Yordanka Velikova
ConceptPose: Training-Free Zero-Shot Object Pose Estimation using Concept Vectors
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Object pose estimation is a fundamental task in computer vision and robotics, yet most methods require extensive, dataset-specific training. Concurrently, large-scale vision language models show remarkable zero-shot capabilities. In this work, we bridge these two worlds by introducing ConceptPose, a framework for object pose estimation that is both training-free and model-free. ConceptPose leverages a vision-language-model (VLM) to create open-vocabulary 3D concept maps, where each point is tagged with a concept vector derived from saliency maps. By establishing robust 3D-3D correspondences across concept maps, our approach allows precise estimation of 6DoF relative pose. Without any object or dataset-specific training, our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on common zero shot relative pose estimation benchmarks, significantly outperforming existing methods by over 62% in ADD(-S) score, including those that utilize extensive dataset-specific training.
US-X Complete: A Multi-Modal Approach to Anatomical 3D Shape Recovery
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound offers a radiation-free, cost-effective solution for real-time visualization of spinal landmarks, paraspinal soft tissues and neurovascular structures, making it valuable for intraoperative guidance during spinal procedures. However, ultrasound suffers from inherent limitations in visualizing complete vertebral anatomy, in particular vertebral bodies, due to acoustic shadowing effects caused by bone. In this work, we present a novel multi-modal deep learning method for completing occluded anatomical structures in 3D ultrasound by leveraging complementary information from a single X-ray image. To enable training, we generate paired training data consisting of: (1) 2D lateral vertebral views that simulate X-ray scans, and (2) 3D partial vertebrae representations that mimic the limited visibility and occlusions encountered during ultrasound spine imaging. Our method integrates morphological information from both imaging modalities and demonstrates significant improvements in vertebral reconstruction (p < 0.001) compared to state of art in 3D ultrasound vertebral completion. We perform phantom studies as an initial step to future clinical translation, and achieve a more accurate, complete volumetric lumbar spine visualization overlayed on the ultrasound scan without the need for registration with preoperative modalities such as computed tomography. This demonstrates that integrating a single X-ray projection mitigates ultrasound's key limitation while preserving its strengths as the primary imaging modality. Code and data can be found at https://github.com/miruna20/US-X-Complete
Shape Completion and Real-Time Visualization in Robotic Ultrasound Spine Acquisitions
Aug 12, 2025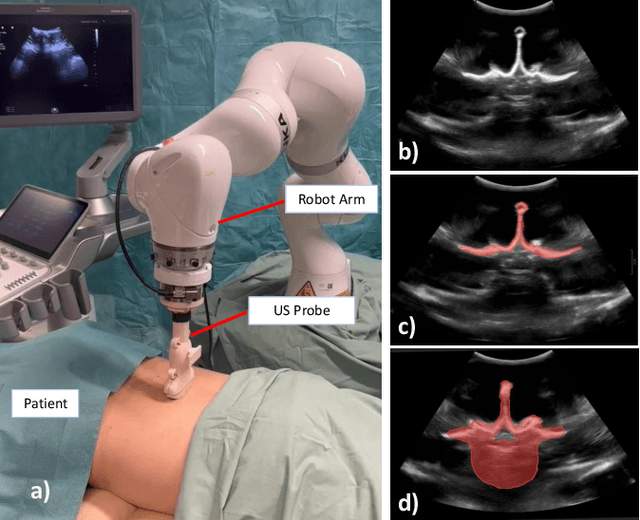
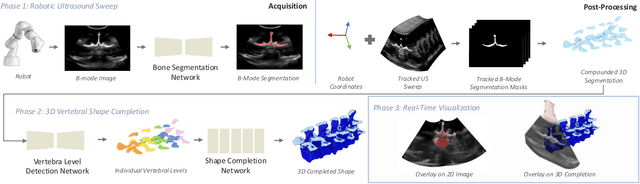
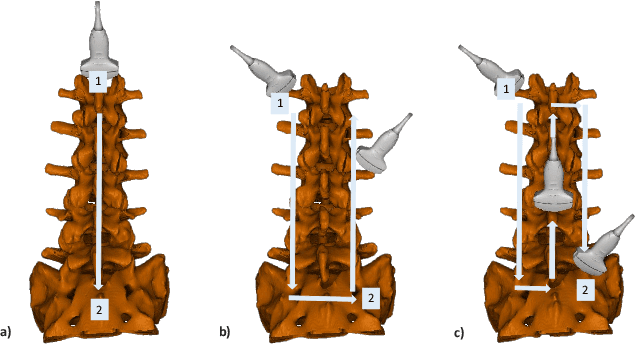
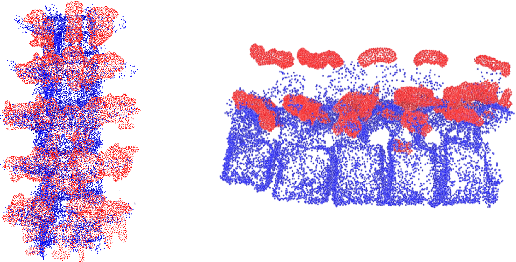
Abstract:Ultrasound (US) imaging is increasingly used in spinal procedures due to its real-time, radiation-free capabilities; however, its effectiveness is hindered by shadowing artifacts that obscure deeper tissue structures. Traditional approaches, such as CT-to-US registration, incorporate anatomical information from preoperative CT scans to guide interventions, but they are limited by complex registration requirements, differences in spine curvature, and the need for recent CT imaging. Recent shape completion methods can offer an alternative by reconstructing spinal structures in US data, while being pretrained on large set of publicly available CT scans. However, these approaches are typically offline and have limited reproducibility. In this work, we introduce a novel integrated system that combines robotic ultrasound with real-time shape completion to enhance spinal visualization. Our robotic platform autonomously acquires US sweeps of the lumbar spine, extracts vertebral surfaces from ultrasound, and reconstructs the complete anatomy using a deep learning-based shape completion network. This framework provides interactive, real-time visualization with the capability to autonomously repeat scans and can enable navigation to target locations. This can contribute to better consistency, reproducibility, and understanding of the underlying anatomy. We validate our approach through quantitative experiments assessing shape completion accuracy and evaluations of multiple spine acquisition protocols on a phantom setup. Additionally, we present qualitative results of the visualization on a volunteer scan.
Deep Spectral Methods for Unsupervised Ultrasound Image Interpretation
Aug 04, 2024Abstract:Ultrasound imaging is challenging to interpret due to non-uniform intensities, low contrast, and inherent artifacts, necessitating extensive training for non-specialists. Advanced representation with clear tissue structure separation could greatly assist clinicians in mapping underlying anatomy and distinguishing between tissue layers. Decomposing an image into semantically meaningful segments is mainly achieved using supervised segmentation algorithms. Unsupervised methods are beneficial, as acquiring large labeled datasets is difficult and costly, but despite their advantages, they still need to be explored in ultrasound. This paper proposes a novel unsupervised deep learning strategy tailored to ultrasound to obtain easily interpretable tissue separations. We integrate key concepts from unsupervised deep spectral methods, which combine spectral graph theory with deep learning methods. We utilize self-supervised transformer features for spectral clustering to generate meaningful segments based on ultrasound-specific metrics and shape and positional priors, ensuring semantic consistency across the dataset. We evaluate our unsupervised deep learning strategy on three ultrasound datasets, showcasing qualitative results across anatomical contexts without label requirements. We also conduct a comparative analysis against other clustering algorithms to demonstrate superior segmentation performance, boundary preservation, and label consistency.
Diffusion as Sound Propagation: Physics-inspired Model for Ultrasound Image Generation
Jul 07, 2024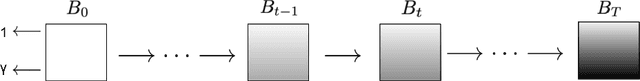
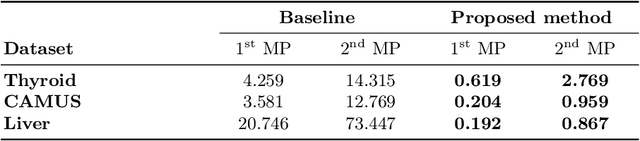
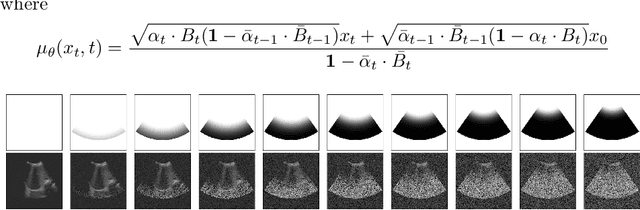
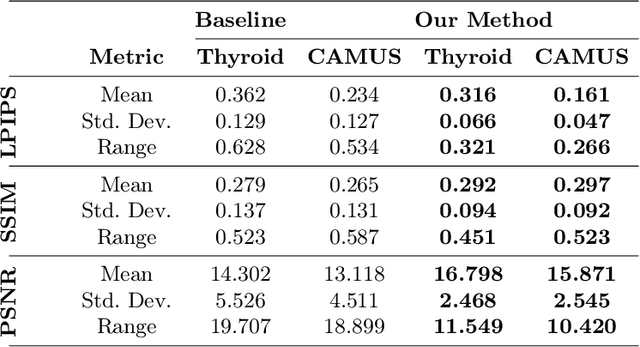
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) methods typically require large datasets to effectively learn data distributions. However, in the medical field, data is often limited in quantity, and acquiring labeled data can be costly. To mitigate this data scarcity, data augmentation techniques are commonly employed. Among these techniques, generative models play a pivotal role in expanding datasets. However, when it comes to ultrasound (US) imaging, the authenticity of generated data often diminishes due to the oversight of ultrasound physics. We propose a novel approach to improve the quality of generated US images by introducing a physics-based diffusion model that is specifically designed for this image modality. The proposed model incorporates an US-specific scheduler scheme that mimics the natural behavior of sound wave propagation in ultrasound imaging. Our analysis demonstrates how the proposed method aids in modeling the attenuation dynamics in US imaging. We present both qualitative and quantitative results based on standard generative model metrics, showing that our proposed method results in overall more plausible images. Our code is available at https://github.com/marinadominguez/diffusion-for-us-images
Shape Completion in the Dark: Completing Vertebrae Morphology from 3D Ultrasound
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Purpose: Ultrasound (US) imaging, while advantageous for its radiation-free nature, is challenging to interpret due to only partially visible organs and a lack of complete 3D information. While performing US-based diagnosis or investigation, medical professionals therefore create a mental map of the 3D anatomy. In this work, we aim to replicate this process and enhance the visual representation of anatomical structures. Methods: We introduce a point-cloud-based probabilistic DL method to complete occluded anatomical structures through 3D shape completion and choose US-based spine examinations as our application. To enable training, we generate synthetic 3D representations of partially occluded spinal views by mimicking US physics and accounting for inherent artifacts. Results: The proposed model performs consistently on synthetic and patient data, with mean and median differences of 2.02 and 0.03 in CD, respectively. Our ablation study demonstrates the importance of US physics-based data generation, reflected in the large mean and median difference of 11.8 CD and 9.55 CD, respectively. Additionally, we demonstrate that anatomic landmarks, such as the spinous process (with reconstruction CD of 4.73) and the facet joints (mean distance to GT of 4.96mm) are preserved in the 3D completion. Conclusion: Our work establishes the feasibility of 3D shape completion for lumbar vertebrae, ensuring the preservation of level-wise characteristics and successful generalization from synthetic to real data. The incorporation of US physics contributes to more accurate patient data completions. Notably, our method preserves essential anatomic landmarks and reconstructs crucial injections sites at their correct locations. The generated data and source code will be made publicly available (https://github.com/miruna20/Shape-Completion-in-the-Dark).
CathFlow: Self-Supervised Segmentation of Catheters in Interventional Ultrasound Using Optical Flow and Transformers
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:In minimally invasive endovascular procedures, contrast-enhanced angiography remains the most robust imaging technique. However, it is at the expense of the patient and clinician's health due to prolonged radiation exposure. As an alternative, interventional ultrasound has notable benefits such as being radiation-free, fast to deploy, and having a small footprint in the operating room. Yet, ultrasound is hard to interpret, and highly prone to artifacts and noise. Additionally, interventional radiologists must undergo extensive training before they become qualified to diagnose and treat patients effectively, leading to a shortage of staff, and a lack of open-source datasets. In this work, we seek to address both problems by introducing a self-supervised deep learning architecture to segment catheters in longitudinal ultrasound images, without demanding any labeled data. The network architecture builds upon AiAReSeg, a segmentation transformer built with the Attention in Attention mechanism, and is capable of learning feature changes across time and space. To facilitate training, we used synthetic ultrasound data based on physics-driven catheter insertion simulations, and translated the data into a unique CT-Ultrasound common domain, CACTUSS, to improve the segmentation performance. We generated ground truth segmentation masks by computing the optical flow between adjacent frames using FlowNet2, and performed thresholding to obtain a binary map estimate. Finally, we validated our model on a test dataset, consisting of unseen synthetic data and images collected from silicon aorta phantoms, thus demonstrating its potential for applications to clinical data in the future.
Implicit Neural Representations for Breathing-compensated Volume Reconstruction in Robotic Ultrasound Aorta Screening
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used in diagnosing and staging abdominal diseases due to its lack of non-ionizing radiation and prevalent availability. However, significant inter-operator variability and inconsistent image acquisition hinder the widespread adoption of extensive screening programs. Robotic ultrasound systems have emerged as a promising solution, offering standardized acquisition protocols and the possibility of automated acquisition. Additionally, these systems enable access to 3D data via robotic tracking, enhancing volumetric reconstruction for improved ultrasound interpretation and precise disease diagnosis. However, the interpretability of 3D US reconstruction of abdominal images can be affected by the patient's breathing motion. This study introduces a method to compensate for breathing motion in 3D US compounding by leveraging implicit neural representations. Our approach employs a robotic ultrasound system for automated screenings. To demonstrate the method's effectiveness, we evaluate our proposed method for the diagnosis and monitoring of abdominal aorta aneurysms as a representative use case. Our experiments demonstrate that our proposed pipeline facilitates robust automated robotic acquisition, mitigating artifacts from breathing motion, and yields smoother 3D reconstructions for enhanced screening and medical diagnosis.
AiAReSeg: Catheter Detection and Segmentation in Interventional Ultrasound using Transformers
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:To date, endovascular surgeries are performed using the golden standard of Fluoroscopy, which uses ionising radiation to visualise catheters and vasculature. Prolonged Fluoroscopic exposure is harmful for the patient and the clinician, and may lead to severe post-operative sequlae such as the development of cancer. Meanwhile, the use of interventional Ultrasound has gained popularity, due to its well-known benefits of small spatial footprint, fast data acquisition, and higher tissue contrast images. However, ultrasound images are hard to interpret, and it is difficult to localise vessels, catheters, and guidewires within them. This work proposes a solution using an adaptation of a state-of-the-art machine learning transformer architecture to detect and segment catheters in axial interventional Ultrasound image sequences. The network architecture was inspired by the Attention in Attention mechanism, temporal tracking networks, and introduced a novel 3D segmentation head that performs 3D deconvolution across time. In order to facilitate training of such deep learning networks, we introduce a new data synthesis pipeline that used physics-based catheter insertion simulations, along with a convolutional ray-casting ultrasound simulator to produce synthetic ultrasound images of endovascular interventions. The proposed method is validated on a hold-out validation dataset, thus demonstrated robustness to ultrasound noise and a wide range of scanning angles. It was also tested on data collected from silicon-based aorta phantoms, thus demonstrated its potential for translation from sim-to-real. This work represents a significant step towards safer and more efficient endovascular surgery using interventional ultrasound.
Can ultrasound confidence maps predict sonographers' labeling variability?
Aug 18, 2023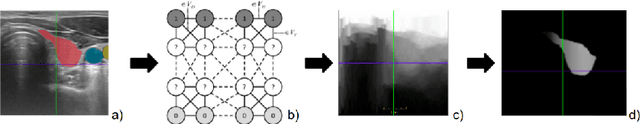
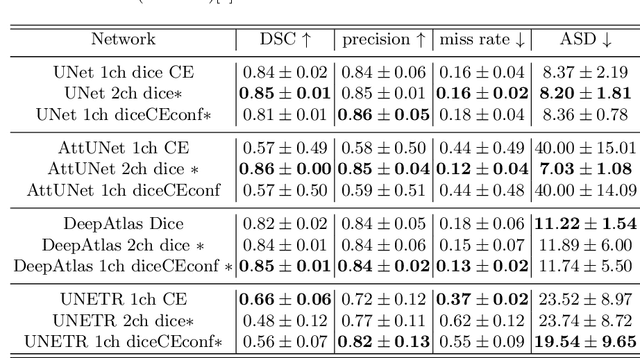
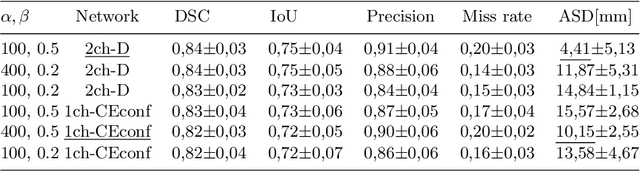
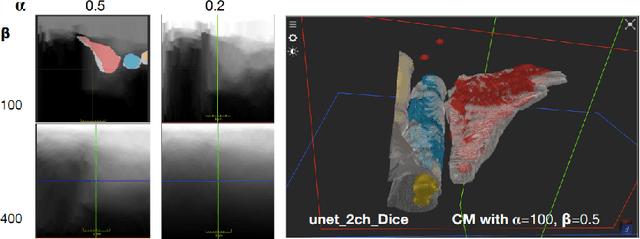
Abstract:Measuring cross-sectional areas in ultrasound images is a standard tool to evaluate disease progress or treatment response. Often addressed today with supervised deep-learning segmentation approaches, existing solutions highly depend upon the quality of experts' annotations. However, the annotation quality in ultrasound is anisotropic and position-variant due to the inherent physical imaging principles, including attenuation, shadows, and missing boundaries, commonly exacerbated with depth. This work proposes a novel approach that guides ultrasound segmentation networks to account for sonographers' uncertainties and generate predictions with variability similar to the experts. We claim that realistic variability can reduce overconfident predictions and improve physicians' acceptance of deep-learning cross-sectional segmentation solutions. Our method provides CM's certainty for each pixel for minimal computational overhead as it can be precalculated directly from the image. We show that there is a correlation between low values in the confidence maps and expert's label uncertainty. Therefore, we propose to give the confidence maps as additional information to the networks. We study the effect of the proposed use of ultrasound CMs in combination with four state-of-the-art neural networks and in two configurations: as a second input channel and as part of the loss. We evaluate our method on 3D ultrasound datasets of the thyroid and lower limb muscles. Our results show ultrasound CMs increase the Dice score, improve the Hausdorff and Average Surface Distances, and decrease the number of isolated pixel predictions. Furthermore, our findings suggest that ultrasound CMs improve the penalization of uncertain areas in the ground truth data, thereby improving problematic interpolations. Our code and example data will be made public at https://github.com/IFL-CAMP/Confidence-segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge