Youtao Zhang
The Stabilizer Bootstrap of Quantum Machine Learning with up to 10000 qubits
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Quantum machine learning is considered one of the flagship applications of quantum computers, where variational quantum circuits could be the leading paradigm both in the near-term quantum devices and the early fault-tolerant quantum computers. However, it is not clear how to identify the regime of quantum advantages from these circuits, and there is no explicit theory to guide the practical design of variational ansatze to achieve better performance. We address these challenges with the stabilizer bootstrap, a method that uses stabilizer-based techniques to optimize quantum neural networks before their quantum execution, together with theoretical proofs and high-performance computing with 10000 qubits or random datasets up to 1000 data. We find that, in a general setup of variational ansatze, the possibility of improvements from the stabilizer bootstrap depends on the structure of the observables and the size of the datasets. The results reveal that configurations exhibit two distinct behaviors: some maintain a constant probability of circuit improvement, while others show an exponential decay in improvement probability as qubit numbers increase. These patterns are termed strong stabilizer enhancement and weak stabilizer enhancement, respectively, with most situations falling in between. Our work seamlessly bridges techniques from fault-tolerant quantum computing with applications of variational quantum algorithms. Not only does it offer practical insights for designing variational circuits tailored to large-scale machine learning challenges, but it also maps out a clear trajectory for defining the boundaries of feasible and practical quantum advantages.
SmartFRZ: An Efficient Training Framework using Attention-Based Layer Freezing
Jan 30, 2024

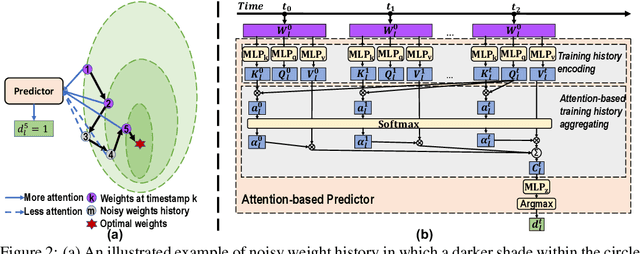

Abstract:There has been a proliferation of artificial intelligence applications, where model training is key to promising high-quality services for these applications. However, the model training process is both time-intensive and energy-intensive, inevitably affecting the user's demand for application efficiency. Layer freezing, an efficient model training technique, has been proposed to improve training efficiency. Although existing layer freezing methods demonstrate the great potential to reduce model training costs, they still remain shortcomings such as lacking generalizability and compromised accuracy. For instance, existing layer freezing methods either require the freeze configurations to be manually defined before training, which does not apply to different networks, or use heuristic freezing criteria that is hard to guarantee decent accuracy in different scenarios. Therefore, there lacks a generic and smart layer freezing method that can automatically perform ``in-situation'' layer freezing for different networks during training processes. To this end, we propose a generic and efficient training framework (SmartFRZ). The core proposed technique in SmartFRZ is attention-guided layer freezing, which can automatically select the appropriate layers to freeze without compromising accuracy. Experimental results show that SmartFRZ effectively reduces the amount of computation in training and achieves significant training acceleration, and outperforms the state-of-the-art layer freezing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge