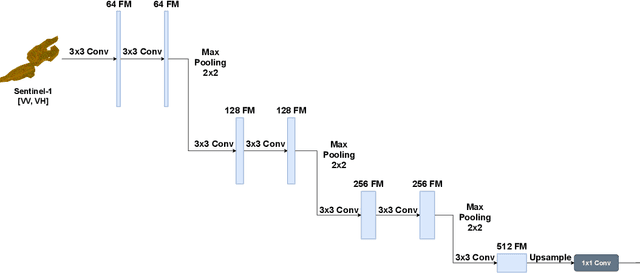
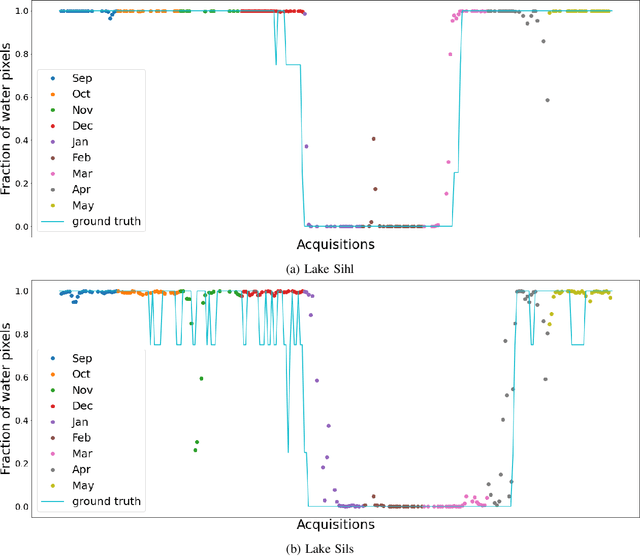
Abstract:Fusing satellite imagery acquired with different sensors has been a long-standing challenge of Earth observation, particularly across different modalities such as optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. Here, we explore the joint analysis of imagery from different sensors in the light of representation learning: we propose to learn a joint, sensor-invariant embedding (feature representation) within a deep neural network. Our application problem is the monitoring of lake ice on Alpine lakes. To reach the temporal resolution requirement of the Swiss Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) office, we combine three image sources: Sentinel-1 SAR (S1-SAR), Terra MODIS and Suomi-NPP VIIRS. The large gaps between the optical and SAR domains and between the sensor resolutions make this a challenging instance of the sensor fusion problem. Our approach can be classified as a feature-level fusion that is learnt in a data-driven manner. The proposed network architecture has separate encoding branches for each image sensor, which feed into a single latent embedding. I.e., a common feature representation shared by all inputs, such that subsequent processing steps deliver comparable output irrespective of which sort of input image was used. By fusing satellite data, we map lake ice at a temporal resolution of <1.5 days. The network produces spatially explicit lake ice maps with pixel-wise accuracies >91.3% (respectively, mIoU scores >60.7%) and generalises well across different lakes and winters. Moreover, it sets a new state-of-the-art for determining the important ice-on and ice-off dates for the target lakes, in many cases meeting the GCOS requirement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge