Yoo Ji Suh
Constructing Vec-tionaries to Extract Latent Message Features from Texts: A Case Study of Moral Appeals
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:While communication research frequently studies latent message features like moral appeals, their quantification remains a challenge. Conventional human coding struggles with scalability and intercoder reliability. While dictionary-based methods are cost-effective and computationally efficient, they often lack contextual sensitivity and are limited by the vocabularies developed for the original applications. In this paper, we present a novel approach to construct vec-tionary measurement tools that boost validated dictionaries with word embeddings through nonlinear optimization. By harnessing semantic relationships encoded by embeddings, vec-tionaries improve the measurement of latent message features by expanding the applicability of original vocabularies to other contexts. Vec-tionaries can also help extract semantic information from texts, especially those in short format, beyond the original vocabulary of a dictionary. Importantly, a vec-tionary can produce additional metrics to capture the valence and ambivalence of a latent feature beyond its strength in texts. Using moral appeals in COVID-19-related tweets as a case study, we illustrate the steps to construct the moral foundations vec-tionary, showcasing its ability to process posts missed by dictionary methods and to produce measurements better aligned with crowdsourced human assessments. Furthermore, additional metrics from the moral foundations vec-tionary unveiled unique insights that facilitated predicting outcomes such as message retransmission.
Smiling Women Pitching Down: Auditing Representational and Presentational Gender Biases in Image Generative AI
May 17, 2023
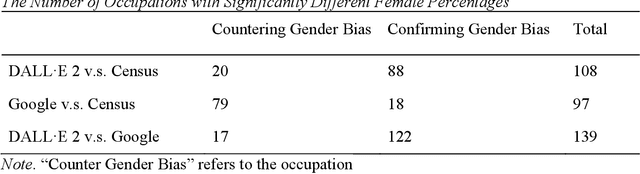
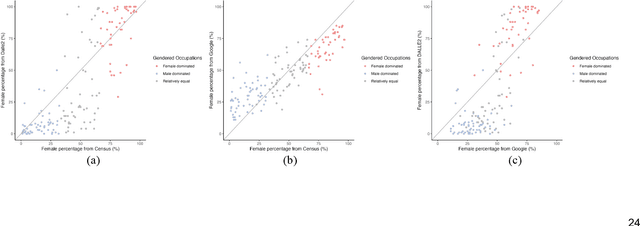
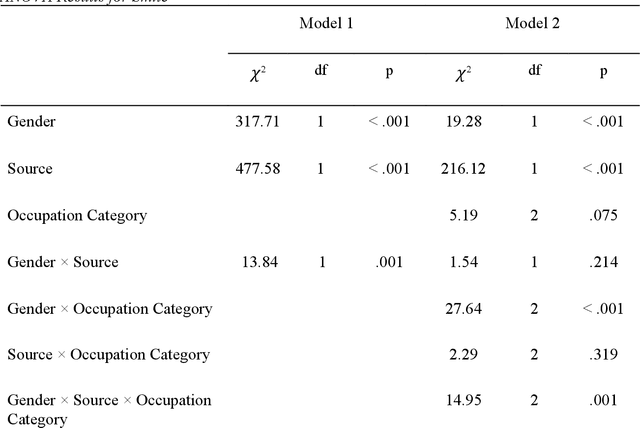
Abstract:Generative AI models like DALL-E 2 can interpret textual prompts and generate high-quality images exhibiting human creativity. Though public enthusiasm is booming, systematic auditing of potential gender biases in AI-generated images remains scarce. We addressed this gap by examining the prevalence of two occupational gender biases (representational and presentational biases) in 15,300 DALL-E 2 images spanning 153 occupations, and assessed potential bias amplification by benchmarking against 2021 census labor statistics and Google Images. Our findings reveal that DALL-E 2 underrepresents women in male-dominated fields while overrepresenting them in female-dominated occupations. Additionally, DALL-E 2 images tend to depict more women than men with smiling faces and downward-pitching heads, particularly in female-dominated (vs. male-dominated) occupations. Our computational algorithm auditing study demonstrates more pronounced representational and presentational biases in DALL-E 2 compared to Google Images and calls for feminist interventions to prevent such bias-laden AI-generated images to feedback into the media ecology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge