Mian Wei
Smiling Women Pitching Down: Auditing Representational and Presentational Gender Biases in Image Generative AI
May 17, 2023
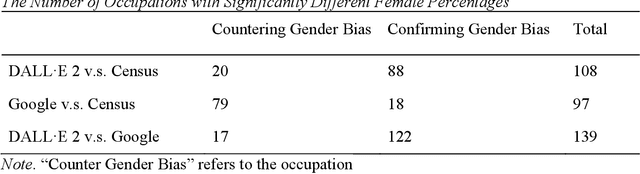
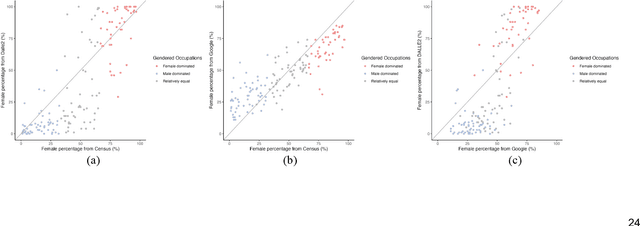
Abstract:Generative AI models like DALL-E 2 can interpret textual prompts and generate high-quality images exhibiting human creativity. Though public enthusiasm is booming, systematic auditing of potential gender biases in AI-generated images remains scarce. We addressed this gap by examining the prevalence of two occupational gender biases (representational and presentational biases) in 15,300 DALL-E 2 images spanning 153 occupations, and assessed potential bias amplification by benchmarking against 2021 census labor statistics and Google Images. Our findings reveal that DALL-E 2 underrepresents women in male-dominated fields while overrepresenting them in female-dominated occupations. Additionally, DALL-E 2 images tend to depict more women than men with smiling faces and downward-pitching heads, particularly in female-dominated (vs. male-dominated) occupations. Our computational algorithm auditing study demonstrates more pronounced representational and presentational biases in DALL-E 2 compared to Google Images and calls for feminist interventions to prevent such bias-laden AI-generated images to feedback into the media ecology.
Stable discovery of interpretable subgroups via calibration in causal studies
Sep 29, 2020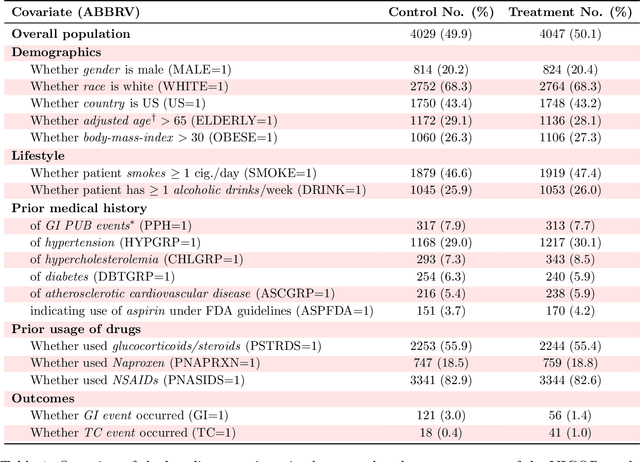
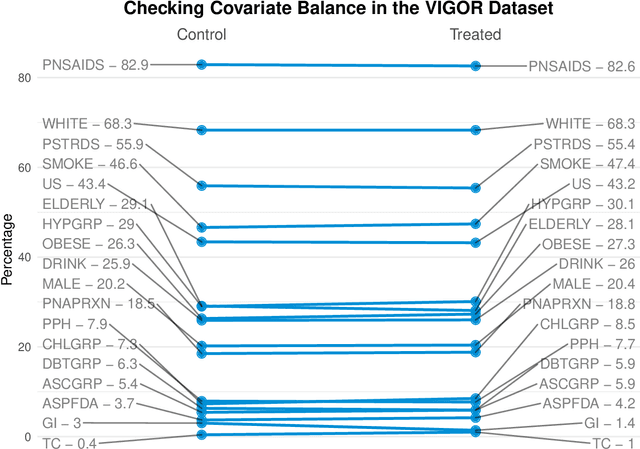
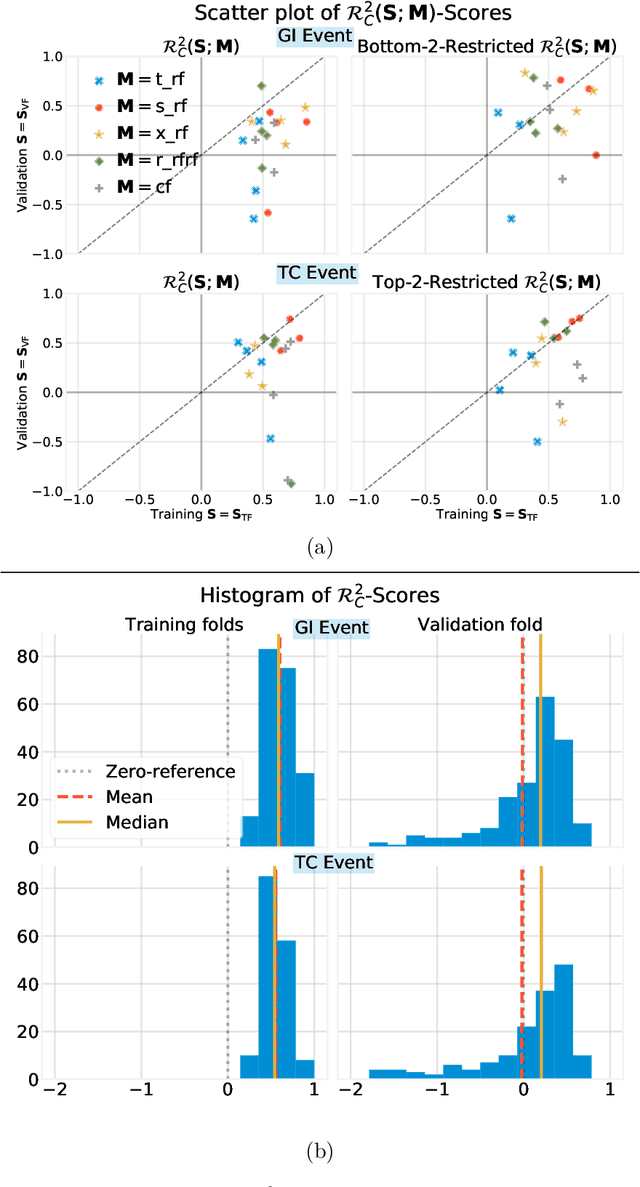
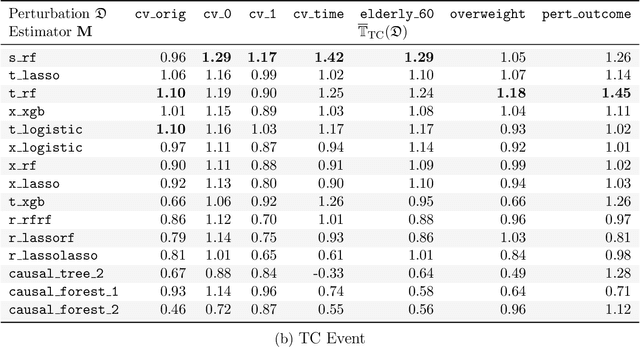
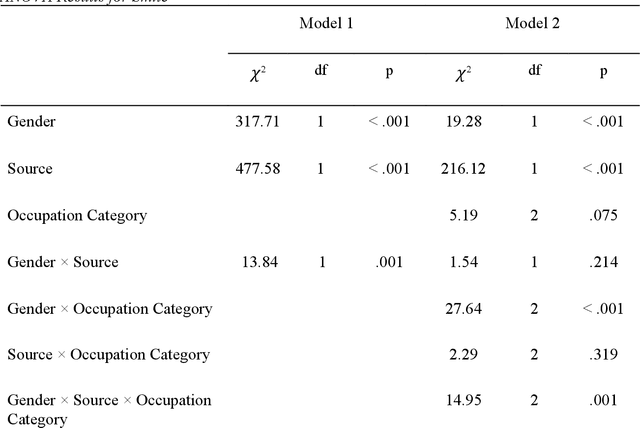
Abstract:Building on Yu and Kumbier's PCS framework and for randomized experiments, we introduce a novel methodology for Stable Discovery of Interpretable Subgroups via Calibration (StaDISC), with large heterogeneous treatment effects. StaDISC was developed during our re-analysis of the 1999-2000 VIGOR study, an 8076 patient randomized controlled trial (RCT), that compared the risk of adverse events from a then newly approved drug, Rofecoxib (Vioxx), to that from an older drug Naproxen. Vioxx was found to, on average and in comparison to Naproxen, reduce the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) events but increase the risk of thrombotic cardiovascular (CVT) events. Applying StaDISC, we fit 18 popular conditional average treatment effect (CATE) estimators for both outcomes and use calibration to demonstrate their poor global performance. However, they are locally well-calibrated and stable, enabling the identification of patient groups with larger than (estimated) average treatment effects. In fact, StaDISC discovers three clinically interpretable subgroups each for the GI outcome (totaling 29.4% of the study size) and the CVT outcome (totaling 11.0%). Complementary analyses of the found subgroups using the 2001-2004 APPROVe study, a separate independently conducted RCT with 2587 patients, provides further supporting evidence for the promise of StaDISC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge